Bicycle facts for kids
A bicycle (or bike) is a small vehicle that a person powers with their own body. It has a seat, two wheels, two pedals, and a metal chain that connects the pedals to the back wheel. A strong frame holds all the parts together. The name "bicycle" comes from "bi-" (meaning two) and "-cycle" (meaning wheel). You ride a bike by pushing the pedals with your feet to make it move forward.
Riding bicycles, also called cycling, is a very important way to travel in many parts of the world. It's also a popular way to have fun, a great way to get exercise, and a well-known sport. Bicycle racing on roads is the second most popular sport to watch globally. Bikes use less energy per mile than any other way humans travel.
Contents
How the Bicycle Was Invented
In 1817, a German professor named Baron Karl von Drais created the first two-wheeled machine. It was made of wood and had two wheels. You could steer the front wheel with handlebars. However, it didn't have pedals. Riders had to push their feet on the ground to make it go.
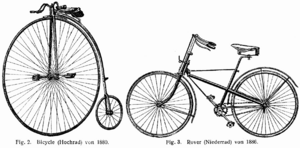
In the 1860s, French inventors added pedals to the front wheel. But it was hard work to turn them! Later, bikes were made only of metal. The front wheel was made very big to go faster. This design was called the penny-farthing bicycle. It was hard to ride because it could fall over easily, and the rider would fall a long way.
Many improvements were made in the 1880s and 1890s. In 1885, the safety bicycle was invented. This bike had two wheels that were the same size. This meant the rider could sit much lower. It was called the "safety bicycle" because it was much easier and safer to ride than the penny-farthing. When you stopped, you could just put your foot down instead of having to get off the bike completely.
Instead of pedaling and steering with the front wheel, the safety bicycle used the front wheel for steering. The pedals turned the back wheel using a chain. Hand brakes also made bikes safer.
In 1888, a Scottish inventor named John Boyd Dunlop re-invented a type of tire filled with air. This made safety bicycles much more comfortable to ride. Soon after, the freewheel was invented. This part inside the back wheel allowed the wheel to spin even if the rider wasn't pedaling. This meant riders couldn't stop the bike by pedaling backward anymore. So, better hand brakes were invented. Another type of brake was made that could stop the bike if the pedals were turned backward. Later, gears were added, which made riding over hills much easier. During this time, the bicycle became very popular.
How a Bicycle Works
Most bikes have a seat, pedals, gears, handlebars, wheels, and brakes. All these parts are attached to a frame. Most also have a gear shifter. When you push the pedals with your feet, they go around in circles. This moves the chain, which then turns the back wheel of the bike. This makes the bike move forward. The front wheel is connected to the handlebars. Turning the handlebars from side to side moves the front wheel, which steers the bike.
Different Kinds of Bicycles

- The city bicycle is made for running errands and traveling in cities. It has a comfy seat but can be heavy. It usually has front and back lights, a bell, and carriers for small bags. It also has mudguards to stop water and mud from splashing the rider. The rider sits upright, which is comfortable and helps with steering in traffic. "Bike share" programs often use city-style bikes.
- The mountain bicycle is used for riding on rough roads and trails. They have many speeds (often more than 20), wide tires, and strong wheels. The tires are specially designed to ride smoothly on hills, grass, and mountains.
- A woman's bicycle often has a different frame design. When women first started riding bikes, they wore long skirts. So, bike makers changed the frame to make it easier for women to get on and off while wearing a skirt. Some utility bikes have a similar design for riders who stop often.
- The tandem bicycle is made for two people. It has two sets of pedals. The cyclists sit one behind the other. The person in front steers the bike. There are even bikes for three or more people! One bike was made for 40 people.
- Folding bicycles can be easily stored in small spaces. You can also carry them long distances on an airplane or other public transport.
- Electric Bicycles have electric motors. These motors are usually inside the front or back wheel. You can choose to ride using only the motor, only the pedals, or both together. In the U.S., electric bikes are treated like regular bicycles if their motor is 750 Watts or less and their top electric speed is 20 MPH. This means you don't need a special license or registration.
- A road bicycle usually has narrow wheels, less than 1 inch (25 mm) wide. Its frame is much lighter than a mountain bike's. Road bikes are good for riding long distances efficiently. Many have clips to attach your shoes to the pedals. Road bicycle racing is a popular sport.
- Recumbent bicycles come in different styles. But all of them have the pedals in front of the seat. The rider leans back while riding. This is more comfortable for many people, but these bikes usually cost more. Some types are very low to the ground, which might make it harder to see in traffic. The fastest bikes in the world are often recumbents.
Bicycle Safety
When riding on streets, it's safest to ride on the same side of the street that cars drive. For example, if cars drive on the right side of the road, you should ride on the right side too. To avoid hitting people, riders must follow signs that say "no bicycling," even if it doesn't seem to make sense at the time.
When it's dark or there's not much light, bicycle lights are very important. It might not be safe to ride when it's completely dark. Riders should wear reflective clothing to be safer in low light. Wearing a helmet makes bicycle riding much safer. More than 300,000 children go to the hospital every year because they were hurt riding a bicycle. Wearing a helmet doesn't mean you can't get hurt if you crash, but it makes serious injuries much less likely. Some bikes have bells or horns that riders can use to warn others they are coming.
Many places have special bike paths that connect houses with shops, schools, and train stations. These paths make bicycling safer. They let cyclists stay away from busy car traffic on dangerous roads.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
1886 Rover safety bicycle at the British Motor Museum. This was the first modern bicycle, with a chain that turned the back wheel and two wheels of similar size. Dunlop's air-filled tire was added in 1888.
-
John Boyd Dunlop on a bicycle around 1915
-
Cyclists' Touring Club sign on display at the National Museum of Scotland
-
A man riding an electric bicycle
-
Balance bicycle for young children
-
A linear-pull brake (also called V-Brake) on the back wheel of a mountain bike
-
Cyclists in Greymouth, New Zealand (around 1898-1905)
-
A bikeway in New York City, USA (2008)
-
City cyclists in Copenhagen, Denmark, at a traffic light
-
"Let go – but stand by"; Frances Willard learning to ride a bicycle
-
A man uses a bicycle to carry goods in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso.
-
Bicycles in Utrecht, Netherlands
-
A bicycle wheel chained in a bike rack after the rest of the bicycle was stolen at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina.
-
A penny-farthing or ordinary bicycle photographed in the Škoda Auto museum in the Czech Republic
-
A bicycle in Plymouth, England, at the start of the 20th century
See also
 In Spanish: Bicicleta para niños
In Spanish: Bicicleta para niños