Finnish War facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Finnish War |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Russo–Swedish Wars and Napoleonic Wars | |||||||||
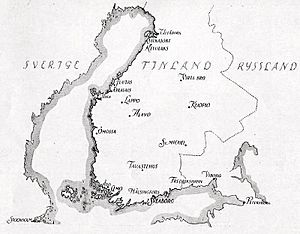 Map of notable locations in Finland during the war |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
Supported by |
Supported by |
||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| Fyodor Buxhoeveden Bogdan von Knorring Pyotr Bagration Barclay de Tolly Nikolay Ivanovich Demidov |
Wilhelm Mauritz Klingspor Carl Johan Adlercreutz Georg Carl von Döbeln |
||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| August 1808: 95,000+ soldiers | August 1808: 36,000+ soldiers | ||||||||
The Finnish War was a big conflict that happened between Russia and Sweden from 1808 to 1809. It was part of the larger Napoleonic Wars that were happening across Europe at the time.
During this war, Sweden lost a large part of its eastern land, which was Finland. After the war, Finland became a special, self-governing part of the Russian Empire, known as the Grand Duchy of Finland.
Contents
What Caused the War?
The Finnish War started because of a big disagreement between Russia and Sweden. At the time, Napoleon Bonaparte ruled France and was very powerful. He wanted all countries to stop trading with Great Britain. This was called the Continental System.
Russia agreed to join Napoleon's system. However, Sweden, led by King Gustav IV Adolf of Sweden, refused to stop trading with Britain. This made Russia angry, and they decided to invade Finland, which was then part of Sweden.
Russia's Goals
Russia had a few reasons for starting the war.
- They wanted to force Sweden to join the Continental System.
- They also wanted to make their capital city, Saint Petersburg, safer by moving the border further away from it.
- Taking Finland would give Russia more control over the Baltic Sea.
Sweden's Position
Sweden was in a tough spot. King Gustav IV Adolf was very determined to stay friends with Britain. He didn't want to give in to Napoleon or Russia. However, Sweden's army was not as strong as Russia's.
Key Events of the War
The war lasted for about a year and a half, with many battles fought in Finland.
The Russian Invasion (1808)
In February 1808, Russian troops crossed the border into Finland without a formal declaration of war. They quickly took over many towns and cities. The Swedish army in Finland was not ready for such a fast attack.
- Taking Sveaborg: One of the most important places was the Sveaborg fortress near Helsinki. It was a very strong fort, but it surrendered to the Russians in May 1808. This was a big loss for Sweden.
Swedish Counterattacks (Summer 1808)
Even though they were losing, the Swedish forces, helped by local Finnish people, fought back bravely.
- Battles and Retreats: There were many battles where Swedish and Finnish soldiers tried to push the Russians back. However, the Russian army was larger and better supplied. The Swedes often had to retreat.
British Support
The United Kingdom sent some help to Sweden, including money and a small number of troops. However, this help was not enough to change the outcome of the war.
The End of the War (1809)
By 1809, the situation for Sweden was very bad. The Russian army had pushed deep into Finland and even crossed into Sweden itself.
Treaty of Fredrikshamn
The war officially ended with the Treaty of Fredrikshamn on September 17, 1809.
- Sweden had to give up all of Finland to Russia.
- Finland became the Grand Duchy of Finland, an autonomous (self-governing) part of the Russian Empire. This meant Finland had its own laws and government, but it was still ruled by the Russian Emperor.
- King Gustav IV Adolf of Sweden was removed from power by his own people because of the war's failure.
What Happened After the War?
The Finnish War had a huge impact on both Sweden and Finland.
For Finland
For Finland, the war marked the beginning of a new era. Even though it was under Russian rule, the Grand Duchy of Finland kept its own language, laws, and culture. This period helped to strengthen a unique Finnish identity.
For Sweden
Sweden lost a large part of its territory and population. The loss of Finland meant that Sweden's role as a major power in Europe became much smaller. It also led to big changes in Sweden's government.
The Finnish War is an important part of history because it changed the map of Northern Europe and shaped the future of Finland.
Images for kids
-
Arrest of Gustav IV.
-
Second to last battle of the war at Ratan near Umeå in Swedish Västerbotten
-
A memorial of the Battle of Kutujoki in Suonenjoki, Finland
See also