Dyeing poison dart frog facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Dyeing poison dart frog |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| D. tinctorius "yellow back" | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Dendrobatidae |
| Genus: | Dendrobates |
| Species: |
D. tinctorius
|
| Binomial name | |
| Dendrobates tinctorius (Cuvier, 1797)
|
|
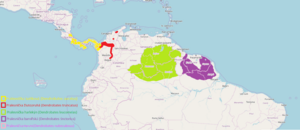 |
|
| Distribution of the five Dendrobates species, with D. tinctorius in purple | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The dyeing poison dart frog (Dendrobates tinctorius) is a super colorful frog. People also call it the cobalt poison frog or just tinc. It's one of the biggest and most colorful types of poison dart frog. These frogs usually grow to be about 50 millimeters (2 inches) long. You can find them in parts of French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, and Brazil.
Contents
Why is it Called "Dyeing"?
The name tinctorius comes from an old story. Some local tribes believed they could use the frog's poison to change the color of parrot feathers. They thought it could make green feathers grow in different colors! This is how the frog got its "dyeing" name, not because of its many natural colors.
Where Dyeing Poison Dart Frogs Live
These frogs live in special spots in the eastern Guiana Shield. They can be found high up, even 600 meters (about 2,000 feet) above sea level. They like rainforests, especially areas where the trees have gaps in their tops. These gaps let sunlight reach the forest floor.
While you might find them near the sea level, they mostly live in higher places like hills or at the bottom of mountains. Their homes are sometimes separated by floods. A cool fact is that Dendrobates tinctorius tadpoles can live in water that has a lot of minerals and even some salt!
What Do Dyeing Poison Dart Frogs Look Like?
The dyeing poison dart frog is quite large for a dart frog. However, some other types, like Phyllobates terribilis, can be even bigger. The smallest dyeing poison dart frogs are about 3.5 centimeters (1.4 inches) long. Most are around 5 centimeters (2 inches), and the biggest ones can reach 7 centimeters (2.8 inches)!
It can be tricky to tell males and females apart. Males are usually smaller and thinner than females. But, males have bigger toe pads. Females have round toe pads, while males have heart-shaped ones. Also, female frogs often have backs that look more arched, while males have backs that are more curved.
Amazing Color Patterns (Morphs)
The dyeing poison dart frog is famous for its incredible variety of colors and patterns. There are over 30 different types, called "morphs"! Each morph has its own unique look, often found in a specific place.
Usually, these frogs have a black body. They have yellow or white stripes on their back, sides, and head. Their lower sides, belly, and throat often have blue stripes. Their legs are usually blue with small black spots. The blue can be light blue, sky blue, or even dark navy blue.
But some morphs are mostly blue, like the "azureus" from Suriname. Others are mostly yellow, like the "Matécho" from French Guiana. The "Citronella" morph from Suriname is bright yellow with black spots and royal blue legs. Even with all these different looks, the frogs are very similar genetically!
How Dyeing Poison Dart Frogs Use Poison
Like many dart frogs, D. tinctorius is poisonous if eaten. They make special chemicals called pumiliotoxins. These toxins help the frog protect itself from animals that might try to eat it. While these toxins are not as strong as some other dart frog poisons, they are strong enough to make most animals not want to eat them.
If you handle these frogs roughly, their toxins can cause pain, muscle cramps, and stiffness. Animals that try to eat these brightly colored frogs quickly learn that their bright colors mean they taste bad and will cause pain. This helps the frogs stay safe! Different color types of D. tinctorius can have different amounts of poison.
There was a story in Brazil about two photographers who touched one of these frogs. One held the frog for a few seconds. The other touched his mouth after touching the frog. Both felt some numbness in their arm or lip. But the feelings went away after about 40 minutes. The effects would have been worse if they had touched the frog longer or had a cut on their skin.
The main toxin in these frogs affects how muscles work. It can cause problems with moving, muscle spasms, or even make muscles stop working. The toxins can also affect the heart and breathing muscles. This is why it's very important never to touch these frogs in the wild!
 | James B. Knighten |
 | Azellia White |
 | Willa Brown |










