Mountain maple facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Mountain maple |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| 1819 illustration | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: |
A. spicatum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acer spicatum Lam. 1786
|
|
 |
|
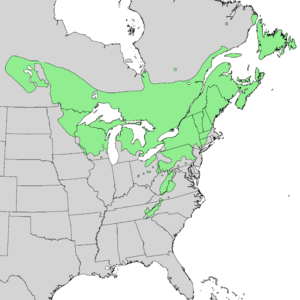
| Generalized natural range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
Acer dedyle Maxim.
Acer montanum W.T.Aiton Acer parviflorum Ehrh. Acer pumilum W.Bartram Acer striatum Du Roi |
|
The Mountain Maple (Acer spicatum), also known as dwarf maple, moose maple, and white maple, is a type of maple tree or shrub. It grows naturally in northeastern North America. You can find it from Saskatchewan in Canada all the way to Newfoundland, and south into Pennsylvania in the United States. It also grows in high, cool places in the southern Appalachian Mountains, reaching as far south as northern Georgia.
Contents
What the Mountain Maple Looks Like
The Mountain Maple is usually a deciduous shrub or a small tree. This means it's a bushy plant that loses its leaves every autumn. It can grow to be about 3 to 8 meters (10 to 26 feet) tall. It has a wide, spreading top with a short trunk and thin branches.
Its leaves grow in pairs, one across from the other. They are simple, meaning each leaf is a single piece, not divided into smaller leaflets. Each leaf is about 6 to 10 centimeters (2.5 to 4 inches) long and wide. They have 3 or 5 shallow, wide points, like gentle bumps. The edges of the leaves are rough and unevenly toothed. The top of the leaf is light green and smooth, while the underside has fine hairs. In autumn, these leaves turn bright yellow to red, making the tree very colorful. The leaves grow on thin stalks that are usually longer than the leaf blade itself.
The bark of the Mountain Maple is thin and a dull gray-brown color. When the tree is young, the bark is smooth, but as it gets older, it becomes a little scaly. The tree produces a fruit called a samara, which is a paired, reddish seed with a wing. These samaras are about 2 to 3 centimeters (0.75 to 1.25 inches) long and become ripe in late summer to early autumn.
Where Mountain Maples Live
This tree likes to live in moist forests where the soil is rich and drains water well. You can often find it on rocky hillsides and next to streams. It also grows in ravines, on cliff faces, and in forested bogs (wetlands). The Mountain Maple often grows in the lower layer of hardwood forests, beneath taller trees.
Animals and the Mountain Maple
Many animals use the Mountain Maple. Large mammals like moose, deer, beavers, and rabbits like to eat its bark. Birds such as ruffed grouse eat the tree's buds.
How People Use Mountain Maple
The sap from the Mountain Maple contains sugar, just like other maple trees. This sap can be boiled down to make maple syrup. The bark of the tree has something called tannins, which were traditionally used to prepare leather.
Native American peoples used parts of the Mountain Maple for different purposes. They would soak the soft inner part (pith) of young twigs to create treatments for eye irritation. They also made poultices (soft, moist masses applied to the body) from boiled root chips. Some people also believe that this plant can help reduce stress in humans.
See also
 In Spanish: Acer spicatum para niños
In Spanish: Acer spicatum para niños




