Urbanization facts for kids
Urbanization is when more and more people move from countryside areas to urban areas, like towns and cities. It also means that cities grow larger as more people live and work there. This change affects how societies live and adapt.
It's important to know that urbanization is different from urban growth. Urbanization looks at the percentage of people living in cities compared to the total population. Urban growth, however, just counts the total number of people living in cities. Experts believe that by 2050, most people in both developing and developed countries will live in cities. This growth could lead to challenges like less land, not enough drinking water, and fewer green spaces.
Urbanization is a big topic that many subjects study. These include urban planning, geography, sociology, architecture, and economics. It's connected to how the world becomes more connected, modern, and industrial. Urbanization is not just a recent trend. It's a huge change in how humans live together. For thousands of years, most people lived in small villages. Now, city life is becoming much more common. This shift from village life to city life is happening very quickly around the world.
Contents
What is Urbanization?
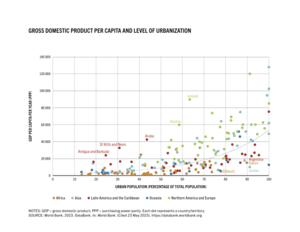
Urbanization describes the process where a country's population moves from rural areas to urban centers. It's about the increasing proportion of people living in cities. This can be measured by how many people live in cities now, or how fast that number is growing. While cities offer many benefits, they also create big social, economic, and environmental challenges. Finding ways to make cities sustainable is a major goal for countries worldwide.
How Cities Grew Over Time
For a long time, from the first cities in places like Indus valley civilization and Egypt until the 1700s, most people lived in the countryside. They worked in farming to feed themselves. Only a small number of people lived in towns, where they traded goods and made things on a small scale. The number of people in cities stayed about the same compared to rural areas.
This changed dramatically in the late 1700s with the British Agricultural Revolution and the Industrial Revolution. New farming methods meant fewer people were needed to work the land. At the same time, factories and businesses grew in cities, offering new jobs. This caused a huge movement of people from farms to industrial cities like Manchester in England. For example, in England and Wales, the number of people living in cities with over 20,000 residents jumped from 17% in 1801 to 54% in 1891.
As cities grew, public transport systems also developed. This made it easier for people to live further from the city center and still get to work. Urbanization spread across Western countries first. Then, after the 1950s, it began to happen in many developing countries too. The United Nations reported that in 2007, for the first time in human history, more than half of the world's population lived in cities.
Researchers have even created videos showing how cities developed across the world from 3700 BC to 2000 AD. This helps us understand the long history of urbanization.
Why People Move to Cities
People move to cities for many reasons. Sometimes it's a personal choice, and sometimes it's part of a bigger plan by governments.
Economic Opportunities in Cities
Cities often offer more job opportunities and better chances to earn money. They have more businesses, services, and wealth. Many people from rural areas move to cities hoping to find work and improve their lives. Cities also tend to have better schools, housing, and safety. Things like having many different people, places, and businesses close together can be very helpful.
Challenges in Rural Areas
Life in the countryside can be difficult. Farmers often face unpredictable weather like droughts or floods, which can make it hard to grow food. Historically, it was also harder to get manufactured goods in rural areas.
A professor from Thailand noted that young people are leaving farms. They see farming as hard work with little pay. This shift can also change traditional ways of life and community values.
Sometimes, people are forced to leave their farms or villages. This can happen due to changes in land use or other pressures. They then move to cities, often hoping for a better life. However, city life can also bring challenges like higher living costs or difficulty finding good jobs.
Cities also offer more specialized services. These include doctors, hospitals, and better educational opportunities. People might move to cities to access these services or to find new social groups. Urbanization can also create new opportunities for women, such as access to education and paid jobs. This can lead to changes in family size.
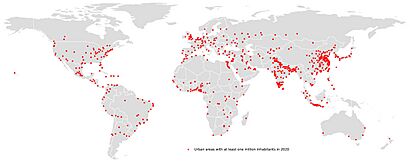
Big Cities Around the World
Some cities or large urban areas become very important in their countries. They attract many people from rural areas and even from other cities. These dominant urban areas are often much larger than other cities in the country. For example, Greater Manila in the Philippines has over 20 million people. This is more than 20% of the country's total population. Greater Seoul in South Korea is another example, home to 50% of the entire national population.
