Alveolus facts for kids
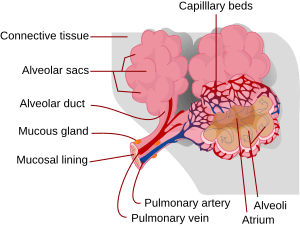
An alveolus (plural: alveoli) is like a tiny, hollow air sac found deep inside your lungs. Even though the word "alveolus" can mean other hollow spaces in the body, it usually refers to these special air sacs in the lungs of mammals, like humans. They are also called pulmonary alveoli.
These tiny air sacs are located at the very ends of the small air passageways in your lungs. Alveoli have super thin walls, only one cell thick! Their walls are also wet, and they are surrounded by a network of tiny blood vessels called capillaries. This special design helps gases to diffuse, or move easily, across their surface.
How Alveoli Help You Breathe
Alveoli play a super important role in helping your body get the oxygen it needs and get rid of waste carbon dioxide. This process is called gas exchange.
Oxygen In
When you breathe in, the air you inhale fills your alveoli with lots of oxygen. At this point, there's more oxygen in the alveoli than in your red blood cells. Because of this difference, oxygen quickly moves from the alveoli into your red blood cells. These red blood cells then carry the oxygen all over your body.
Carbon Dioxide Out
When you breathe out, the opposite happens. Your body's cells have used oxygen and produced carbon dioxide as a waste product. This carbon dioxide travels in your blood back to the lungs. Inside the alveoli, there's less carbon dioxide than in your red blood cells. So, carbon dioxide moves from your red blood cells into the alveoli. Then, when you exhale, you breathe out this carbon dioxide.
Amazing Numbers
Your lungs are packed with these tiny air sacs! An average human lung has about 480 million alveoli. If you were to flatten out all the alveoli in your lungs, their total surface area would be around 75 square meters. That's about the size of a tennis court! This huge surface area makes gas exchange super efficient.
See also
 In Spanish: Alvéolo para niños
In Spanish: Alvéolo para niños