Auriga (constellation) facts for kids
| Constellation | |
List of stars in Auriga
|
|
| Abbreviation | Aur |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Aurigae |
| Pronunciation |
|
| Symbolism | the Charioteer |
| Right ascension | 6 |
| Declination | +40 |
| Quadrant | NQ1 |
| Area | 657 sq. deg. (21st) |
| Main stars | 5, 8 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars |
65 |
| Stars with planets | 7 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 4 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 2 |
| Brightest star | Capella (α Aur) (0.08m) |
| Messier objects | 3 |
| Meteor showers |
|
| Bordering constellations |
|
| Visible at latitudes between +90° and −40°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of late February to early March. |
|
Auriga is a cool constellation you can spot in the northern sky! Its name comes from a Latin word meaning "charioteer," which is someone who drives a vehicle pulled by animals. A long time ago, in the 2nd century, a famous astronomer named Ptolemy wrote about Auriga in his list of 48 constellations.
Contents
Exploring the Auriga Constellation
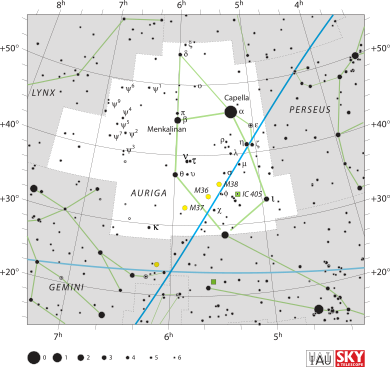
Auriga is a large constellation, ranking as the 21st biggest in the night sky. It covers an area of 657 square degrees. You can find it in the first quadrant of the Northern Hemisphere.
Where to Find Auriga
The best time to see Auriga is from late February to early March. It's a northern constellation, so it's easiest to see from places north of the equator. It borders several other constellations, including Camelopardalis, Perseus, Taurus, Gemini, and Lynx.
Bright Stars of Auriga
Auriga is home to some very bright stars. The brightest star in Auriga is called Capella. It's also known as Alpha Aurigae. Capella is a very bright star, shining with a magnitude of 0.08. It's actually a system of four stars!
- Capella (Alpha Aurigae): This is the sixth brightest star in the entire night sky. It's a yellow giant star system.
- Epsilon Aurigae: This is a fascinating star system. It's an eclipsing binary star, meaning one star passes in front of another. This causes its brightness to dim every 27 years!
- QY Aurigae: This is one of the closest stars in Auriga to our Sun. It's about 20.74 light-years away.
Cool Objects in Auriga
Auriga has several interesting deep-sky objects that astronomers love to study. These include star clusters and nebulae.
Star Clusters
There are three famous Messier objects in Auriga. These are open star clusters, which are groups of stars born from the same giant molecular cloud.
- Messier 36 (M36): This is an open cluster with about 60 stars. It's around 4,300 light-years away from Earth.
- Messier 37 (M37): This is the richest and most compact of the three Messier clusters in Auriga. It has over 500 stars and is about 4,500 light-years away.
- Messier 38 (M38): Also known as the "Starfish Cluster," M38 has a unique cross shape. It's about 4,200 light-years away.
Nebulae
Auriga also contains beautiful nebulae, which are giant clouds of gas and dust in space.
- The Flaming Star Nebula (IC 405): This nebula is lit up by a hot, blue star called AE Aurigae. It looks like it's on fire!
- IC 410: This nebula is home to a group of newly formed stars.
Meteor Showers
If you like watching shooting stars, Auriga is known for two meteor showers:
- Aurigids
- Delta Aurigids
These are times when Earth passes through trails of dust left by comets, causing meteors to streak across the sky.
Images for kids
-
A painting by Peter Paul Rubens entitled Finding of Erichthonius; Erichthonius and Auriga are often associated.
-
A picture of NGC 1893 obtained by the Spitzer Space Telescope. An association of recently formed stars is surrounded by the nebula IC 410.
See also
 In Spanish: Auriga (constelación) para niños
In Spanish: Auriga (constelación) para niños