Zalmoxes facts for kids
Quick facts for kids ZalmoxesTemporal range: Upper Cretaceous 70–65 mya
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Superorder: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Infraorder: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: |
Zalmoxes
|
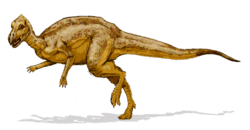
Zalmoxes was a type of dinosaur that lived a very long time ago. It belonged to a group called ornithopods. These dinosaurs were plant-eaters, just like Zalmoxes. This ancient animal lived during the Upper Cretaceous period, about 70 to 65 million years ago, in the area we now call Romania. It was a distant cousin of the well-known dinosaur, Iguanodon.
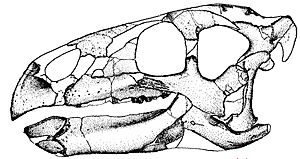
Scientists have found many parts of the Zalmoxes skeleton. They know almost everything about its bones, except for the very end of its tail, its hands, and its feet. This helps us understand what it looked like and how it lived.
Contents
What Was Zalmoxes?
Zalmoxes is a genus of dinosaur. A genus is a group of very similar animals. There are two main types, or species, of Zalmoxes that scientists know about: Zalmoxes robustus and Zalmoxes shqiperorum. Both were plant-eating dinosaurs.
How Big Was Zalmoxes?
Zalmoxes was not a giant dinosaur. It was a medium-sized plant-eater.
- Zalmoxes robustus was about 2.5 to 3 meters (8 to 10 feet) long. That's roughly the length of a small car.
- Zalmoxes shqiperorum was a bit smaller, around 2 to 2.5 meters (6.5 to 8 feet) long.
These dinosaurs were smaller than many of their relatives, like Iguanodon. Scientists think they might have been smaller because they lived on islands. Animals on islands sometimes evolve to be smaller over time, which is called island dwarfism.
What Did Zalmoxes Eat?
Like all ornithopods, Zalmoxes was a herbivore. This means it ate plants. It likely used its strong beak-like mouth and grinding teeth to munch on tough plants, ferns, and other vegetation that grew in its environment.
Where Did Zalmoxes Live?
Zalmoxes lived in what is now Romania, specifically in an area called the Hațeg Island. This was an island during the Late Cretaceous period. The island was home to many unique dinosaurs and other animals.
The Hațeg Island Ecosystem
The Hațeg Island was a fascinating place. Because it was an island, the animals there evolved differently from those on larger landmasses.
- Many of the dinosaurs, including Zalmoxes, were smaller than their relatives found elsewhere.
- The island had a warm, humid climate.
- It was covered in lush forests and swamps.
Zalmoxes shared its home with other interesting dinosaurs, such as the dwarf Titanosaur Magyarosaurus and the large Azhdarchid Pterosaur Hatzegopteryx.
Discovery and Fossils
The first fossils of Zalmoxes were found in the late 1800s in Transylvania, Romania. They were discovered by a famous paleontologist named Franz Nopcsa. He was one of the first to suggest that dinosaurs might have lived on islands.
What Fossils Tell Us
Scientists have found many parts of Zalmoxes skeletons. These include:
- Skulls and jaws, which show its plant-eating teeth.
- Vertebrae (backbones), including the sacrum (bones near the hips).
- Ribs and limb bones.
These fossils help scientists understand how Zalmoxes moved, what it ate, and how it was related to other dinosaurs. The fact that most of its skeleton is known helps us create a good picture of this ancient animal.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Zalmoxes para niños
In Spanish: Zalmoxes para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |