Etruria facts for kids
Etruria was an ancient region in Central Italy. It was located between the Arno and Tiber rivers. Today, this area covers most of Tuscany, northern Lazio, and north-western Umbria. The Etruscans lived here. They were an old civilization that grew strong around 800 BC. They became part of the Roman Republic around 300 BC.
Contents
The Etruscan People and Their Land
The ancient people of Etruria were called the Etruscans. They had a rich culture with many city-states. These cities first appeared around 900 BC. The Etruscans became very powerful between 700 and 500 BC.
By 650 BC, the Etruscans were a leading culture in Italy. They were more powerful than other groups like the Ligures. Their influence spread beyond Etruria. It reached the Po River Valley, Latium, and Campania. They also traded with Greek colonies in Southern Italy and Sicily.
Archaeologists have found proof of trade with Egypt. For example, fine Egyptian cups were found in Etruscan tombs. This trade happened either directly with Egypt or through Greek or Phoenician sailors.
Rome was greatly influenced by the Etruscans. Even though the Ciminian Forest separated them, Etruscan kings ruled Rome for a time. The last Etruscan king, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was removed in 509 BC. This led to the start of the Roman Republic.
The Etruscans helped shape Roman architecture and traditions. Important buildings like the Capitolium and the Cloaca Maxima were built under Etruscan kings. They also introduced new foods, the Latin alphabet, and new ways of building.
Parts of Etruria
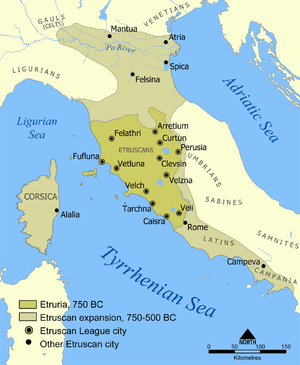
Etruria is usually split into two main areas: Northern Etruria and Southern Etruria. There were also Etruscan colonies further north and south.
- Northern Etruria: This area covered much of modern Tuscany. It stretched from the Arno river in the north to the Apennines in the east. It also included Etruscan lands north of Perugia in modern Umbria.
- Southern Etruria: This included small parts of southern Tuscany. It also covered all of northern and central Lazio, reaching almost to Rome.
Etruscan Colonies
The Etruscans also set up colonies in other parts of Italy:
- Etruria Padana (Padanian Etruria): These were lands in Emilia-Romagna and the southern parts of Lombardy and Veneto in northern Italy.
- Etruria Campana (Campanian Etruria): These were lands in southern Lazio and Campania in southern Italy.
Important Etruscan Cities
Here are some of the main cities of Etruria, with their modern Italian names in bold:
- Arritim (Arretium, Arezzo)
- Atria (Adria)
- Caisra (Caere, Cerveteri)
- Clevsin (Clusium, Chiusi)
- Curtun (Cortonium, Cortona)
- Felathri (Volaterrae, Volterra)
- Fufluna (Populonium, Populonia)
- Parusia (Perusia, Perugia)
- Tarchna (Tarracina, Terracina)
- Tarchnal (Tarquinii, Tarquinia)
- Veii (Veii, Veio)
- Vetluna (Vetulonium, Vetulonia)
- Vipsul (Faesulae, Fiesole)
- Velch (Vulci, Volci)
- Velzna (Volsiniia, Volsinii)
Between 600 BC and 500 BC, twelve Etruscan city-states formed a group called the Etruscan League. They used Etruscan as their official language for meetings. When the Roman Republic conquered Etruria, Latin became the official language.
Etruria Under Roman Rule
When Augustus organized Roman Italy, Etruria became a region called Regio VII. Its borders were the Tiber river, the Tyrrhenian Sea, the Apuan Alps, and the Apennines. These borders were very similar to Etruria's borders before the Romans took over in 509 BC.
Etruria in More Recent Times
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany (which existed from 1569–1801 and 1814–1859) was sometimes called Magnus Ducatus Etruriae in Latin. The name Etruria was also used for the Kingdom of Etruria. This was a short-lived state created by Napoleon I of France between 1801 and 1807.
A famous book about Etruscan places is Sketches of Etruscan Places and Other Italian Essays by D. H. Lawrence.
See also
 In Spanish: Etruria para niños
In Spanish: Etruria para niños