Amygdala facts for kids
| Brain: Amygdala | ||
|---|---|---|
Quick facts for kids
|
||
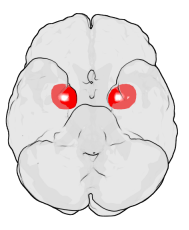
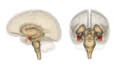
| Location of the amygdalae in the human brain | ||
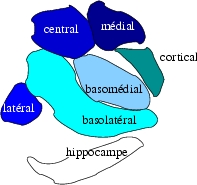
| Subdivisions of the amygdala | ||
| Latin | corpus amygdaloideum | |
The amygdala is a tiny, almond-shaped part of your brain. You actually have two amygdalae (that's the plural form), one on each side of your head. They are located deep inside your temporal lobes. The word "amygdala" comes from Latin and Greek, meaning 'almond' or 'tonsil', because of its shape.
Scientists have found that the amygdala plays a super important role in how we process memory, make decisions, and experience emotions. This includes strong feelings like fear, worry (which is like anxiety), and even anger (aggression). The amygdala is considered a key part of the limbic system, which is a group of brain structures involved in emotion, motivation, and memory.
Contents
How the Amygdala Works
The amygdala helps us understand and react to our feelings. Each of your two amygdalae has special jobs, but they work together. They help you store, remember, and understand emotions.
Emotions and the Amygdala
Studies show that if the right amygdala is stimulated, people might feel negative emotions like fear or sadness. But if the left amygdala is stimulated, people might feel happy, or sometimes still feel fear, anxiety, or sadness. Some research also suggests the left amygdala is involved in the brain's "reward system," which makes you feel good when you do something positive.
The right side of your amygdala is often linked to negative emotions. It helps you show fear and process things that make you feel scared. This helps you learn to avoid dangerous situations and figure out what might be a threat around you.
Memory and the Amygdala
The right amygdala is also connected to a type of memory called declarative memory. This is the memory of facts and events you can consciously remember, like what you had for breakfast or who invented the lightbulb. It also helps you remember personal experiences, like your first day of school or a fun trip. This is called Episodic memory. The right amygdala helps connect these memories to the time and place they happened, along with the emotions you felt.
The amygdala also helps with memory consolidation. This is the process where new memories are slowly turned into long-term memories. So, after you learn something new, your amygdala helps make sure that information sticks in your brain for a long time.
Creativity and the Amygdala
Some interesting research using Rorschach tests (which are inkblot tests) found a link between the size of the amygdala and creativity. People who gave more unique answers to the inkblots tended to have larger amygdalae. Since artists often give unique answers, this suggests that a larger amygdala might be connected to creative thinking.
Amygdala and Feelings
The amygdala plays a role in our mental well-being. It's connected to how we feel and react to the world. For example, some studies have shown that children with anxiety disorders might have a smaller left amygdala. The left amygdala has also been linked to social anxiety and other conditions like obsessive-compulsive disorder and post-traumatic stress.
In some studies, people with certain personality traits showed different amygdala activity. For instance, people with borderline personality disorder sometimes had more activity in their left amygdala. They might even see neutral faces as threatening. People with psychopathy might show less fear response. Also, those with ADHD sometimes show more amygdala activity when facing scary situations.
For people experiencing sadness or low mood, the left amygdala might be extra active when they look at faces, especially fearful ones. This extra activity can become normal when they receive help or medication. The amygdala also acts differently in people with bipolar disorder. Some studies found that adults and teens with bipolar disorder had smaller amygdala volumes. Many scientists are also studying the connections between the amygdala and autism.
Images for kids
-
MRI coronal view of the right amygdala
See also
 In Spanish: Cuerpo amigdalino para niños
In Spanish: Cuerpo amigdalino para niños
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |