Corkbark tree facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Corkbark tree |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Hakea divaricata near Alice Springs | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Hakea
|
| Species: |
divaricata
|
 |
|
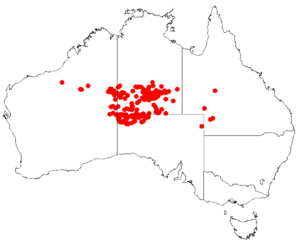
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
The Corkbark tree, also known as needlewood or fork-leaved corkwood, is a special tree or shrub found in the middle of Australia. It belongs to the Proteaceae plant family. This slow-growing plant can have up to 120 beautiful cream or greenish-yellow flowers. These flowers grow in long clusters from June to November.
Many Indigenous groups have their own names for the Corkbark tree. For example, the Alyawarre people call it ntywey-arrengk. The Eastern Arrernte call it untyeye, and the Western Arrernte call it ntyweye. The Kaytetye know it as ntyarleyarle or ntyeye. The Pintupi Luritja and Pitjantjatjara people call it piruwa or ularama. The Warlpiri call it kumpalpa, piriwa, or yarrkampi.
Contents
What Does the Corkbark Tree Look Like?
The Corkbark tree (Hakea divaricata) is usually an upright shrub or a small tree. It can grow from 2 to 7 meters (about 6.5 to 23 feet) tall. It has a dark, corky trunk with deep grooves.
Branches and Leaves
The smaller branches of the tree are red and smooth. Sometimes, they might have soft, short hairs. The leaves are stiff and prickly. They are arranged one after another along the stem. Each leaf is about 7 to 20 centimeters (2.7 to 7.8 inches) long. They are very thin, like needles, only about 0.8 to 2.3 millimeters (0.03 to 0.09 inches) wide. Each leaf ends in a sharp point.
Most leaves split into several smaller segments. These segments can be from 0.3 to 12 centimeters (0.1 to 4.7 inches) long. Young leaves might have soft hairs, but they quickly become smooth.
Flowers and Fruit
The flowers grow in clusters on a stem that is 5 to 14 centimeters (2 to 5.5 inches) long. There are usually 65 to 120 flowers in each cluster. The flowers are cream, greenish-yellow, or bright yellow. Each flower has a stalk about 4 to 10 millimeters (0.15 to 0.39 inches) long. These stalks are covered in white or dark brown hairs.
After the flowers, the tree produces fruit. The fruit is shaped like an oblong or egg. It is about 2.3 to 4 centimeters (0.9 to 1.5 inches) long. The fruit has a long, pointed beak, which can sometimes be curved. Inside the fruit, the seeds are large and have a wing on one side.
How Was the Corkbark Tree Named?
The Corkbark tree, Hakea divaricata, was first officially described by a botanist named Lawrence Alexander Sidney Johnson. He wrote about it in 1962.
Its Scientific Name
The second part of its scientific name, divaricata, comes from a Latin word. Divaricatus means "spread apart." This refers to how the segments of its leaves spread out.
This tree is part of a group called the "corkwood group." These trees are often found in dry areas of Australia. Other trees in this group include Hakea chordophylla and Hakea ivoryi.
Where Does the Corkbark Tree Grow?
The needlewood hakea is mostly found in central Australia. You can see it in the southern part of the Northern Territory. It also grows in the Pilbara and northern Goldfields regions of Western Australia. You can find it in southwest Queensland and the Far North of South Australia.
Its Home Environment
This tree likes to grow on red sand plains. It can also be found around the bottom of hills and near rockholes. Sometimes, it grows in the valleys between sand dunes or along watercourses. It grows well in sandy soils, especially near sandstone or limestone. It is often part of open woodlands, like those with mulga trees.
How People Use the Corkbark Tree
The Corkbark tree is sometimes planted in gardens or along streets. It is a good choice for dry areas because it can handle both frost and drought. If there is a fire, the needlewood hakea can grow back from its special underground stem called a lignotuber.
Traditional Uses
Indigenous Australian peoples have used this plant for many things.
- They ate the fruit flesh.
- They used the roots as a source of water.
- They could get gum from the tree.
- The wood was used to make weapons, tools, and traps.
- They also collected honey from the flowers.
- Sometimes, they soaked the flowers in water to make a sweet drink.


