Florida cottonmouth facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Florida cottonmouth |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Viperidae |
| Genus: | Agkistrodon |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: |
A. p. conanti
|
| Trinomial name | |
| Agkistrodon piscivorus conanti Gloyd, 1969
|
|
The Florida cottonmouth, also known as the green-tailed moccasin, is a type of pitviper snake. Its scientific name is Agkistrodon piscivorus conanti. This snake is a subspecies of the Agkistrodon piscivorus and belongs to the Viperidae family. Like all pitvipers, it is a venomous snake. You can find this snake in the southeastern United States, especially in Florida.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The second part of the snake's scientific name, conanti, is a special tribute. It honors a famous American herpetologist (someone who studies reptiles and amphibians) named Roger Conant.
How to Spot a Florida Cottonmouth
Adult Florida cottonmouths can grow quite long, up to about 1.9 meters (74.5 inches) including their tail. Some have even been recorded weighing around 4.6 kilograms (10 pounds)!
Their patterns are similar to other cottonmouths, but the Florida cottonmouth has some unique markings on its head. Even on older, darker snakes, you can clearly see dark brown stripes behind their eyes. These stripes have thin, light lines above and below them. They also have two dark stripes on the front of their lower jaw and two dark vertical stripes on the tip of their snout. Younger snakes usually have more noticeable patterns on their backs, while older ones might lose some of these patterns.
Other Names for This Snake
People call the Florida cottonmouth by many different names. Some of these include: aquatic copperhead, aquatic moccasin, cotton-mouthed snake, gaper, gapper, lake moccasin, mangrove rattler, moccasin viper, North American water viper, pond moccasin, river pit viper, short-tailed moccasin, small-tailed rattler, snap jaw, stub-tail moccasin, swamp lion, swamp moccasin, trap jaw, water mamba, water moccasin, water pilot, water pit moccasin, water rattlesnake, white mouth moccasin, and worm-tailed moccasin.
Where Do They Live?
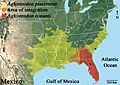
The Florida cottonmouth lives in the United States, mainly in southern Georgia and all across Florida. They also live on many islands off the coast. In some areas, like southern South Carolina, western Georgia, and parts of Alabama, they mix with other types of cottonmouths.
Their Home Environment
These snakes love wet places! In areas like the Okefenokee Swamp in Georgia, they can be found in thick bushes near cypress ponds and around the edges of wooded water areas. They also live where island woods meet pine forests.
In the Everglades, Florida cottonmouths have been found in clumps of palmetto plants, even far from water. They often gather around water holes that are drying up. This is probably because more prey, like fish and frogs, get stuck in the shrinking water, making it easier for the snakes to find food. They prefer watery places, wet prairies, and cypress flats. However, they usually avoid pine forests or dry scrub areas, though some have been seen in wet pine-palmetto areas during very dry times.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Florida cottonmouths give birth to live young, meaning the babies hatch inside the mother and are born alive. There isn't a specific time of year when they mate, but most baby snakes are born during the summer months. Females usually only have babies every other year. A mother cottonmouth can give birth to anywhere from one to 15 young at a time. When they are born, these baby snakes are typically about 18 centimeters (7 inches) long.
- Agkistrodon piscivorus at the TIGR Reptile Database. Accessed 1 December 2007.
Images for kids
-
A Florida cottonmouth in Big Cypress National Preserve, Florida.
 | Roy Wilkins |
 | John Lewis |
 | Linda Carol Brown |