Common land facts for kids
Common land is a special type of land where local people have certain rights. Imagine a big field or forest where people can do things like let their sheep or cattle eat grass, collect firewood for their homes, or even cut turf (grass and soil) for fuel. These shared rights are what make it "common" land.
Long ago, in medieval England, common land was usually part of a larger manor. A manor was a big estate owned by a lord of the manor. Even though the lord owned the land, the people living on it, called tenants, had these special rights to use parts of it.
Over time, the idea of "commons" grew to include other shared resources, not just land. But today, when we say "common land," we mostly mean the land itself where these rights are used. A person who has a right to use common land is called a commoner.
Common lands still exist today in places like Great Britain and the United States. However, there's much less common land now than there was in the 1600s. Back then, there were millions of acres of common land.
Contents
What is Common Land?
Common land is an area where many people can use the land for specific purposes. These uses are called "rights of common." They are not owned by one person, but shared by a community.
Types of Common Rights
Common rights allow people to use the land in different ways. Here are some examples:
- Pasture: This is the right to let farm animals, like cows, sheep, or horses, graze (eat grass) on the land.
- Pannage: This right allows pigs to feed on acorns or nuts in woodlands.
- Estovers: This is the right to collect wood for fuel, repairs, or fencing.
- Turbary: This right allows people to cut turf (peat or sod) for fuel.
- Piscary: This is the right to fish in a common pond or river.
These rights were very important for people's survival in the past. They helped families get food, fuel, and materials they needed.
History of Common Land
Common land has a long history, especially in England. It dates back to the Middle Ages.
Medieval Origins
In medieval times, most land was part of a manor. The lord of the manor owned the land, but villagers had traditional rights to use certain areas. These areas were often woodlands, pastures, or wasteland. These rights were passed down through generations.
The Enclosure Movement
From the 1600s to the 1800s, a big change happened called the "Enclosure Movement." Land that was once common was fenced off and became private property. This was done to make farming more efficient. However, it meant that many poor people lost their rights to use the land, which caused hardship.
Common Land Today
Even after the Enclosure Movement, some common land still exists. It is now protected by laws.
Protecting Common Land
Today, common land is often valued for its natural beauty and for wildlife. It's also important for public recreation, like walking or hiking. Laws help protect these areas from being built on or damaged. Many common lands are now important places for nature and people.
Related Topics
Images for kids
-
Modern-day pannage, or "common of mast", in the New Forest
-
Poohsticks Bridge in Ashdown Forest, an area of common land.
-
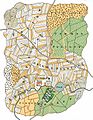
Conjectural map of a mediaeval English manor. The part allocated to "common pasture" is shown in the north-east section, shaded green.
-
View of the Scafell massif from Yewbarrow, Wasdale, Cumbria. In the valley bottom are older enclosures and higher up on the fell-side are later enclosures on poorer land with substantial walls following boundary lines regardless of terrain. Above those is the unenclosed common land
-
The windmill on Wimbledon Common.
See also
 In Spanish: Bien comunal para niños
In Spanish: Bien comunal para niños
 | Leon Lynch |
 | Milton P. Webster |
 | Ferdinand Smith |