Bioturbation facts for kids
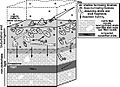
Bioturbation is when living things like animals or plants mix up and change the soil or sediment. Think of it like tiny engineers constantly stirring the ground! This mixing happens in many places, from the dirt in your backyard to the mud at the bottom of oceans and lakes.
Any animal that lives in the soil or on the bottom of a body of water can cause bioturbation. They move the sediment around by digging burrows, eating tiny bits of it, or even by building little tunnels and homes.
Contents
Who are the Bioturbators?
Many different creatures are involved in bioturbation. Some common ones include:
- Worms: Like annelids (ringed worms), which include earthworms on land and many types of worms in the water. They dig tunnels and eat their way through the soil or mud.
- Shellfish: Such as bivalves like mussels and clams. They often burrow into the sediment to hide or find food.
- Snails: Called gastropods, these creatures can move across the surface or even burrow into the sediment, disturbing it as they go.
- Sea cucumbers: These holothurians are bottom-dwellers that often swallow large amounts of sediment to get their food, then release it, mixing it up.
- Other animals: Many insects, crabs, and even larger animals like walruses (when they dig for food) can cause bioturbation.
Why is Bioturbation Important?
Bioturbation might seem like just a lot of digging, but it's super important for the environment:
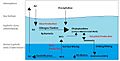
- Mixing nutrients: It helps move nutrients and oxygen deeper into the soil or sediment. This is good for other living things that live there.
- Changing the ground: It changes how the soil or sediment is structured, making it softer or creating new pathways for water to flow.
- Affecting chemicals: The mixing can change how chemicals move and react in the ground, which is important for things like the nitrogen cycle in marine environments.
Bioturbation and Fossils
Bioturbation can also affect what we find in fossils.
- When a place has a lot of bioturbation, the sediment is constantly being stirred. This means that soft-bodied animals, which don't have hard shells or bones, usually don't leave clear traces or impressions. Their bodies get mixed up and destroyed before they can become fossils.
- However, in places where the sediment is undisturbed, we can find amazing lagerstätten. These are special fossil sites where even small, soft-bodied invertebrates (animals without backbones) have left clear impressions. This is because the sediment settled gently and wasn't mixed around, preserving their delicate forms.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bioturbación para niños
In Spanish: Bioturbación para niños