Aristotelia chilensis facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Aristotelia chilensis |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Maqui tree with fruits | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Oxalidales |
| Family: | Elaeocarpaceae |
| Genus: | Aristotelia |
| Species: |
A. chilensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Aristotelia chilensis (Molina) Stuntz
|
|
 |
|
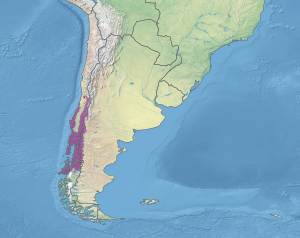
| The native area of the rainforest | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Aristotelia chilensis, often called Maqui or Maquiberry, is a special tree from South America. It grows naturally in the Valdivian temperate rainforests of Chile and parts of southern Argentina. People sometimes plant these trees in their gardens to grow their small, tasty fruits, which are known as maqui berries. However, most of the maqui berries you find in stores come from wild trees.
Contents
Description
The Maqui Tree
The Maqui tree (Aristotelia chilensis) is a small evergreen tree. This means it keeps its leaves all year round. It can grow to be about 4 to 5 meters (13 to 16 feet) tall. The tree has a smooth bark and many thin, flexible branches. Its leaves are simple, hang down, and are shaped like an oval with a pointed end. They feel a bit like leather and have jagged edges. You can easily see the veins on the leaves, and their stems are a bright red color.
In early spring, the Maqui tree sheds its old leaves. It uses the energy from these old leaves to grow new ones and to make flowers.
Flowers and Berries
When the Maqui tree flowers in late spring, it produces small, white flowers. These flowers are unisexual, meaning each flower has either male or female parts, but not both. These flowers eventually turn into small, edible fruits.
The fruits are tiny, purple-black berries, about 4 to 6 millimeters (0.16 to 0.24 inches) wide. Each berry usually has 4 to 8 seeds inside. A Maqui tree that is seven years old can produce up to 10 kilograms (22 pounds) of berries each year! The berries taste a bit like blackberries. Because of this, the tree is sometimes called the Chilean wineberry. In Chile, people call it maqui or maque.
Where Maqui Grows
The Maqui tree is native to Chile and Argentina, along the southwest coast of South America. It grows naturally in the Chilean rainforests. Its natural home stretches across a large area in Chile, from the Coquimbo region down to the Aysén region. This area covers about 170,000 hectares (420,000 acres).
Maqui in Nature
Maqui berries are a favorite food for birds when summer ends. Sadly, when people cut down the Valdivian temperate rainforests in Chile, it makes it harder for birds to spread the Maqui seeds. This can cause problems for the Maqui trees, making them less healthy over time.
Harvesting and Growing Maqui
People collect Maqui berries from wild plants every year between December and March. Many families, especially the Mapuche people, gather these berries near the Andes Mountains. To harvest them, they collect the side branches of the trees. Then, they shake the branches to separate the berries and leaves. After that, they use machines to separate the berries from the leaves.
The collected berries are sold in local markets. The price can be between $6.50 and $15 per kilogram. On average, about 220 kilograms (485 pounds) of berries are harvested from one hectare of land each year. However, because it's hard to reach some areas and transport the berries, only about 90 short tons (82,000 kg) are collected each year in total.
Maqui trees are mostly planted in home gardens and are not grown on large farms. This is why most of the berries you see for sale are picked from wild trees. Maqui trees don't like frost very much, but they can handle growing near the sea. They grow best in soil that drains water well and gets lots of sunshine. They also need some protection from cold, strong winds. The soil should be a little bit acidic and have a good amount of nutrients.
You can plant Maqui trees in areas with mild winters, like USDA zones 8 to 12. They are grown in Spain and in some warmer, wetter parts of Britain. In colder areas, winter frosts might damage the tree's branches, but this often makes new shoots grow in the spring.
How to Grow New Maqui Plants
Maqui seeds can sprout without needing a cold period first. If you live in an area where it might freeze, it's best to plant the seeds in a greenhouse in the spring. If the young plants grow big enough by autumn, you can move them into their own small pots. These potted plants should stay in the greenhouse for their first winter to protect them from the cold.
The next year, after the last expected frost in spring, you can plant the young Maqui trees outside in their permanent spots. During their first winter outdoors, they will need some protection from frost.
You can also grow new Maqui plants from cuttings. This means taking a piece of a branch, about 15 to 30 centimeters (6 to 12 inches) long, and planting it in a pot. These cuttings usually grow roots and can be planted outside the following spring.
Healthy Maqui Berries
Scientists have studied Maqui berries and found they are full of healthy compounds called anthocyanins. These are the natural colors that give the berries their deep purple-black color. Maqui berries are known for having a good amount of these anthocyanins.
Studies have also shown that Maqui berries have strong antioxidant properties. This means they can help protect your body's cells from damage. Some research suggests that Maqui berries can help protect against "bad cholesterol" and keep your body's cells healthy.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Maqui para niños
In Spanish: Maqui para niños


