Fort Crawford (Alabama) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Fort Crawford |
|
|---|---|
| East Brewton, Alabama in United States | |
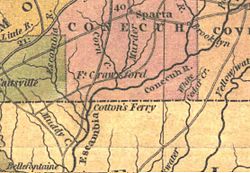
Fort Crawford (located in the center) as portrayed in Henry Schenck Tanner's 1830 The Traveler's Pocket Map of Alabama.
|
|
| Coordinates | 31°06′03″N 87°02′44″W / 31.10083°N 87.04556°W |
| Type | Stockade fort |
| Site information | |
| Owner | Private |
| Controlled by | Private |
| Open to the public |
No |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1816 |
| Built by | United States Army |
| In use | 1816-1821 |
| Battles/wars | First Seminole War |
| Events | |
|
Alabama Register of Landmarks and Heritage
|
|
| Designated | January 18, 1978 |
Fort Crawford was an important fort built long ago to protect settlers. It was located in what is now East Brewton, Alabama. This fort played a key role in defending the area and supporting military actions during a time of change in the United States.
Contents
Building Fort Crawford
After the Creek War, a big conflict, General Andrew Jackson gave an order. He told Major General Edmund P. Gaines to build a fort. This fort would help keep settlers safe from some Native American groups. These groups were sometimes called the Red Sticks.
General Gaines then told Major David E. Twiggs to start building. Major Twiggs left Fort Montgomery to find a good spot. The fort was built right on the edge of the new Alabama Territory. It was also near Spanish West Florida, which was controlled by Spain. The fort was placed on the bank of Murder Creek.
Who Was Fort Crawford Named For?
The fort was named Fort Crawford, but it's not totally clear why. It might have been named after 2nd Lieutenant Joel Crawford. Or it could have been named for William H. Crawford. He was a very important person who served as the US Secretary of War and the US Secretary of the Treasury.
What Did the Fort Look Like?
Major John M. Davis described Fort Crawford. He said it had two blockhouses. These were strong, small forts, usually made of logs. They were placed at opposite corners of the fort. The walls of the fort itself were made from several buildings joined together. Inside the fort, there was a medical building for sick or injured soldiers. There was also an artificer shop, where skilled workers made and repaired things. A guard house was also part of the fort.
Fort Crawford's Role in Conflicts
Fort Crawford was a busy place during the First Seminole War. This was a conflict involving the United States Army and some Native American groups. The fort was used as a base for soldiers. From here, they would go on missions against some Red Stick groups in the Florida Panhandle.
After an event known as the Butler Massacre, soldiers were sent from Fort Crawford. These soldiers, along with Choctaw allies, were led by Major White Youngs. They went to Fort Dale to help chase after the Red Sticks involved in the massacre.
Getting Supplies to the Fort
Getting supplies to Fort Crawford was often difficult. Supplies were sent from Fort Montgomery, but they often arrived late. General Gaines wrote to Jose Masot, who was the governor of West Florida (a Spanish territory). He asked if supplies could be sent up the Conecuh River from Pensacola.
Governor Masot allowed three ships to bring supplies to Fort Crawford through Pensacola. However, he did not allow regular supply routes this way. General Jackson, who was at Fort Gadsden, also asked Governor Masot for permission for ships to pass through Pensacola. Masot allowed two ships, the Mobiliana and the Italiana, to bring supplies. But he wouldn't let the Italiana make a second trip without the United States paying special fees to Spain.
Jackson sent an officer named Lieutenant Cross to Pensacola to talk about getting the supplies without paying these fees. But Governor Masot would not agree. However, Masot did agree to hand over some Native American groups who were fighting to the United States. These groups were then taken back to Fort Crawford.
In a letter to George W. Campbell, General Jackson explained his reasons for taking control of Pensacola on May 23, 1818. He said one reason was that Spain had seized Fort Crawford's supplies. Another reason was that Spain was helping some Native American groups who were fighting.
The End of Fort Crawford's Use
Fort Crawford was no longer needed for its main purpose after 1821. This was when the Adams–Onís Treaty took effect. Through this treaty, Florida became part of the United States. So, Fort Crawford was no longer on the border of Spanish territory.
In 1817, a road was built that connected Fort Crawford to Fort Gaines. A post office also operated at Fort Crawford until at least 1824.
Where is Fort Crawford Today?
Maps from the 1800s show where Fort Crawford was located. However, even with special searches by archaeologists, the exact original site of the fort has not been found yet.