Henry Gantt facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Henry Gantt
|
|
|---|---|

Henry L. Gantt, 1916
|
|
| Born |
Henry Laurence Gantt
May 20, 1861 Calvert County, Maryland, U.S.
|
| Died | November 23, 1919 (aged 58) Montclair, New Jersey, U.S.
|
| Nationality | American |
| Citizenship | United States |
| Alma mater | Johns Hopkins University (A.B.) Stevens Institute of Technology (M.E.) |
| Known for | Gantt chart |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Scientific management |
| Influences | |
Henry Laurence Gantt (/ɡænt/; May 20, 1861 – November 23, 1919) was an American mechanical engineer and management consultant. He is famous for his work in developing scientific management. This is a way of organizing work to make it more efficient.
Gantt created the Gantt chart in the 1910s. These charts are still very important today. They help people plan and manage big projects. For example, they were used for building the Hoover Dam and the Interstate highway system.
Contents
Henry Gantt's Early Life and Education
Growing Up in Maryland
Henry Gantt was born in Calvert County, Maryland, in 1861. This was at the start of the American Civil War. His family lived on a plantation. After the war, they lost their land and moved to Baltimore.
School and College
Henry went to McDonogh School and finished in 1878. Then, he studied at Johns Hopkins University, graduating in 1880. He taught at McDonogh School for three years. Later, he earned a Master of Engineering degree from the Stevens Institute of Technology in New Jersey. In 1899, Henry Gantt married Mary E. Snow.
Henry Gantt's Career and Ideas
Starting Work
In 1884, Gantt began his career as a draughtsman. He worked at a company called Poole & Hunt in Baltimore. In 1887, he joined Frederick Winslow Taylor, another famous engineer. They worked together at Midvale Steel and Bethlehem Steel until 1893. They focused on making factories run better.
New Management Ideas
Later, Henry Gantt became a consultant for businesses. He invented the Gantt chart, which became very popular. He also created the 'task and bonus' system for paying workers. This system rewarded employees for doing their work well and improving. He also found ways to measure how efficient workers were.
Gantt believed that businesses had a social responsibility. This means they should care about the well-being of the community. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) honors him with an annual medal.
Henry Gantt's Important Work
Henry Gantt left behind several important ideas for how to manage projects and businesses:
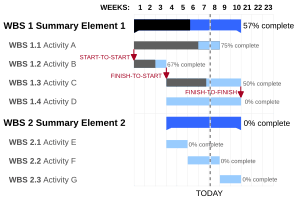
- The Gantt Chart: This is a visual tool that helps plan and track tasks in a project. It shows when tasks start, when they end, and how much progress has been made. It's still used a lot today!
- Industrial Efficiency: Gantt believed that factories and businesses could work much better. He thought that by carefully studying how things were done, companies could remove mistakes and waste.
- The Task and Bonus System: He created a pay system where managers got a bonus. This bonus depended on how well they taught their employees to work better. It encouraged managers to help their teams improve.
- Social Responsibility of Business: Gantt felt that businesses should not just focus on making money. He thought they also had a duty to help the society around them.
What are Gantt Charts?
Henry Gantt made many different kinds of charts. He designed them so that managers could quickly see if work was on time, ahead of time, or behind schedule. Today, many computer programs for project management use these same ideas.
Gantt described two main types of records:
- The "man's record" showed what each worker was supposed to do and what they actually did.
- The "daily balance of work" showed how much work needed to be done and how much was completed.
He gave an example of orders that would take many days to finish. His charts would show how much was done each day. They also showed the total amount completed for each part. This helped everyone see the progress clearly.
Ideas from Work, Wages, and Profits (1916)
In his 1916 book, Work, Wages, and Profits, Gantt talked a lot about scheduling. This means planning when tasks should happen. He suggested giving foremen (supervisors) a list of jobs to do each day. He also stressed the need to coordinate activities. This helps avoid problems where one task holds up another.
Ideas from Organizing for Work (1919)
In his 1919 book, Organizing for Work, Gantt shared two main ideas for his charts:
- First, measure activities by the time it takes to finish them.
- Second, use the chart space to show the amount of activity that should have been done in that time.
He showed a progress chart that used thin lines to show how many items were made each month. A thick line showed the total for the whole year. This made it easy to see how much was produced over time.
Henry Gantt and Karol Adamiecki
Interestingly, a similar way of showing project schedules was invented in 1896 by Karol Adamiecki. However, Adamiecki published his work in a language that was not widely known in Western countries. So, Henry Gantt was able to make a similar method popular. This is why the charts are usually called Gantt Charts today.
See also
 In Spanish: Henry Gantt para niños
In Spanish: Henry Gantt para niños