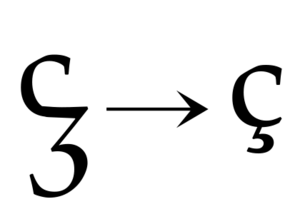Visigothic script facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Visigothic script |
|
|---|---|
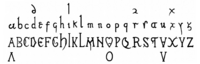
Alphabet in Visigothic script
|
|
| Type | Alphabetic |
| Spoken languages | Medieval Latin |
| Time period | 7th century to 13th century |
| Parent systems |
Latin
|
| Sister systems | Beneventan, Merovingian |
| Note: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols in Unicode. | |
Visigothic script was a special style of handwriting used during the Middle Ages. It began in the kingdom of the Visigoths in Hispania, which is now mostly Spain and Portugal. People used this script from around the late 600s until the 1200s. It was mainly used in the Iberian Peninsula but also a little in southern France.
This script became very good between the 800s and 1000s. It developed from an older style called Uncial script. Because of this, Visigothic script shares many features with Uncial, like a similar way of writing the letter "g".
Contents
What Makes Visigothic Script Special?
Visigothic script has several unique features that help us recognize it:
- The letter "a" often looks open at the top, almost like the letter "u".
- The letters "r" and "s" can look very similar to each other.
- The letter "i" is often written very long, like the modern letter "l".
- The letter "d" has two main forms. One has a straight line going up, and the other has a line that slants to the left.
- The letter "t" has a hook that curves to the left when written alone. It also changes its shape when joined with other letters.
One very interesting letter is the special Visigothic "z" (ꝣ). This letter was later adopted into another writing style called Carolingian handwriting. Over time, this special "z" changed and became the "c-cedilla" (ç) that we sometimes see today in words like "façade."

Different Styles of Visigothic Script
Visigothic script wasn't just one single style. It had different forms for different purposes:
- Book-hand: This was a formal style used for writing important books, especially religious ones.
- Display script: A special style with tall, thin capital letters was developed for titles and headings.
- Cursive: This was a faster, more flowing style used for everyday documents and official papers. It had two main types:
- Leonese cursive: Used by Christians in the northern parts of the Iberian Peninsula.
- Mozarabic cursive: Used by Christians who lived in the southern areas controlled by Muslims.
Similar Scripts
Visigothic script shares many similarities with other old European writing styles. Two of its "sister" scripts are Beneventan script and Merovingian script. These scripts also developed around the same time and have some common features.
| Preview | Ꝣ | ꝣ | Ç | ç | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER VISIGOTHIC Z | LATIN SMALL LETTER VISIGOTHIC Z | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER C WITH CEDILLA | LATIN SMALL LETTER C WITH CEDILLA | ||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 42850 | U+A762 | 42851 | U+A763 | 199 | U+00C7 | 231 | U+00E7 |
| UTF-8 | 234 157 162 | EA 9D A2 | 234 157 163 | EA 9D A3 | 195 135 | C3 87 | 195 167 | C3 A7 |
| Numeric character reference | Ꝣ |
Ꝣ |
ꝣ |
ꝣ |
Ç |
Ç |
ç |
ç |
| Named character reference | Ç | ç | ||||||
See also
 In Spanish: Escritura visigótica para niños
In Spanish: Escritura visigótica para niños
 | Stephanie Wilson |
 | Charles Bolden |
 | Ronald McNair |
 | Frederick D. Gregory |