Limbic system facts for kids
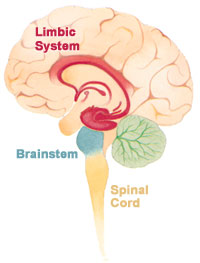
The limbic system is a group of important parts in your brain. These parts are found on both sides of the thalamus, right under the main part of your brain, the cerebrum. It's not really a separate system. Instead, it's a collection of structures from different brain areas working together. The limbic system helps with many things. These include your emotions, how you behave, what motivations you have, your long-term memory, and even your sense of smell.
Contents
What is the limbic system?
The limbic system was first described as a set of brain parts. These parts surround the border between the two halves of the cerebrum and the brainstem. The word "limbic" comes from the Latin word limbus, which means "border" or "edge".
Scientists later found that these areas were important for emotions and motivation. They also found that other parts of the brain connected to them. Today, the limbic system is seen as one of many brain areas. It helps control how your body works automatically, like your heart rate. The exact parts that make up the limbic system can be a bit tricky. This is because scientists are always learning more about the brain.
Some of the main parts that are considered part of the limbic system include:
- Limbic lobe: A part of the cerebral cortex.
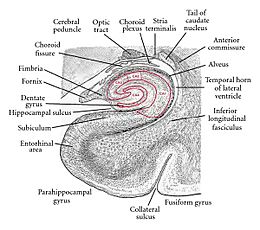
- Hippocampus: This part is key for forming new memories.
- Amygdala: This part is deep inside the temporal lobes. It is linked to many emotional processes.
- Hypothalamus: This is a central control area for the limbic system. It helps regulate many automatic body processes.
- Thalamus: This part receives signals from other limbic areas. It is involved in memory processing.
- Nucleus accumbens: This area is involved in feelings of reward and pleasure.
How does the limbic system work?
The limbic system and its connected areas are involved in many important functions. These include motivation, emotion, learning, and memory. It acts as a meeting point where deeper brain structures connect with the cerebral cortex.
The limbic system works by affecting your endocrine system. This system produces hormones. It also affects your autonomic nervous system. This system controls automatic body functions. The limbic system is also closely connected to the nucleus accumbens. This connection helps with feelings of reward.
It also works with the basal ganglia. These are brain structures that help control your movements. They get information from the cerebral cortex. Then they send signals to parts of the brain that control movement. For example, a part called the striatum helps control your posture and movement. If there isn't enough of a chemical called dopamine in the striatum, it can lead to problems like Parkinson's disease.
The limbic system is also strongly linked to the prefrontal cortex. This part of your brain is involved in planning and decision-making. Some scientists think this connection helps us feel good when we solve problems. In the past, doctors sometimes cut this connection in a surgery called a prefrontal lobotomy. This was done to try and help with severe emotional problems. However, patients often became very quiet and lost all their motivation.
The limbic system is not just a part of the cerebrum. It works closely with the cerebral cortex. These interactions are important for many things. They help with your sense of smell, emotions, and memory. They also help control automatic body functions. Problems with the limbic system can be linked to conditions like epilepsy and schizophrenia.
The hippocampus and memory
The hippocampus is a very important part of the limbic system. It is one of the most studied areas. It plays a big role in how we think and remember.
Spatial memory
One of the main jobs of the hippocampus is spatial memory. This is your memory for places and how to get around. Different parts of the hippocampus help with this. For example, the dorsal hippocampus helps create new brain cells. These new cells help you remember places better. They make your memories stronger. This helps connect your memories of places with how you felt about them.
The left hippocampus is important for remembering these spatial memories later. It helps put together "what," "when," and "where" information. This allows you to recall a complete memory. Another area, the parahippocampal region, also helps with memory recall.
Learning
The hippocampus also has a huge impact on learning. Studies show that the hippocampus responds well to mental and physical training. When you learn new things, new brain cells and connections form in the hippocampus. This process is called neurogenesis. These new cells help improve your learning abilities. They make the hippocampus more active. This helps it contribute more to the learning process.
The amygdala and emotions
The amygdala is another key part of the limbic system. It is often seen as one of the most important parts for emotions.
Memory and emotions
Like the hippocampus, the amygdala affects memory. But it's more about emotional memories. It helps us remember events that have strong feelings attached to them. The amygdala helps store and recall these emotional memories. It helps charge cues so that emotional events can be found and remembered.
Attention and feelings
The amygdala is also important for attention and emotional processes. Attention is your ability to focus on some things while ignoring others. The amygdala helps you decide what to pay attention to.
Historically, the amygdala was thought to be mainly linked to fear. It was believed to help us react to danger. But now, scientists know it does more. It helps us understand a situation and respond in the right way. The amygdala is involved in many emotional processes. It helps with the creation of new brain cells. These cells are important for strong spatial memory and learning. They also help the amygdala work properly. If these cells are not working well, it can lead to problems like anxiety disorders.
Social understanding
The amygdala also helps us understand social situations. Specifically, it helps us evaluate faces. Studies show that the amygdala plays a key role in judging faces. It helps us decide if someone seems trustworthy. People with damage to their amygdala sometimes have trouble telling the difference between trust and betrayal. They might trust people who have done them wrong. The amygdala also helps us form first impressions of people. This shows that it is important for overall social understanding.
History of the limbic system
How the term "limbic" came to be
The word limbic comes from the Latin word limbus. This means "border" or "edge." Paul Broca, a French physician, first used this term in 1878. He called this part of the brain le grand lobe limbique. He noticed its position, sandwiched between other brain parts.
The term "limbic system" was officially introduced in 1949 by Paul D. MacLean. In 1937, James Papez described his model of emotion, called the Papez circuit. This helped scientists understand the limbic system's role in emotions.
The first proof that the limbic system was responsible for emotions came in 1939. Heinrich Kluver and Paul Bucy found that removing parts of the temporal lobes in monkeys changed their behavior. The monkeys became less aggressive. They also had trouble recognizing familiar objects.
MacLean expanded on these ideas. He included more structures in a wider "limbic system." He also developed the idea of the "triune brain." This theory tries to explain how the human brain evolved. It suggests that our brain has three main parts. The oldest part, the R-complex, is like a reptile brain. It controls basic functions like breathing. The limbic system evolved in early mammals. It helps control "fight-or-flight" responses and reactions to pleasure and pain. The newest part, the neocortex, controls speech and reasoning.
Ongoing discussions
Some scientists, like Joseph E. LeDoux and Edmund Rolls, think the term limbic system might be outdated. They argue that the limbic system was once thought to be only about emotions. But now we know that the neocortex and other parts are also involved in emotions and thinking.
For example, the hippocampus is part of the limbic system. It is very important for memory. If the hippocampus is damaged, it can cause severe memory problems. Also, the "borders" of the limbic system have changed as we learn more about the brain.
So, while the limbic system is closely linked to emotions, it's best to think of it as one part of a larger system. This larger system processes emotions. The limbic system helps sort and organize basic sensory information. Then it sends this information to other brain areas for more complex emotional processing.
See also
 In Spanish: Sistema límbico para niños
In Spanish: Sistema límbico para niños