FreeOTFE facts for kids
 |
|
FreeOTFE running on Windows XP
|
|
| Developer(s) | Sarah Dean |
|---|---|
| Stable release |
5.21 / 7 February 2010
|
| Written in | C, Delphi (GUI) |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows and Windows Mobile |
| Available in | Croatian, Czech, English, French, German, Greek, Italian, Japanese, Russian and Spanish |
| Type | Disk encryption software |
| License | Free and open-source software that requires attribution |
FreeOTFE was a computer program that helped keep your digital information safe. It used something called "on-the-fly disk encryption." This means it scrambled data automatically as you saved it. It was an open source program, meaning its code was available for anyone to see and use.
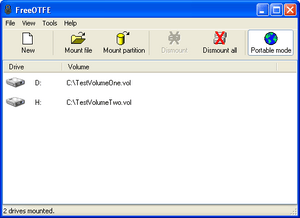
FreeOTFE worked on Microsoft Windows computers and Windows Mobile phones. It could make a special "virtual drive." This was like a secret folder on your computer or USB stick. Anything you put in this folder was automatically scrambled. This made it unreadable to others without the right key. Other programs like TrueCrypt and Microsoft's BitLocker do similar things.
The person who created FreeOTFE, Sarah Dean, stopped working on it around 2011. The official FreeOTFE website became unavailable in June 2013. However, you can still find the original program on a mirror site at Sourceforge. In June 2014, a new version of the project, called LibreCrypt, started on GitHub.
Contents
What FreeOTFE Did
FreeOTFE was first released in 2004. It was one of the first open source programs for disk encryption. It had a special design that allowed other people to add new ways of scrambling data if they wanted to.
This software could work with encrypted files from Linux computers. This meant you could read and write data that was encrypted on a Linux system using FreeOTFE on Windows. It was also the first open source program of its kind to support Windows Vista and older handheld devices called PDAs.
FreeOTFE also let you create "hidden volumes." These were like secret compartments within your encrypted data. This feature helped keep your information even more private. You could also use FreeOTFE to encrypt entire parts of your computer's storage, but not the main part where the operating system was installed.
Using FreeOTFE on the Go
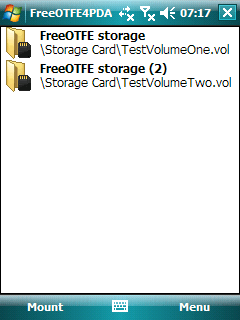
FreeOTFE had a "portable" mode. This meant you could keep the program and your encrypted data on a USB drive. You could then carry it with you. This allowed you to use FreeOTFE on different Windows computers without fully installing the program. It would "mount" your encrypted data, making it accessible like a regular drive.
To use this portable mode, you usually needed special permissions on the computer. This was because it had to temporarily install small programs called "device drivers." These drivers helped create the virtual encrypted drives.
Using FreeOTFE Without Installation
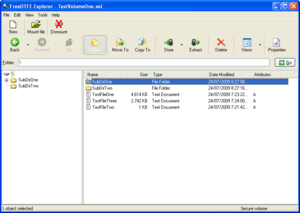
FreeOTFE also came with another program called "FreeOTFE Explorer." This program was even more portable. It didn't need any special permissions or driver installations.
This was very useful for using encrypted data on public computers. For example, you could use it on computers in libraries or at public kiosks. These places often don't let you install new software or have administrator rights.
FreeOTFE Explorer worked a bit differently. It didn't create a virtual drive that encrypted data as you saved it. Instead, it let you open encrypted files and take out or put in other files. It worked a lot like programs that handle ZIP or RAR files.
How FreeOTFE Scrambled Data
FreeOTFE offered many ways to scramble and protect your data. This made it very flexible.
Scrambling Methods (Ciphers)
FreeOTFE used several different methods, called ciphers, to encrypt data. Some of these included:
It included all the top ciphers that were considered for the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). Each cipher could also use different "keylengths," which made the encryption even stronger.
Data Check Methods (Hashes)
FreeOTFE also used many different "hash algorithms." These are like digital fingerprints that help check if data has been changed. Some of the hash algorithms it used were:
- MD2
- MD4
- MD5
- RIPEMD-128
- RIPEMD-160
- RIPEMD-224
- RIPEMD-320
- SHA-1
- SHA-224
- SHA-256
- SHA-384
- SHA-512
- Tiger
- Whirlpool
See also
 In Spanish: FreeOTFE para niños
In Spanish: FreeOTFE para niños
- Disk encryption
- Disk encryption software
- On-the-fly encryption
- Comparison of disk encryption software
 | Calvin Brent |
 | Walter T. Bailey |
 | Martha Cassell Thompson |
 | Alberta Jeannette Cassell |