Capped conebill facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Capped conebill |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| A male in Ecuador | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Conirostrum
|
| Species: |
albifrons
|
 |
|
The capped conebill (Conirostrum albifrons) is a small, colorful bird. It belongs to the Thraupidae family, which includes many types of tanagers.
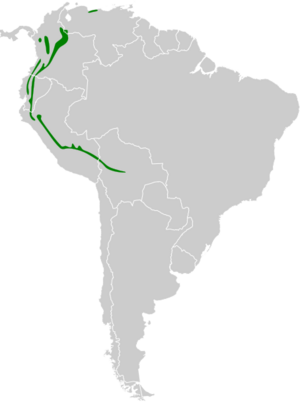
You can find this bird in several South American countries. These include Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela. It likes to live in moist montane forests, which are forests found in mountains. It can also live in areas where forests have been changed by people.
About Its Name
The capped conebill got its scientific name, Conirostrum albifrons, a long time ago. The name Conirostrum comes from Latin words. "Conus" means "cone," and "rostrum" means "beak" or "bill." This describes its cone-shaped beak.
The second part, albifrons, means "white-fronted." This refers to the white cap on the head of some male birds.
There are six different types, or subspecies, of the capped conebill. They are all slightly different depending on where they live:
- C. a. albifrons - Found in central and eastern Andes of Colombia and Venezuela.
- C. a. centralandium - Lives in parts of Colombia, from Antioquia to Cauca.
- C. a. cyanonotum - Found in the coastal mountains of Venezuela.
- C. a. atrocyaneum - Lives in the Andes of southwest Colombia, Ecuador, and northern Peru.
- C. a. sordidum - Ranges from Junín in Peru to La Paz in Bolivia.
- C. a. lugens - Found in the Yungas region of eastern Bolivia.
What It Looks Like
The capped conebill is about 13 to 14 centimeters (5 to 5.5 inches) long. It weighs between 11.7 and 21.5 grams (about 0.4 to 0.75 ounces).
Male birds can look a bit different depending on their group:
- Males in the "albifrons" group have a bright white cap on their head. Their face, chest, and neck are a dark, slaty-black color. Their shoulders and tail are a pretty liberty blue, and their back is navy blue.
- Males in the "atrocyaneum" group have a deep blue cap, back, wings, and tail. Their shoulders are a grayish-blue, and their chest, neck, and face are slaty gray.
Female birds look different from the males. They have a light blue cap and a blue-gray head. Their body is a dark yellow, and their back and wings are olive green.
Both male and female capped conebills have a black, slightly curved beak. They also have gray legs.
Where It Lives
The capped conebill lives in specific areas of South America. One group lives in Venezuela, near the state of Miranda. Other groups live along the Andes mountains, stretching from Colombia down to Peru. You can also find them in the yungas regions of Peru and Bolivia.
These birds prefer to live in tropical montane cloud forests. These are special forests high up in the mountains, usually between 2,000 and 2,800 meters (about 6,500 to 9,200 feet) above sea level.
Its Conservation Status
The IUCN currently lists the capped conebill as a species of "Least Concern." This means it is not in immediate danger of disappearing. However, scientists believe that its population might be slowly decreasing.


