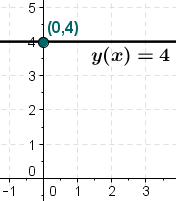Constant function facts for kids
In mathematics, a constant function is a special type of function. It's like a machine where no matter what you put in, you always get the same answer out! For example, imagine a function that always gives you the number 4. So, if you put in 1, you get 4. If you put in 100, you still get 4. This is a constant function because its output value never changes.
Contents
What is a Constant Function?
A constant function is usually written as 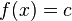 or
or 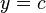 . Here, 'c' stands for a specific number that never changes.
. Here, 'c' stands for a specific number that never changes.
- The function y=c has two variables, x and y, and one constant number, c. Even if you don't see x in the equation y=c, it's still there as the input.
- The constant c can be any real number. Before you work with a constant function, you replace c with an actual number, like 5 or -2.
- The domain is all the possible input values for x. For constant functions, you can usually put in any real number.
- The range is all the possible output values. For a constant function, the output is always just the value of c. So, the range is just that single number.
Example: The function 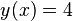 (or just
(or just 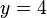 ) is a constant function. Here, the output value c is 4.
) is a constant function. Here, the output value c is 4.
- The domain (what you can put in for x) is all real numbers.
- The range (what you get out for y) is just the number {4}.
- No matter what number you put in for x, the answer is always 4. For instance, y(0)=4, y(-2.7)=4, y(π)=4.
Graphing a Constant Function
The graph of a constant function 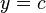 is always a horizontal line on a graph. This line crosses the y-axis at the point (0,c).
is always a horizontal line on a graph. This line crosses the y-axis at the point (0,c).
- If c is not 0 (like y=5 or y=-3), the constant function is a polynomial with a degree of zero.
- The y-intercept (where the line crosses the y-axis) is the point (0,c).
- This function has no x-intercept (it never crosses the x-axis) unless c is 0.
- If c is 0, then you have the function y=0. This is called the identically zero function.
- In this case, every real number x is a root (meaning the function's value is 0).
- The graph of y=0 is the x-axis itself.
- A constant function is an even function. This means the y-axis acts like a mirror, showing that the graph is the same on both sides.
How Constant Functions Change (or Don't!)
In calculus, the derivative of a function tells us how fast its output value is changing. A constant function never changes its output value. Because of this, its derivative is always 0.
This is often written as: 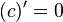 .
.
Example: The function 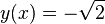 is a constant function. The derivative of y is always 0. So,
is a constant function. The derivative of y is always 0. So, 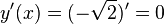 .
.
The opposite is also true: if a function's derivative is 0 everywhere, then that function must be a constant function.
Real-World Examples
Constant functions might seem simple, but they appear in many places:
- Store Prices: Imagine a store where every item costs 1 euro. No matter what item (input) you pick, the price (output) is always 1 euro. This is a constant function.
- Temperature: If the temperature outside stays at 20 degrees Celsius all day, then the temperature over time is a constant function.
- Elevation: If you are walking on a perfectly flat path, your elevation above sea level is a constant function of how far you have walked.
More Examples
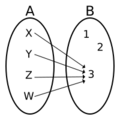
- Let f be a function where A={X,Y,Z,W} and B={1,2,3}. If f(a)=3 for every a in A, then f is a constant function. Every input from A gives the output 3.
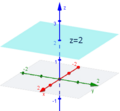
- The function z(x,y)=2 is a constant function in 3D space. No matter what x and y values you pick, z is always 2. Its graph is a flat plane that is parallel to the x0y plane, passing through the point (0,0,2).
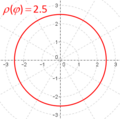
- The polar function ρ(φ)=2.5 is a constant function. It maps every angle φ to a radius ρ of 2.5. The graph of this function is a circle with a radius of 2.5.
Images for kids
Related topics
See also
 In Spanish: Función constante para niños
In Spanish: Función constante para niños