Danelaw facts for kids
The Danelaw was a special area in northern and eastern England that was controlled by Danish Vikings for a long time. This period lasted from the late 9th century until the early 11th century. The name "Danelaw" comes from an old English phrase, Dena lagu, which means "Danes' law." It shows that the laws and customs in this part of England were different from the rest of the country.
Contents
What was the Danelaw?
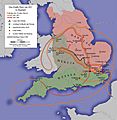
The Danelaw was not just one place, but a collection of areas where the Vikings had settled and set up their own rules. These areas included parts of what are now Northumbria, East Anglia, and the Midlands. The Vikings, also known as Norsemen, were fierce warriors and explorers from Scandinavia. They came to England looking for new lands and riches.
The Vikings started raiding England in the late 8th century. Over time, they began to settle down and farm the land. They built towns and created their own kingdoms. The Danelaw was the result of these settlements. It was a place where Danish laws and traditions were followed, even though it was on English soil.
How did the Danelaw start?
The story of the Danelaw began with Viking raids on England. These raids became more organized, and soon, large Viking armies arrived. One of the most famous was the "Great Heathen Army" in the mid-9th century. This army conquered several Anglo-Saxon kingdoms.
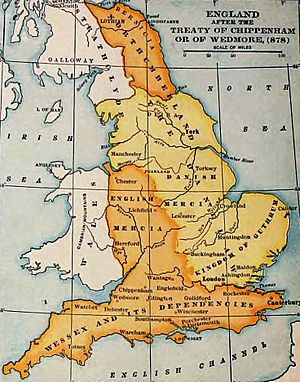
The English king, Alfred the Great of Wessex, fought bravely against the Vikings. After many battles, he managed to defeat the Viking leader, Guthrum, at the Battle of Edington in 878 AD. This led to a peace treaty called the Treaty of Wedmore.
This treaty divided England into two main parts. The Anglo-Saxons, led by King Alfred, controlled the south and west. The Vikings controlled the north and east, which became known as the Danelaw. This agreement helped bring some peace, but it also meant that a large part of England was now under Viking rule.
Life in the Danelaw
Life in the Danelaw was a mix of Viking and English cultures. The Vikings brought their own language, laws, and ways of doing things. Many English people continued to live there, and over time, the two cultures began to blend.
- Laws and Government: The Danelaw had its own legal system, which was based on Danish customs. These laws were often different from the Anglo-Saxon laws in the rest of England. For example, Viking laws sometimes gave more rights to women.
- Language: The Danish language had a big impact on English. Many words we use today, like "sky," "leg," "take," and "anger," come from Old Norse, the language of the Vikings.
- Towns and Trade: The Vikings were also great traders. They helped develop important towns like York (which they called Jorvik) and Lincoln. These towns became busy centers for trade and craft.
- Farming: Like the English, the Vikings were farmers. They settled on the land and grew crops. They also raised animals.
The end of the Danelaw
The Danelaw did not last forever as a separate Viking territory. Over time, English kings began to fight back and slowly regain control of these lands. King Alfred's son, Edward the Elder, and his daughter, Æthelflæd, Lady of the Mercians, were very successful in these efforts.
By the mid-10th century, most of the Danelaw was back under English rule. However, Viking influence remained strong, especially in places like York. Even after the English kings took back control, many Danish customs and laws continued to be used.
Later, in the early 11th century, England was again conquered by a Danish king, Canute the Great. He ruled over a large North Sea empire that included England, Denmark, and Norway. But even under Canute, the idea of the Danelaw as a separate legal area began to fade.
Legacy of the Danelaw
Even though the Danelaw no longer exists, its history has left a lasting mark on England.
- Place Names: Many towns and villages in northern and eastern England still have names that come from Old Norse. For example, names ending in "-by" (like Grimsby or Derby) mean "farm" or "settlement" in Old Norse. Names ending in "-thorpe" (like Scunthorpe) mean "village."
- Language: As mentioned, many English words have Viking origins.
- Laws: Some legal traditions in England might have been influenced by Danish laws.
- Culture: The blending of Anglo-Saxon and Viking cultures helped shape the identity of the English people.
The Danelaw was an important period in English history. It shows how different cultures can meet, clash, and eventually blend together, leaving a rich legacy for future generations.
Images for kids
-
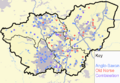
Toponymy within present day South Yorkshire, the former Kingdom of Jorvik, showing the lasting legacy of Danish settlement
See also
 In Spanish: Danelaw para niños
In Spanish: Danelaw para niños