Hair follicle facts for kids
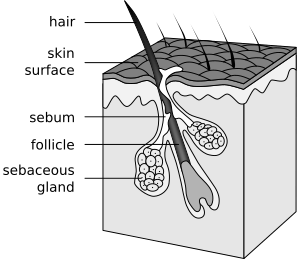
A hair follicle is a tiny part of your skin that grows a hair. It works by packing old cells tightly together. Attached to the top of each follicle are small sebaceous glands. These glands make an oily substance called sebum. You can find these glands almost everywhere on your skin, except on your palms, lips, and the soles of your feet. The thicker your hair, the more sebaceous glands it usually has.
There's also a tiny muscle attached to the follicle, called the arrector pili. This muscle makes your hair stand up straight. When it contracts, it can also make the skin around the hair stick up a little, creating what we call goose bumps. Special stem cells are found near this muscle. They are very important for growing new hair, especially during the Anagen stage.
On average, healthy hair follicles on your scalp grow about 0.5 inches (13 mm) each month.
Contents
How Hair Follicles Are Built
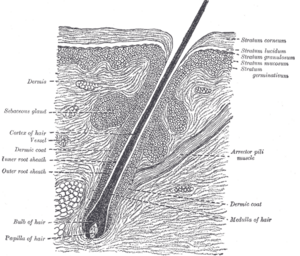
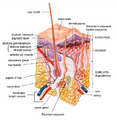
Hair follicles have several important parts that work together to grow hair.
The Papilla
At the very bottom of the hair follicle is a structure called the papilla. It's mostly made of connective tissue and has a tiny capillary (a very small blood vessel). Cells in the papilla usually don't divide much.
The Hair Matrix
Around the papilla is the hair matrix. This area is full of epithelial cells. It also contains melanocytes, which are cells that give your hair its color. The cells in the hair matrix divide very quickly. These dividing cells form the main parts of your hair and the inner root sheath. Because these cells grow so fast, some medical treatments like chemotherapy or radiotherapy can sometimes cause temporary hair loss.
The Root Sheath
The root sheath has two parts: an outer (external) and an inner (internal) root sheath. The inner root sheath has three layers: Henle's layer, Huxley's layer, and an inner cuticle. This inner cuticle connects directly to the outer layer of the hair itself.
The Hair Fiber
The hair fiber is the part we see as hair. It has an outer cuticle (which connects to the root sheath), a middle part called the cortex, and an inner core called the medulla.
The Bulge
The bulge is found in the outer root sheath, right where the arrector pili muscle connects. This area holds different types of stem cells. These stem cells provide new cells for the entire hair follicle. They also help the skin heal after an injury.
Other Parts of the Follicle
Other parts connected to the hair follicle include the arrector pili muscles, sebaceous glands (which make oil), and apocrine sweat glands. Hair follicles also have nerve receptors that help you feel when your hair moves.
Hair Growth Cycles
Hair doesn't just grow all the time; it goes through different phases in a cycle.
- Anagen is the active growth phase.
- Catagen is a short transition phase.
- Telogen is the resting phase.
There's also a shedding phase called exogen, where hair falls out. Normally, most of your hair (up to 90%) is in the anagen phase. About 10–14% are in telogen, and 1–2% are in catagen. The length of these cycles changes depending on where the hair is on your body. For example, eyebrow hair cycles in about 4 months, while scalp hair takes 3–4 years. This is why your eyebrows don't grow as long as the hair on your head! Chemical signals, like epidermal growth factor, help control these growth cycles.
Anagen Phase: Growing Hair
The anagen phase is when your hair follicles are actively growing. Cells at the root of the hair divide quickly, making the hair shaft longer. During this phase, hair grows about 1 cm (0.4 inches) every 28 days. Hair on your scalp stays in this active growth phase for 2–7 years. The exact time is determined by your genes. When the anagen phase ends, a signal tells the follicle to move into the catagen phase.
Catagen Phase: Transition Time
The catagen phase is a short stage that happens right after the anagen phase. It signals that the active growth of a hair is ending. This phase lasts for about 2–3 weeks. During this time, a "club hair" forms.
Telogen Phase: Resting Hair
The telogen phase is the resting period for the hair follicle. The "club hair" is the final result of a hair follicle in this stage. It's a dead, fully hardened hair. It's normal to shed about 50 to 100 club hairs from a healthy scalp every day.
Hair Growth Cycle Times
The time each phase lasts can be different for everyone. Hair color and follicle shape can also affect these timings.
- Scalp Hair:
- Anagen phase: 2–3 years (sometimes much longer)
- Catagen phase: 2–3 weeks
- Telogen phase: Around 3 months
- Eyebrow Hair (and similar):
- Anagen phase: 4–7 months
- Catagen phase: 3–4 weeks
- Telogen phase: About 9 months
Images for kids
-
Male hair loss
See also
 In Spanish: Folículo piloso para niños
In Spanish: Folículo piloso para niños