Hearing loss facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Hearing loss |
|
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Hearing impaired, Hard of hearing; anakusis or anacusis is total deafness |
 |
|
| The international symbol of deafness and hearing loss | |
| Symptoms | Decreased ability to hear |
| Complications | Social isolation, dementia |
| Types | Conductive, sensorineural, and mixed hearing loss, central auditory dysfunction |
| Causes | Genetics, aging, exposure to noise, some infections, birth complications, trauma to the ear, certain medications or toxins |
| Diagnostic method | Hearing tests |
| Prevention | Immunization, proper care around pregnancy, avoiding loud noise, avoiding certain medications |
| Treatment | Hearing aids, sign language, cochlear implants, subtitles |
| Frequency | 1.33 billion / 18.5% (2015) |
Hearing loss means you can't hear sounds as well as you should, or sometimes, not at all. It can happen in one ear or both. Some people are born with hearing loss, while others develop it later in life.
For kids, hearing problems can make it harder to learn to speak and understand language. For adults, it can cause problems with talking to others and at work. Hearing loss can be temporary, meaning it gets better, or permanent, meaning it lasts forever.
Sometimes, hearing loss happens as people get older. This usually affects both ears. It's caused by tiny cells in the ear called cochlear hair cells wearing out. Hearing loss can also make some people, especially older ones, feel lonely.
People who are Deaf usually have very little or no hearing.
Many things can cause hearing loss, such as:
- Your genetics (it runs in your family)
- Getting older
- Being around very loud noises
- Some infections
- Problems during birth
- An injury to the ear
- Certain medicines or toxins
A common cause is chronic ear infections, which are ear infections that keep coming back. Also, some infections a mother gets during pregnancy, like rubella, can cause hearing loss in her baby.
Doctors diagnose hearing loss with hearing tests. These tests check if a person can hear sounds at a certain level. For example, if you can't hear sounds quieter than 25 decibels in at least one ear, you have hearing loss. It's a good idea for all newborn babies to have their hearing checked.
Hearing loss can be mild, moderate, severe, or profound (meaning very severe). There are three main types: conductive hearing loss (problems with sound reaching the inner ear), sensorineural hearing loss (problems with the inner ear or nerves), and mixed hearing loss (a mix of both).
Contents
Understanding Hearing Loss
- Hearing loss means your ability to hear sounds is not as good as it should be.
- Deafness means you can't understand speech, even if the sound is made louder. If someone has profound deafness, they might not hear even very loud sounds. In total deafness, no sounds are heard at all.
- Speech perception is not just hearing sounds, but also understanding what people are saying. Some rare types of hearing loss only affect how well you understand speech.
It's important to use respectful words when talking about people with hearing loss. Many people in the deaf community don't like terms like "hearing impaired," "deaf-mute," or "deaf and dumb." These words can be offensive.
How Hearing Loss is Diagnosed
To find out if someone has hearing loss, doctors play different sounds and see if the person can hear them. Hearing tests check how well you hear sounds at different pitches. An audiologist is a specialist who performs these tests.
Preventing Hearing Loss
About half of all hearing loss cases worldwide could be prevented. For children under 15, about 60% of hearing loss can be avoided. Here are some ways to prevent it:
- Get vaccinations: Vaccines against diseases like rubella, measles, mumps, and meningitis can prevent hearing loss caused by these infections.
- Care during pregnancy: Good care during pregnancy can help prevent birth problems that might lead to hearing loss.
- Avoid loud noise: This is one of the most important ways to prevent hearing loss. Loud noises can damage your ears.
- Be careful with medicines: Some medicines can harm your hearing.
The World Health Organization (WHO) also suggests preventing premature birth (babies born too early) as a way to prevent hearing loss. World Hearing Day is an event held every year to teach people about preventing hearing damage.
Protecting Your Ears from Noise
Loud noise is the biggest risk factor for hearing loss that you can prevent. It's important to protect your ears, especially if you are around loud sounds often.
- Use hearing protectors: If you are in a noisy place, like a concert or a workshop, wear earplugs or earmuffs. These can block out harmful noise.
- Choose quieter tools: If you use power tools, try to pick ones that are less noisy.
- Limit exposure: Try not to be around very loud noises for too long.
Some hearing protectors block all noise, while others let you hear certain sounds. It's important that hearing protectors fit well so they can work properly.
Hearing Screening
It's important to check hearing regularly, especially for kids.
- Newborns: All newborn babies should have their hearing checked.
- School-age children: The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children have their hearing tested when they start school, and then at ages 6, 8, 10, and at least once in middle school and high school.
- Adults: Adults should also have their hearing checked regularly, especially as they get older. This helps catch any problems early.
Managing Hearing Loss
How hearing loss is managed depends on what caused it, how severe it is, and what type it is.
For many people, especially those with age-related or noise-induced hearing loss, the hearing loss gets worse over time and cannot be reversed. There are no approved medicines or treatments that can cure this type of hearing loss.
However, there are many helpful tools and strategies:
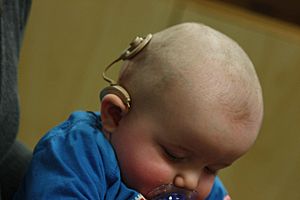
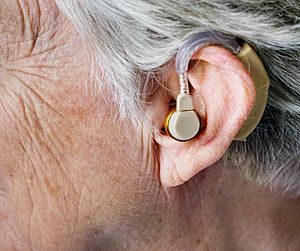
- Hearing aids: These small electronic devices fit in or behind your ear and make sounds louder.
- Cochlear implants: These are devices surgically placed in the ear that help send sound signals to the brain. They are used for more severe hearing loss.
- Assistive technology: These are devices that help with hearing in different situations, like special phones or alarm clocks.
- Closed captioning and lip reading: These help people understand speech by reading text on a screen or watching someone's lips as they speak.
- Sign language: This is a visual language that uses hand movements, facial expressions, and body language to communicate.
For people with hearing loss in both ears, doctors can help decide if using hearing aids in one ear or both ears is better.
Related pages
- Deafness
- Conductive hearing loss
- Noise-induced hearing loss
- cochlear implant
- hearing aid
- Sign language
Images for kids
-
The sign for "friend" in American Sign Language
See also
 In Spanish: Sordera para niños
In Spanish: Sordera para niños