How Urbanization Affects Money and Jobs
As cities grow, living costs can become very high. This can make it hard for working-class families to afford homes. Historically, cities often developed with wealthier areas in one part and poorer areas in another. This was sometimes due to things like wind carrying smoke from factories.
Today, similar challenges affect many developing countries. Fast city growth can make inequality worse. The push for quick growth can sometimes lead to unfair city development. Many people who move from rural areas to cities hoping for jobs might end up living in slums. This happens when they can't find work or afford proper housing.
While city development can be seen negatively, it also has many benefits. It can lower transport costs, create new jobs, and improve education and housing. Living in cities allows people to be close to their workplaces and enjoy a wider variety of goods and services. However, crowded conditions and high costs can also make competition tougher in city markets.
In many developing countries, young people might not have access to financial help or business advice. This makes it hard for them to start their own businesses. Providing good schools and support for young people is important for a fair society.
Urbanization and Our Environment
Urbanization has a big impact on the environment, both good and bad.
City Heat Islands
One effect is the creation of Urban heat islands. These are areas in cities that are much warmer than the surrounding rural areas. This happens because buildings and roads absorb and hold heat from the sun. In the countryside, plants and soil evaporate water, which cools the air. But in cities, there are fewer plants. Cars, factories, and air conditioning units also release heat, making cities even warmer. Cities can be 1 to 3 degrees Celsius warmer than nearby areas. This also makes the soil drier and reduces how much carbon dioxide plants can absorb.
Water Pollution in Cities
Urban runoff is another environmental issue. When it rains in cities, water flows over rooftops, roads, and parking lots. This water picks up pollutants and flows into storm drains. Often, this polluted water goes directly into nearby rivers, streams, or oceans without being cleaned.
This can lead to eutrophication in water bodies. Eutrophication means there are too many nutrients, like nitrogen and phosphorus, in the water. These come from pollutants washed into the water. This causes too much algae to grow, called algal blooms. These blooms block sunlight and use up oxygen, harming other aquatic life. When the algae die, they release carbon dioxide, making the ocean more acidic. This is called ocean acidification. Ocean acidification makes it hard for sea creatures to build their shells and skeletons.
Dealing with City Waste
Rapid city growth also means more food waste. This is food that is thrown away because it's unused, expired, or spoiled. More food waste leads to more methane gas in landfills, which is bad for the environment. It also attracts pests like rodents and insects, which can spread diseases.
Managing waste in cities is a big challenge. Historically, solutions focused on cheap ways to get rid of waste, like burning it or putting it in landfills. Today, there's a growing focus on reducing waste, recycling, and finding ways to reuse materials. People are also becoming more aware of how their consumption habits, like fast fashion, affect the environment.
How Cities Change Animal Homes
Urbanization can affect biodiversity by breaking up natural habitats. This is called habitat fragmentation. It means that roads, buildings, and railways divide natural areas. This can make it harder for animals to find food, water, or places to hide. For example, some aquatic insects have fewer species in urban areas because they can't easily move between fragmented habitats.
However, sometimes urbanization can also help certain species. Some birds, for instance, can adapt to city life and find food in developed areas. Careful planning, like creating green corridors, can help connect habitats and allow animals to move more easily through urban regions.
How Urbanization Affects Health and Life
Eating Habits in Cities
When people move from rural areas to cities, their eating habits often change. Rural diets usually have more grains, fruits, and vegetables, and less fat. City dwellers often eat more processed foods, which have more meat, sugar, refined grains, and fats. This is partly because city life can be busy, and people have less time to cook. They might also have more money to spend on convenience foods.
This can lead to problems like food deserts. These are areas where it's hard to find fresh, healthy food, like in supermarkets. Instead, there might be many fast-food restaurants or convenience stores. Studies show that living far from grocery stores is linked to higher rates of obesity and other health issues. Children in urban areas might have a lower risk of being underfed but a higher risk of being overweight.
Spreading of Illnesses
Cities, with many people living close together, can make it easier for communicable diseases to spread. These can include respiratory infections or stomach illnesses. Diseases that need insects to spread, like dengue fever, can also be more common in urban areas.
