Allegheny chinquapin facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Allegheny chinquapin |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Leaves and flowers of Allegheny chinquapin | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Fagaceae |
| Genus: | Castanea |
| Species: |
C. pumila
|
| Binomial name | |
| Castanea pumila |
|
 |
|
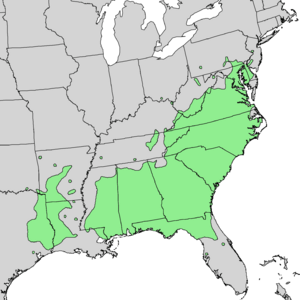
| Natural range | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Castanea pumila, often called the Allegheny chinquapin, is a type of chestnut tree. People also call it the American chinquapin or dwarf chestnut. It grows naturally in the southeastern United States. You can find it from Maryland down to central Florida. It also grows west to eastern Texas and north to southern Missouri and Kentucky. This plant likes dry, sandy, or rocky areas. It often grows with oak and hickory trees. It does best in soil that drains well, in sunny or partly shady spots.
Contents
What Does the Allegheny Chinquapin Look Like?
The Allegheny chinquapin is usually a spreading bush or a small tree. It can grow to be about 2 to 8 meters (6 to 26 feet) tall. Its bark is reddish or grayish-brown. It has small grooves and scaly plates.
Leaves and Flowers
The leaves are simple and shaped like a narrow oval or spear. They are yellowish-green on top. The underside is paler and has fine hairs. Each leaf is about 7.5 to 15 centimeters (3 to 6 inches) long. They are about 3 to 5 centimeters (1 to 2 inches) wide. The leaves have parallel veins that end in short, pointed teeth.
The flowers appear in early summer. Both male and female flowers grow on the same plant. The male flowers are small and pale yellow to white. They grow on upright spikes called catkins, which are about 10 to 15 centimeters (4 to 6 inches) long. These catkins are attached at the base of each leaf. The female flowers are tiny, about 3 millimeters (0.1 inches) long. They are found at the base of some of the catkins.
Fruit and Nuts
The fruit of the chinquapin is a golden-colored, spiny shell. This shell is called a cupule. It is about 2 to 3 centimeters (0.8 to 1.2 inches) across. It has many sharp spines. The fruit ripens in the autumn. Inside each spiny shell is one shiny, dark brown nut. This nut is oval-shaped and can be eaten.
Sometimes, the Allegheny chinquapin can mix with the American chestnut. When they do, they create a natural hybrid tree. This hybrid is known as Castanea × neglecta.
Where Does the Allegheny Chinquapin Grow?
The Allegheny chinquapin is very similar to the American chestnut, which is called Castanea dentata. Both trees can grow in the same places. You can tell them apart by their nuts. The chinquapin nut is smaller, about half the size of a chestnut. It is also round, not flattened on one side like a chestnut. The leaves of the Allegheny chinquapin are also smaller than the American chestnut's. They have less clear teeth along their edges.
Dealing with Chestnut Blight
A big problem for chestnut trees is a fungus called chestnut blight. This fungus caused a lot of damage to American chestnut trees. Luckily, the Allegheny chinquapin is not as easily harmed by this blight. Even if the chinquapin gets the blight, it can still send out new shoots from its base. These new shoots can grow and produce fruit. However, chinquapins can still get sick. Many reports show trees with lots of disease and cankers.
How People Use Allegheny Chinquapin
The first written record of the Allegheny chinquapin was made in 1612. John Smith, from Jamestown, wrote about it. He saw Native Americans using the tree and its nuts.
Traditional Uses
Native Americans used the chinquapin in many ways. They made a special drink from the leaves. This drink helped with headaches and fevers. The bark, leaves, wood, and nut husks of the plant all contain something called tannin.
Food and Wood
The nuts of the chinquapin can be eaten. People can blanch them (quickly boil them), dry them, and then rehydrate them to eat. The wood of the chinquapin is strong and lasts a long time. It is sometimes used for fences or as fuel for fires. However, the tree is usually too small to be important for selling its wood.
Helping Wildlife
Chinquapin plants are also used to attract wild animals. If the base of the plant is cut or hurt, it will grow many new stems. These stems create a thick cover that turkeys like to use. Squirrels and rabbits eat the nuts. White-tailed deer also eat the leaves of the plant.
See also
 In Spanish: Castanea pumila para niños
In Spanish: Castanea pumila para niños



