German colonization of the Americas facts for kids
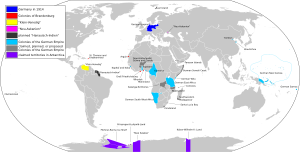
German attempts to settle in the Americas happened in the 1500s and 1600s. These efforts included areas like German Venezuela (also known as Klein-Venedig), St. Thomas, and Crab Island. These were small parts of the larger European colonization of the Americas.
Contents
History of German Settlements
Klein-Venedig: Little Venice
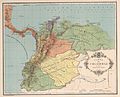
Klein-Venedig means "Little Venice" in German. This was the most important German settlement in the Americas. It lasted from 1528 to 1546.
The Welser family, who were rich bankers from Augsburg, Germany, got the rights to this land. Emperor Charles V gave them these rights because he owed them a lot of money. The Welsers' main goal was to find the legendary golden city of El Dorado.
The first leader of this project was Ambrosius Ehinger. He founded the city of Maracaibo in 1529. Many German settlers died from tropical diseases. They also faced frequent wars with the Native Americans.
The Welsers brought German miners to the colony. They also brought about 4,000 enslaved Africans to work on sugar cane farms. Eventually, Emperor Charles V took back the land from the Welser family.
Brandenburg-Prussia's Trading Post
The Brandenburgisch-Africanische Compagnie was a company from Brandenburg (which later became Kingdom of Prussia). They set up trading posts in Africa. In 1685, they rented a trading post on St. Thomas from a Danish company.
However, in 1693, the Danes took over the post. They seized its warehouse and all its goods without warning. There were no permanent German settlers in this area.
Courland's Caribbean Colony
The Duchy of Courland was a small state led by Germans. It was part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Courland leased a place called New Courland (Neu-Kurland) on the island of Tobago in the Caribbean.
This colony struggled and was restarted several times. Courland also tried to set up a settlement near modern Toco on the island of Trinidad.
Hanau's Grand Plan
The counties of Hanau-Lichtenberg and Hanau-Münzenberg were led by Frederick Casimir. He and his advisor, Johann Becher, planned a very expensive project. They wanted to lease land in Guiana from the Dutch West India Company.
Frederick Casimir called his new area the Hanauish-Indies (Hanauisch-Indien). But he ended up owing huge amounts of money. This debt eventually forced his relatives to take control of his rule.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Colonización alemana de América para niños
In Spanish: Colonización alemana de América para niños
- German interest in the Caribbean, German efforts in 1867–1917
- German colonial empire, after 1880
- German colonization of Valdivia, Osorno and Llanquihue
- Nueva Germania
- Pozuzo, a Peruvian community of German origin.
- Blumenau