Real number facts for kids
A real number is any number you can think of that can be written as a decimal. This includes numbers like 3, -5, 0.75, and even numbers like π (pi) or the square root of 2. When people just say "number," they usually mean a real number.
The special symbol for real numbers is a bold R or 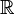 .
.
You can imagine real numbers as points on an infinitely long number line. There's a mark for zero (0), and every other number is placed in its correct order.
Some real numbers are positive. These are numbers "bigger than zero." Numbers like 1, 5, or 0.25 are positive.
Other real numbers are negative. These are numbers "smaller than zero." They are like a mirror image of positive numbers but have a minus sign (–) in front of them, like -1, -5, or -0.25.
There are an endless number of real numbers. No matter how many you count, there are always more. Also, there are no empty spaces between any two real numbers. This means you can always find another real number between any two different real numbers, no matter how close they are.
When you add a positive number to another number, that number gets bigger. If you add zero to a number, the number stays the same. If you add a negative number, the original number gets smaller.
Real numbers are special because there are "more" of them than there are integers. Even though both are infinite, you can't list all real numbers in a sequence without missing some. This is why we say integers are countable and real numbers are uncountable.
Simpler number systems are part of the real numbers. For example, rational numbers (like fractions) and integers are all real numbers. There are also more complex number systems, like complex numbers, which include real numbers but also other types of numbers.
Exploring Different Types of Real Numbers
Not all real numbers are the same. We often group them into smaller sets based on their features. Here are some of these special groups:
- Natural numbers: These are the numbers you use for counting, like 1, 2, 3, and so on. They are positive and have no decimals.
- Whole numbers: These include all the natural numbers, plus zero (0). So, 0, 1, 2, 3, etc., are whole numbers.
- Integers: This group includes all whole numbers, plus their negative partners. So, ..., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ... are integers. They have no decimals.
- Rational numbers: These are real numbers that can be written as a simple fraction, like 1/2, 3/4, or -7/1. All integers are also rational numbers.
- Irrational numbers: These are real numbers that cannot be written as a simple fraction. Their decimal forms go on forever without repeating a pattern. A famous example is π.
- Transcendental numbers: These are a special type of irrational number. You can't get them by solving an equation that only uses integers. Pi (π) is also a transcendental number.
The number 0 (zero) is very important. It's the "identity element" for addition. This means that adding zero to any number doesn't change that number. For multiplication, the identity element is 1.
One famous irrational number is 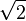 (the square root of 2). If you draw a square with sides that are exactly one unit long, the distance between its opposite corners will be
(the square root of 2). If you draw a square with sides that are exactly one unit long, the distance between its opposite corners will be 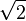 .
.
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Número real para niños
In Spanish: Número real para niños
 | William Lucy |
 | Charles Hayes |
 | Cleveland Robinson |

