Visual programming language facts for kids
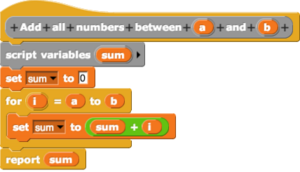
Imagine building a computer program like you're putting together Lego blocks! That's what a visual programming language (often called VPL or block coding) lets you do. Instead of typing out complicated code, you use pictures, shapes, or blocks to create your programs. It's like drawing a plan for your computer to follow.
VPLs help you arrange visual pieces on a screen. These pieces can be boxes, arrows, or colorful blocks. They represent different parts of your program. You connect them to show how your program should work. Many VPLs are used in low-code development platforms. These platforms help people build apps faster with less traditional coding.
Contents
What is Visual Programming?
Visual programming languages make coding easier to understand. They use visual elements instead of just text. Think of them as different ways to draw your program.
- Icon-based languages: These use small pictures or symbols.
- Form-based languages: These let you design programs using forms, like those you fill out online.
- Diagram languages: These use diagrams, like flowcharts, to show how a program moves from one step to another.
Visual programming helps people learn to code and supports experienced programmers in three main ways:
- Making fewer mistakes: VPLs use blocks or diagrams. These help you put program pieces together correctly. This means fewer "syntax errors," which are like grammar mistakes in code.
- Understanding what code means: VPLs can show you what each block or symbol does. They might have built-in help or descriptions. This makes it easier to grasp the purpose of different parts of your program.
- Seeing how programs work: VPLs let you test your program step-by-step. You can see how it reacts to different situations. For example, in games made with AgentCubes, you can change things to see how your game characters respond. With a Thymio robot, you can move it to see which sensors activate.
Since 2005, many VPLs have started using a method called dataflow programming. This lets you see what your program is doing right away. It also helps computers run many tasks at once, which is a big challenge for future programming.
It's important to know that tools like Microsoft Visual Studio (for languages like Visual Basic or C#) are not true visual programming languages. Even though they have helpful visual tools, you still write the actual program code using text.
Different Kinds of Visual Languages
Visual programming languages come in many forms. Some combine ideas from different types. The best type often depends on what you want to create.
- Block-based programming: This is very popular for learning to code. Programs like Scratch and Blockly use colorful blocks. You drag and drop them to build your code.
- Flowcharts: These use shapes and arrows to show the steps of a process. They are great for planning how a program will work.
- Drag-and-drop interfaces: These let you design how an app looks. You drag buttons, text boxes, and other items onto a screen.
- Node graphs: These connect "nodes" (boxes) with lines. Each node does a specific task. They are often used in game development and visual effects.
- Dataflow programming: In this type, data flows through a series of operations. It's like a pipeline where information moves from one step to the next.
- Iconic programming: This uses small pictures or icons to represent commands. It simplifies tasks, especially for mobile apps.
- State machines: These show how a system changes its "state" (like being "on" or "off") based on different events. They are useful for game characters or control systems.
- Timeline-based programming: Common in animation and video editing software. You arrange events along a timeline.
Powerful Visual Languages
Most visual programming languages are made for students or for specific tasks. They help new programmers learn the basics. However, some projects aim to create VPLs that are as powerful as text-based languages. These "general-purpose" VPLs could be used for any software project.
For example, projects like Envision and PWCT are working towards this goal. It's common for a VPL to be built using a text-based language. But with general-purpose VPLs, you can even create new text-based languages using visual tools! This makes programming more abstract. It helps developers focus on the big picture of a program, not just tiny code details.
Examples of Visual Languages
Here are some well-known visual programming languages:
For Learning and Education
These languages are perfect for students and beginners.
- AgentCubes: Helps you design 3D and 2D games and simulations.
- Alice: Used to program 3D virtual worlds and animations.
- App Inventor for Android: A tool to create Android apps. It uses blocks similar to Blockly.
- Blockly: A library that helps create block-based visual programming languages. It's famous for being used in Scratch.
- Catrobat: A block-based language for making animations, apps, and games.
- Flowcode: A visual tool for programming small computer chips (microcontrollers) and Windows programs.
