Yellow-backed oriole facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Yellow-backed oriole |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Icteridae |
| Genus: | Icterus |
| Species: |
I. chrysater
|
| Binomial name | |
| Icterus chrysater (Lesson, 1844)
|
|
 |
|
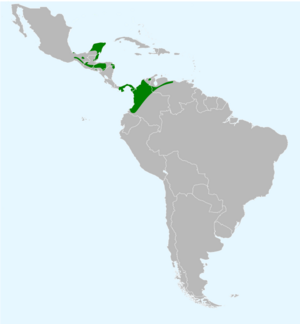
| Range of I. chrysater | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The yellow-backed oriole (Icterus chrysater) is a bright and beautiful bird. It is part of the Icteridae family, which includes many colorful birds. These orioles are known for their striking yellow and black feathers.
Contents
About the Yellow-Backed Oriole
Yellow-backed orioles are medium-sized birds. They are about 21.5 centimeters (8.5 inches) long from their beak to their tail. Both male and female birds look very similar, which is called being "sexually monomorphic." Their skin and claws are bluish-black. Adult birds have a black beak, but the bottom part of the beak is bluish-grey.
Colors and Patterns
Adult male orioles have very bright yellow and black feathers. Their wings, tail, shoulders, throat, and face are black. The rest of their body, like their back and belly, is a very bright yellow. Female orioles look a lot like males. However, their yellow parts might look a bit greener. It can be hard to tell males and females apart just by looking at them in nature.
Young yellow-backed orioles look like adult females. But their green colors are even stronger. Also, their flight feathers, which are black in adults, are dark brown. Young birds also have an olive-colored line near their eyes, which helps tell them apart.
Another bird that looks similar is the South American yellow oriole (Icterus nigrogularis).
Where They Live and What They Like
Yellow-backed orioles live across Central America and northern South America. They are found in different groups that live in separate areas. One group, called I. c. giraudii, lives in southern Central America. This includes countries like Nicaragua, Panama, and Colombia. Other groups, I. c. chrysater and I. c. mayanensis, live in northern Central America and southern Mexico.
You can find these birds in many countries. This includes Belize, Colombia, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, and Venezuela.
Their Favorite Places
Yellow-backed orioles can live in many different places. But they especially like open forests with a mix of pine and oak trees. They also enjoy dry scrub forests. Sometimes, you can even spot them in banana farms. They have also moved into lowland forests where trees lose their leaves.
These birds usually live in areas that are less than 900 meters (about 3,000 feet) high. However, in Central and South America, they are often seen living at heights greater than 1,000 meters (about 3,300 feet). The highest they have been seen living is around 3,000 meters (about 9,800 feet).
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Yellow-backed orioles are monogamous. This means they have only one mate at a time. Like many birds in the Icterus family, they breed once a year with the same partner.
Building Nests
Their nests are like shallow, hanging baskets. They usually hang from the very edge of a tree branch. These birds seem to prefer attaching their nests to the tips of palm leaves. They weave their nests using fine grasses, which makes them feel springy. These nests are usually hung high up in tall, grown-up trees, at least 7 meters (about 23 feet) off the ground.
Their Eggs
The eggs of the yellow-backed oriole are whitish. They have purple scribbles that are mostly found near the wider end of the egg. The eggs also often have brown lines spread evenly across them.
Behavior
Social Life
Yellow-backed orioles have been seen gathering in small groups. These groups can have up to eight birds. They are probably family units, with birds of different ages. Sometimes, these orioles join other types of birds in mixed flocks. These flocks might include wrens, jays, and other medium-sized orioles.
Sounds and Songs
This bird has a clear, whistling voice. Their song sounds a bit like the Spot-breasted oriole's song. It usually has a series of clear notes. But in some areas, like southern Central America, their song can sound a bit more muffled or warbled.
Both male and female yellow-backed orioles sing. This is common for orioles that live in warm, tropical places. They usually sing from high up in trees.
Their most common call sounds like a "nasal ‘chert’." They also make other sounds, like a "whistling chatter" and a "nasal alarm" call.
What They Eat and How They Find Food
Their Diet
Yellow-backed orioles mostly eat insects. Their diet includes caterpillars, wasps, ants, weevils, and other small creatures with hard shells. They also eat bananas. Sometimes, they drink nectar from flowers, like those of the balsa tree and Heliconia plants.
How They Find Food
These birds often look for food in family groups or in pairs. They hunt insects by poking into the bark of trees. They also search among the leaves of epiphytes, which are plants that grow on other plants. When they are looking for nectar, they sometimes "nectar rob." This means they make a hole at the bottom of a flower that hasn't opened yet to get to the sweet nectar inside.


