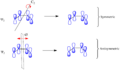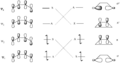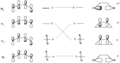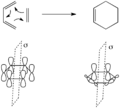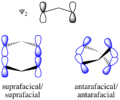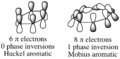Woodward–Hoffmann rules facts for kids
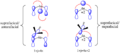
The Woodward–Hoffmann rules are a set of important guidelines in organic chemistry. They help scientists predict how certain chemical reactions will happen. Specifically, they predict the 3D shape, or stereochemistry, of molecules after a type of reaction called a pericyclic reaction.
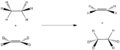
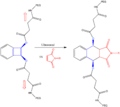
Pericyclic reactions are special rearrangement reactions. In these reactions, atoms within a molecule move around to form a new structure, often a ring shape. Think of it like rearranging LEGO bricks that are already connected to make a new shape.
These rules were created by two brilliant chemists: Robert Burns Woodward from Harvard University and Roald Hoffmann from Cornell University.
Roald Hoffmann won the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work on these rules. He shared the prize with Kenichi Fukui, who had a similar idea. Robert Woodward did not share the prize because he had passed away two years earlier. The Nobel Prize is usually only given to people who are still alive. However, Woodward had already won a Nobel Prize in Chemistry for a different amazing discovery.
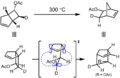
Recently, scientists found something interesting. A study in the journal Nature showed that pushing or pulling on molecules (called mechanical stress) can change how these reactions happen. Sometimes, this stress can even make reactions produce results that seem to go against the Woodward–Hoffmann rules!
Contents
What are Pericyclic Reactions?
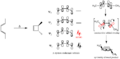
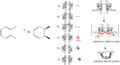
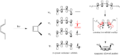
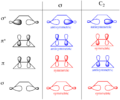
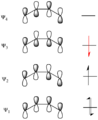
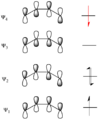
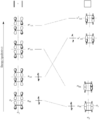
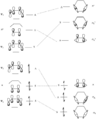
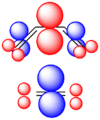
Pericyclic reactions are a special group of chemical reactions. They involve a continuous, circular movement of electrons. Imagine a circle of dancers holding hands and all moving at the same time to switch places. This is similar to how electrons move in these reactions.
These reactions are important because they create new bonds and break old ones in a very organized way. This organized movement helps chemists predict the final shape of the molecule.
Why are These Rules Important?
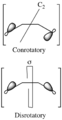
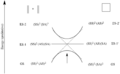
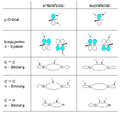
The Woodward–Hoffmann rules are like a map for chemists. They help predict the exact 3D shape of the products from pericyclic reactions. Knowing the 3D shape is very important in chemistry. It affects how molecules interact with each other. For example, in medicine, the 3D shape of a drug molecule can decide if it works or not.
These rules help chemists design new molecules and understand how natural processes work. They show how the symmetry of electron orbitals plays a big role in chemical reactions.
How Mechanical Stress Affects Reactions
Scientists usually think about chemical reactions happening with heat or light. But the new research shows that physical force, like stretching or squeezing a molecule, can also change a reaction's path.
This is a new and exciting area of chemistry. It means we might be able to control reactions in new ways. By applying mechanical stress, chemists could potentially make molecules that are difficult to create otherwise. This opens up new possibilities for making new materials or medicines.
Related Discoveries
- Woodward's rules are another set of rules developed by Robert Woodward. They are used to calculate how much UV light a molecule absorbs. This helps chemists figure out what a molecule looks like.
- Torquoselectivity is a concept related to how molecules twist during certain reactions. It's another way to understand the 3D outcomes of chemical changes.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Reglas de Woodward-Hoffmann para niños
In Spanish: Reglas de Woodward-Hoffmann para niños