Plant pathology facts for kids
Plant pathology, also called phytopathology, is the study of plant diseases. Just like people and animals, plants can get sick! These diseases can be caused by tiny living things called pathogens, or by problems in their environment.
Pathogens are germs that cause disease. For plants, these can include fungi (like molds), oomycetes (water molds), bacteria, plant viruses, and even smaller things like viroids and phytoplasmas. Tiny worms called nematodes and some parasitic plants can also make plants sick.
Plant pathology does not usually include damage from insects, mites, or larger animals that eat plants. Instead, plant pathologists study how to find out what is making a plant sick, how the disease spreads, and how it affects farmers and the economy. They also look at how plants can fight off diseases and how to manage plant health. This field is super important for agriculture because healthy plants mean more food for everyone!
Contents
What Makes Plants Sick?
Plants can get sick from many different things. These causes are usually split into two main groups: living things (pathogens) and non-living things (environmental problems).
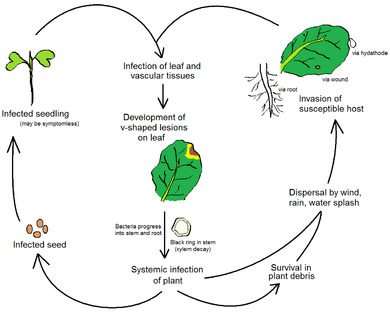
Living Causes of Plant Diseases
- Fungi and Oomycetes: These are common causes of plant diseases. Fungi can cause problems like powdery mildew (which looks like white powder on leaves) or rice blast (a serious disease of rice plants). Oomycetes are similar to fungi but are actually a different group of organisms, often causing "damping-off" in seedlings or late blight in potatoes.
- Bacteria: Tiny bacteria can cause diseases like crown gall, which makes tumors grow on plant stems. They can also cause wilting or spots on leaves.
- Viruses and Viroids: Plant viruses, like Tobacco mosaic virus, can make leaves look spotty or crinkled. Viroids are even smaller than viruses and can also cause diseases.
- Phytoplasmas: These are very tiny bacteria that live inside plants and can cause problems like "witches' broom," where plants grow many small, weak shoots.
- Nematodes: These are microscopic worms that live in the soil and can attack plant roots. Some, like root-knot nematodes, cause galls (swollen bumps) on roots, making it hard for the plant to get water and nutrients.
- Parasitic Plants: Some plants, like dodder, steal nutrients directly from other plants, weakening them.
Non-Living Causes of Plant Problems
Plants can also get sick from things that aren't living organisms. These include:
- Bad Weather: Too much or too little water, extreme heat or cold, or strong winds can all harm plants.
- Poor Soil: Soil that doesn't have enough nutrients, or has too many harmful chemicals, can make plants unhealthy.
- Pollution: Air pollution or contaminated water can damage plant tissues.
- Nutrient Problems: Plants need specific nutrients to grow. If they don't get enough of certain nutrients, or get too much of others, they can show signs of disease.
How Plant Pathologists Help
Plant pathologists are like plant doctors. They work to understand plant diseases and find ways to protect crops. Here's what they do:
- Identify Diseases: They figure out what is making a plant sick. This can involve looking at symptoms, using microscopes, or doing lab tests.
- Study Disease Cycles: They learn how diseases spread, how pathogens survive, and what conditions make them worse. This helps in predicting outbreaks.
- Develop Solutions: They work on ways to prevent and control diseases. This might include creating disease-resistant plant varieties, using special sprays, or advising farmers on best practices.
- Protect Our Food: By keeping plants healthy, plant pathologists help ensure we have enough food, fiber, and other plant products. This is vital for feeding the world's population.
Images for kids
-
Vitis vinifera with "Ca. Phytoplasma vitis" infection
See also
 In Spanish: Fitopatología para niños
In Spanish: Fitopatología para niños
 | Isaac Myers |
 | D. Hamilton Jackson |
 | A. Philip Randolph |