Epigenetics facts for kids
Epigenetics is about how your genes work. It's the study of changes in how genes act, but these changes are not caused by changes in your DNA code itself. Think of it like this: your DNA is the instruction book, and epigenetics is about how certain pages are read more often, or not at all, without changing the words on the pages.
These changes can last for a cell's whole life. They can even be passed on to new cells when cells divide. But remember, the actual DNA sequence stays the same. Instead, other things make your genes behave differently. One way this happens is through something called DNA methylation.
Epigenetic changes can affect how you develop, even into adulthood.
What is Epigenetics?
Epigenetics is the study of how genes are turned on or off. It looks at how genes become active as living things grow. So, anything that affects how an organism develops, other than its DNA code, can be called epigenetic.
A more specific way to think about it is this: Epigenetics studies changes in gene function. These changes can be passed down when cells divide. They are not caused by changes in the DNA sequence itself.
Sometimes, the term "epigenetics" is used for changes that aren't passed down. An example is how histones are changed. Histones are proteins that DNA wraps around. So, some definitions don't require the changes to be passed on.
How Epigenetics Works
The best example of epigenetic changes is how cells become different. When an embryo develops, simple stem cells turn into many different types of cells. For example, a single fertilized egg cell divides and changes. It becomes neurons (nerve cells), muscle cells, skin cells, and blood vessels.
As the embryo grows, some genes are turned on. Others are turned off or slowed down. This process is called gene regulation. Many tiny parts inside the cell's nucleus help control what the genes do.
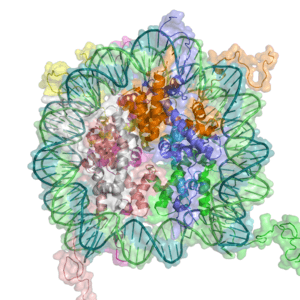
Your DNA and histones together form something called chromatin. Epigenetic changes to this chromatin are copied when cells divide. This creates groups of cells that are all alike. These groups form a tissue.
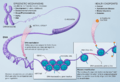
When new life begins through meiosis, most epigenetic changes are reset. This means the genes go back to their basic state. So, the process starts fresh for each new generation. There are a few rare exceptions, but these exceptions never involve changing the DNA code itself.
This process is different from mutations in DNA. Genetic mutations actually change the DNA sequence. Mutations can happen in any cell. However, only mutations in cells involved in reproduction can affect offspring.
Images for kids
-
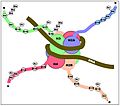
Some changes to histones can turn genes on or off. The top picture shows changes that activate genes. The bottom picture shows changes that turn genes off. Nucleosomes are made of histone proteins. DNA wraps around these proteins to form chromatin. Changes like methylation and acetylation on the histone tails help control gene activity.
See also
 In Spanish: Epigenética para niños
In Spanish: Epigenética para niños