Asthma and City Air
Urbanization is also linked to a higher risk of asthma. As communities become more urban, the number of people with asthma often increases. This is especially true in cities with high levels of air pollution, often from traffic. Children living in poor urban areas can be more affected by asthma due to this pollution and other environmental allergens. However, good city planning and controlling emissions can help reduce these effects.
Staying Active in Urban Areas
One positive effect of urbanization can be an increase in physical activity. People in rural areas sometimes have higher rates of obesity and are less active than city residents. This can be due to factors like long distances to travel, unsafe roads for walking or biking, and fewer parks or trails.
In cities, it's often easier to be active. Neighborhoods with sidewalks, street lights, and traffic signals encourage walking. Having parks, gyms, and other places to exercise nearby also helps. Easy access to public transportation means people often walk or bike to bus stops or train stations. These features make it easier for city residents to meet recommended physical activity levels.
City Life and Mental Well-being
City life can also affect mental health. The fast pace and changes in social structures can sometimes lead to feelings of stress or insecurity. This might be due to concerns about personal safety or social difficulties. Overcrowding and less social support can also contribute to stress.
One study in Sweden found that people living in cities had a slightly higher chance of developing depression. This suggests that while cities offer many benefits, they also present unique challenges for mental well-being.
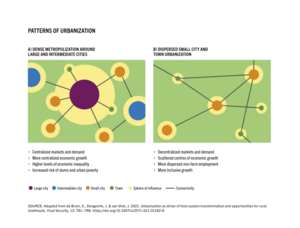
Different Ways Cities Grow
Cities can grow in different ways, depending on how they are planned and built.
Moving to the Suburbs
Sometimes, people move from the city center to areas just outside, called suburbs. This creates new centers of activity outside the main downtown area. Places like Los Angeles are good examples of this type of growth. However, in some areas, people are now moving back into city centers, especially due to high transport costs.
Planning Our Cities
Some cities are built with a clear plan from the start. This is called planned urbanization. Ancient cities often had plans for military or design reasons. Today, city planners use ideas like new urbanism and smart growth. These methods aim to create cities that are good for the environment, the economy, and the people living there. They focus on things like making areas walkable, having different types of buildings close together, and protecting natural land. The goal is to create fair, strong, and appealing cities.
Water Challenges in Cities
As cities grow, providing enough clean water for everyone becomes a major challenge. This is known as water scarcity. Cities need careful planning to manage their water resources sustainably.
Urbanization Around the Globe
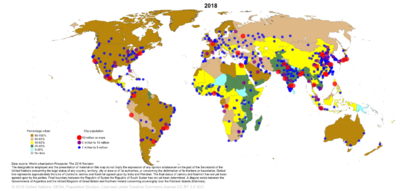
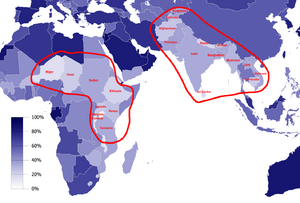
Today, most countries in the world are urbanized. In 2020, about 56.2% of the global population lived in cities. However, there are big differences between regions. Countries in Europe, the Middle East, the Americas, and East Asia are mostly urbanized. But in parts of Africa and Asia, many countries still have a low percentage of people living in cities.
As of 2022, countries like the United States, Canada, Japan, Australia, and many in South America have over 80% of their populations living in urban areas. In fact, South America is the most urbanized continent, with more than 80% of its people living in cities.
See also
 In Spanish: Proceso de urbanización para niños
In Spanish: Proceso de urbanización para niños
- Back to the land
- City-state
- Counterurbanization
- Division of labour
- Exurb
- Ghetto
- Human population planning
- Human migration
- Megalopolis (city type)
- Political demography
- Pseudo-urbanization
- Push and pull factors in migration
- Synurbization
- Urban ecology
- Urban exploration
- Urban history
- Urban metabolism
- Urban morphology
- Urban studies
- Urbanization by country
- White flight
Historical
- Neolithic Revolution
- Oppidum
- Polis
- Urban revolution
Regional
- Urbanization in Africa
- Urbanization in China
- Urbanization in India
- Urbanization in Pakistan
- Urbanization in the United States
 | Ernest Everett Just |
 | Mary Jackson |
 | Emmett Chappelle |
 | Marie Maynard Daly |