- Flowgorithm: Lets you create flowcharts that can run as programs.
- Greenfoot: An environment for Java, great for learning and making games.
- Hopscotch: An iPad app for creating mobile apps with a visual language.
- Kodu: A visual tool from Microsoft for programming games in a 3D world.
- mBlock: An extension of Scratch for controlling Arduino hardware.
- Open Roberta: An online programming environment for kids from Fraunhofer IAIS.
- Raptor: A tool from the USAF for drawing executable flowcharts.
- Scratch: Created by MIT, it's very popular for kids to learn coding and make stories, games, and animations.
- ScratchJr: A simpler version of Scratch for younger children (5-7 years old).
- Snap!: An advanced version of Scratch, used for teaching at UC Berkeley.
- StarLogo: A language for creating simulations with many "agents" or characters.
- ToonTalk: A programming system designed for children.
- Visual Logic: For creating flowcharts that can run.
For Multimedia and Art
These VPLs help artists and designers create amazing visual and audio experiences.
- Blender: A free 3D graphics program. It uses node graphs for creating textures and visual effects.
- Houdini (software): Software for visual effects, modeling, and animation.
- Isadora: A program for macOS and Microsoft Windows that focuses on real-time video manipulation.
- Max: A visual environment for making interactive music and multimedia.
- Pure Data: A free visual language for creating interactive computer music and multimedia.
- TouchDesigner: A visual language for real-time multimedia content.
For Video Games
Many game engines use visual programming to make game development easier.
- Buildbox: A tool for creating games without coding.
- Clickteam Fusion: A 2D game creation software with an event editor.
- Construct: An HTML5-based 2D game editor.
- CryEngine: Has a node-based visual language called FlowGraph.
- Dreams: A PlayStation game where players create any kind of game using a visual language.
- Game Builder Garage: A 3D and 2D game creation tool for the Nintendo Switch.
- GameMaker Studio: Uses a drag-and-drop system for game creation.
- Godot: Allows game scripts and graphics shaders to be built with node-graph visual languages.
- Human Resource Machine: A puzzle game based on visual programming.
- Kodu: A Microsoft tool for programming games with a 3D interface.
- Rec Room: Includes a game creation system with a node-based visual language called Circuits.
- RPG Maker: A series of tools for creating role-playing games with event editors.
- Unity: A popular game engine that includes a visual scripting system (formerly known as Bolt).
- Unreal Engine 4: Features a node-based visual language called Blueprints for game logic and shaders.
Many modern video games also use "behavior trees." These are simple visual programming languages. They help model how non-player characters (NPCs) act in a game.
For Systems and Simulations
These VPLs help engineers and scientists model and understand complex systems.
- DRAKON: A graphical language developed for the Soviet Buran space program.
- Flowcode: A graphical language for programming embedded microprocessors.
- GNU Radio: A toolkit for building software-defined radios and signal processing systems.
- LabVIEW: A graphical language designed for engineers and scientists.
- Ladder logic: A language that looks like electrical relay circuits, used in industrial controllers.
- NXT-G: A visual language for the Lego Mindstorms NXT robotics kit.
- Node-RED: A software system for quickly developing applications, especially for connecting devices.
- OpenDX: For visualizing scientific data using a visual programming language.
- Orange: An open-source visual tool for data mining and machine learning.
- Simulink: A graphical environment for modeling and simulating complex systems.
- STELLA: A VPL for modeling how systems change over time.
For Automation
These tools help automate tasks and processes.
- Automator: A tool on macOS for automating repetitive tasks.
- CiMPLE: A visual language for teaching robotics.
Miscellaneous Visual Languages
Other interesting visual programming tools.
- Bubble: For creating web applications without writing code.
- Piet: An unusual language where programs are images made of colored pixels.
- PWCT: A free, open-source visual programming language for software development.
- Shortcuts: An Apple app for creating automated tasks (macros) on Apple devices.
See also
- Cognitive dimensions of notations - How easy a language is to use and understand.
- Dataflow programming
- Drag and drop
- Low-code development platform
- No-code development platform
- Programming game
- Unified Modeling Language
- Visual language