Bassin-de-Chambly facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Bassin de Chambly |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Location | Chambly, Montérégie, Quebec, Canada |
| Coordinates | 45°27′40″N 73°17′00″W / 45.46111°N 73.28333°W |
| Primary inflows | (clockwise) ruisseau Wilson, rivière des Hurons, Richelieu River, Chambly Canal |
| Primary outflows | Richelieu River |
| Basin countries | Canada |
| Max. length | 1.98 mi (3.18 km) |
| Max. width | 1.34 mi (2.16 km) |
| Residence time | years |
| Surface elevation | 11 to 100 ft (3.4 to 30.5 m) |
| Settlements | Richelieu, Saint-Mathias-sur-Richelieu, Carignan and Chambly |
The Bassin de Chambly (which means Chambly Basin in English) is a large area of water. It's like a wide part of the Richelieu River in Quebec, Canada. You can find it near the rapids of Chambly, in a region called Montérégie.
This basin touches different towns and areas. These include Richelieu, Saint-Mathias-sur-Richelieu, Carignan, and Chambly.
The Chambly Basin is a popular spot for fun activities. People enjoy boating, going on vacation, and visiting historical places. The Chambly Canal National Historic Site of Canada is a big attraction here.
The surface of the basin usually freezes in winter. This happens from mid-December until the end of March. It's generally safe to walk on the ice from late December to early March. The amount of water in the basin changes with the seasons and how much rain or snow falls.
Contents
Exploring the Geography of Chambly Basin
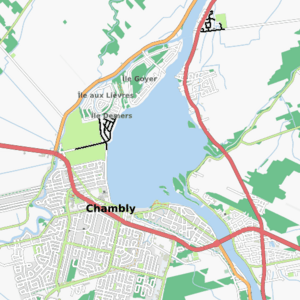
The Chambly Basin looks a bit like a football from above. The Richelieu River flows into it from the southeast. It passes through the Chambly rapids for about 1.35 kilometres (0.84 mi). These rapids are downstream from the Yule bridge, which connects Chambly and Richelieu. The rapids end near a group of small islands on the basin's southeastern side.
Rivers and Canals Flowing In
The Rivière des Hurons flows into the middle of the basin's eastern side. The Chambly Canal also adds its water to the basin. This happens on the south shore, near the Chambly Canal National Historic Site.
Islands of the Basin
The western part of the basin has several islands. These include Île aux Lièvres, Demers Island, Île au Foin, and Goyer Island. Demers Island and Goyer Island have homes on them. Small channels of water separate these islands. All these islands are part of the town of Carignan. The Acadia River flows on the west side of Chambly. It drains into the basin at the northeast point of Goyer Island. This is about 1.0 kilometre (0.62 mi) downstream from the northern edge of the Chambly Basin.
A Glimpse into History
The Chambly Basin has been known for a long time.
First European Sightings
Samuel de Champlain was the first European to see this body of water. He saw it in 1609. He wrote that "The entrance to the jump is a kind of lake, where the water goes down, which contains some three circuit leagues." This means it was a wide area of water.
Early Descriptions
In the Jesuit Relations from 1665, there's another description. It says, "This basin is like a small lake, a league and a half of a turn, six to eight feet deep." This gives us an idea of its size and depth back then.
What's in a Name?
The name "Bassin de Chambly" tells us a bit about the place.
Meaning of "Bassin"
"Bassin" (basin) describes a shallow area of water. It's where things like sand and mud can settle.
Why "Chambly"?
The "Chambly" part of the name comes from the seigneury of Chambly. This was a historical land division. The basin is right in the middle of where that seigneury used to be.
The name "Chambly basin" was officially recognized on December 5, 1968. This was done by the Place Names Bank of the Commission de toponymie du Québec.
Image Gallery