Avenanthramide facts for kids
Avenanthramides are natural compounds found mostly in oats. They are also found in some butterfly eggs and in carnation flowers that have a fungus. Scientists have studied these compounds and found that they can help with many things.
Avenanthramides are known to:
- Reduce inflammation (swelling and redness)
- Act as antioxidants (protect cells from damage)
- Stop itching
- Lessen irritation
- Help prevent hardening of the arteries
Because of these helpful properties, extracts from oat kernels that contain avenanthramides are used in many products. You can find them in skin care, hair care, baby products, and even sunscreens. The name avenanthramides was first used by a scientist named Collins when he found these compounds in oats.
Contents
History of Oats in Skin Care
People have used oats for skin care for a very long time. About 4,000 years ago, in ancient Egypt and the Arabian Peninsula, wild oats were already being used on the skin.
Oat baths were a common way to treat:
Ancient Roman writers like Pliny also wrote about using oats for skin issues. In the 1800s, oatmeal baths were often used to calm itchy, inflamed skin. By the 1930s, more studies showed that oats could clean skin, relieve itching, and protect it.
Colloidal Oatmeal
In 2003, a special type of oat product called colloidal oatmeal was officially approved as a skin protector by the FDA in the US. For a long time, people didn't know exactly *what* in oats made them so helpful.
Then, scientists started paying more attention to avenanthramides. These compounds were first separated and studied in the 1980s. Since then, many similar avenanthramides have been found. We now know they have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. They might even help people with allergies or heart problems.
Studies in 1999 showed that avenanthramides are absorbed by the human body and stay active after you eat them. More recent studies found that eating a small amount of avenanthramides daily for eight weeks can boost their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory power.
How Oats Use Avenanthramides
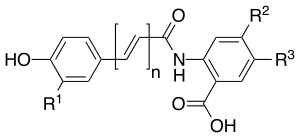
Oats (Avena sativa) make avenanthramides as a way to defend themselves. They act like natural shields against tiny invaders, especially fungi that can harm the plant. These defensive chemicals were first found in parts of oat plants that were infected by a specific fungus.
Medical and Personal Care Uses
Avenanthramides are very useful in health and beauty products.
Reducing Inflammation and Itch
Studies show that avenanthramides can greatly reduce inflammation. Inflammation is your body's natural way of protecting itself from harm, like infections or injuries. It's controlled by special messengers called cytokines. Avenanthramides can lower the production of these inflammatory messengers. This means they help calm down swelling and redness.
Avenanthramides also help reduce itching. Their ability to stop itching is similar to how well some common anti-itch creams work.
Lessening Redness
Avenanthramides can also act like antihistamines. This means they can significantly reduce both itching and redness on the skin.
How They Work
Avenanthramides help reduce inflammation by calming down certain processes in your body's cells. They can stop the release of inflammatory chemicals that cause itchy skin diseases. This can help break the "itch-scratch cycle" often seen in conditions like atopic dermatitis and eczema. By reducing itching and scratching, avenanthramides help protect the skin's natural barrier.
Their structure is similar to a medicine used to block histamine, which is a chemical that causes allergic reactions and itching. All these effects show that avenanthramides are strong anti-inflammatory agents, making them very important for skin care.
Antioxidant Power
Avenanthramides are also powerful antioxidants. Antioxidants are substances that protect your body's cells from damage caused by "oxidative stress." This stress can lead to serious health problems like cancer and heart disease. Different types of avenanthramides have different antioxidant strengths.
As a Dietary Supplement
Avenanthramides from oats show strong antioxidant effects both in lab tests and in living things. Some studies suggest their antioxidant power is much greater than other well-known antioxidants. One specific avenanthramide, Aven-C, is thought to be a main reason for oats' antioxidant benefits.
Studies on animals have shown that a diet including avenanthramides can boost the activity of other natural antioxidants in the body, like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase. This helps protect the body from damage.
Biosynthesis
The amount of avenanthramides found in oats can change. It depends on things like the type of oat plant, where it's grown, the year it was harvested, and even the specific part of the plant. For example, oats grown in dry places might produce fewer avenanthramides. This is because dry conditions are not good for certain fungi that usually make the oats produce more of these protective compounds.
Chemical Stability
Avenanthramides are affected by their environment, like temperature and light.
pH Levels
Not all avenanthramides react the same way to different pH levels (how acidic or basic something is) and temperatures. For example, Avenanthramide A stays pretty stable even at high temperatures. But Avenanthramide B is more sensitive to heat, and Avenanthramide C can change a lot at high pH levels and high temperatures.
UV Light
Avenanthramides are also affected by UV light, like sunlight. Some studies show that they can change their shape when exposed to UV light.
Man-Made Avenanthramides
Scientists can also create avenanthramides in a lab. Several types of avenanthramides have been made artificially. These man-made versions were found to be exactly the same as the ones taken from oats.
Images for kids
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |