Background radiation facts for kids
Background radiation is the natural radiation all around us, all the time. It comes from many different places, like the ground, the air, and even space! We can't see, smell, or feel it, but it's always there.
Tiny bits of matter called isotopes are naturally radioactive. This means they slowly break down over time. When they break down, they release tiny particles or energy, which we call radiation. This natural radiation is what we mean by "background radiation."
Contents
Where Does Background Radiation Come From?
Background radiation comes from several natural sources. These sources are found all over Earth.
Radiation from the Ground
The ground beneath our feet contains natural radioactive materials. These are found in soil, rocks, and even the water we drink. These materials have been part of Earth since it was formed.
Radon Gas
One of the biggest sources of natural background radiation is a gas called radon. Radon gas comes from the ground. It forms when tiny amounts of uranium and thorium in rocks and soil break down. Radon can seep into homes and buildings through cracks in the foundation. When we breathe in air, we might breathe in tiny amounts of radon. This gas and its related particles make up a big part of the radiation we get.
Radiation from Space
We also get radiation from outer space! This is called cosmic radiation. It comes from the Sun and other stars. These rays travel through space and reach Earth. Our atmosphere helps protect us from most of it. However, some cosmic radiation still reaches the ground. If you fly in an airplane, you get a little more cosmic radiation because you are higher up in the atmosphere.
Radiation in Our Bodies
Did you know that even our own bodies have tiny amounts of natural radiation? This comes from radioactive materials we take in through food and water. For example, a small amount of potassium in our bodies is naturally radioactive.
How Much Background Radiation Do We Get?
The amount of background radiation people get can be different depending on where they live. On average, people around the world get about 2.4 millisieverts (mSv) of natural radiation each year. A millisievert is a unit used to measure radiation dose.
To give you an idea, this natural amount is usually more than the radiation we get from things like X-rays at the doctor's office. For example, in 2008, the average amount of artificial radiation (like from medical scans) was about 0.6 mSv per year.
The amount of natural background radiation can vary a lot. In some places, like parts of Finland, people might get more than 7 mSv per year. This is still considered safe. Scientists and doctors study these levels to make sure they understand how radiation affects us.
Images for kids
-
This display shows the background gamma radiation level outside a museum. It's very close to the world average natural background radiation.
-
Cloud chambers helped early scientists see tiny particles from cosmic rays and other background radiation.
-
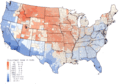
This map shows the estimated radiation doses to people's thyroids in the United States from past atmospheric nuclear testing.