Duodenum facts for kids
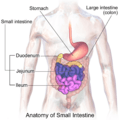
The duodenum is the first and shortest part of your small intestine. It's like a mixing bowl where most of your food gets broken down. It receives special liquids from your pancreas and liver to help with digestion.
Contents
Structure of the Duodenum
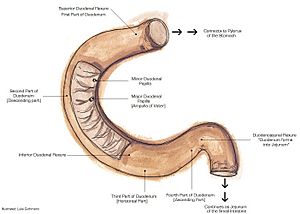
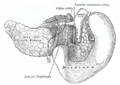
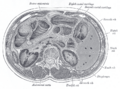
The duodenum is about 25–30 cm (10-12 inches) long and shaped like the letter C. It sits right next to your stomach. It has four main sections. Most of the duodenum is "retroperitoneal," meaning it's behind the main lining of your belly.
First Part: The Start
The first part of the duodenum is also called the superior part. It connects directly from the end of your stomach. The very first bit, called the duodenal bulb, is slightly wider. This part is somewhat movable and is connected to your liver by a special tissue called the hepatoduodenal ligament. This section ends at a bend called the superior duodenal flexure.
Second Part: Going Down
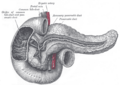
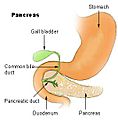
The second part, or descending part, starts at the superior duodenal flexure. It goes downwards. This is a very important part because the main tubes from your pancreas (the pancreatic duct) and liver (the common bile duct) open into it. These tubes bring important digestive juices and bile to help break down food.
Third Part: Going Across
The third part, also known as the horizontal part or inferior part, starts after the second part turns. It goes sideways, passing in front of some big blood vessels like the inferior vena cava and the abdominal aorta. Two other important blood vessels, the superior mesenteric artery and superior mesenteric vein, also cross in front of this part.
Fourth Part: Going Up
The fourth part, or ascending part, goes upwards. It then connects to the next part of your small intestine, called the jejunum, at a spot called the duodenojejunal flexure.
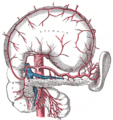
Blood Supply for the Duodenum
The duodenum gets its blood from two main sources. The upper part gets blood from the gastroduodenal artery. The lower parts (the third and fourth sections) get blood from the superior mesenteric artery. These two blood supplies connect, creating a backup system for blood flow.
After the blood delivers oxygen and nutrients, it's collected by veins. These veins eventually drain into the portal system, which carries blood to the liver.
Lymphatic Drainage
The duodenum also has a system of lymphatic vessels. These vessels collect extra fluid and waste, helping to keep your body healthy. They follow the same path as the blood vessels and eventually drain into lymph nodes near the stomach and pancreas.
Looking Closer: Histology
If you look at the duodenum under a microscope, you'd see its inner lining, called the mucosa, has tiny finger-like projections called villi. These villi help absorb nutrients. The duodenum also has special glands called Brunner's glands. These glands make mucus and a substance called bicarbonate. This bicarbonate helps to make the acidic food coming from your stomach less acidic, protecting the duodenum.
What the Duodenum Does
The duodenum is super important for breaking down food using special enzymes. The villi on its inner surface are shaped like leaves, which helps them absorb nutrients. The special Brunner's glands found only in the duodenum make mucus to protect its lining.
The duodenum also helps control how fast food leaves your stomach. When acidic and fatty food from your stomach enters the duodenum, it releases hormones like secretin and cholecystokinin. These hormones tell your liver and gall bladder to release bile, and your pancreas to release more digestive enzymes (like trypsin, lipase, and amylase) and bicarbonate. All these liquids work together to digest your food even more.
Genes and Proteins
Many different genes are active in the cells of your duodenum. These genes create proteins that help the duodenum do its job. For example, some proteins are digestive enzymes, while others help with things like controlling blood pressure or taking in vitamin A.
Additional images
Images for kids
-
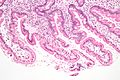
Micrograph showing giardiasis on a duodenal biopsy (H&E stain)
-
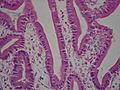
Duodenum with brush border (microvillus)
See also
 In Spanish: Duodeno para niños
In Spanish: Duodeno para niños