Mechanical engineering facts for kids
Mechanical engineering is a super cool field of engineering that focuses on designing, building, and maintaining physical machines. It's all about how things move and how forces make them work!
Mechanical engineers use ideas from engineering physics, mathematics, and materials science to create and improve all sorts of mechanical systems. It's one of the oldest and widest areas of engineering.
To do their job, mechanical engineers need to understand things like how things move (mechanics), how heat works (thermodynamics), and what different materials are made of. They also use special computer tools like computer-aided design (CAD) to help them create and test their ideas.
They design everything from factories and industrial equipment to heating and cooling systems, transport vehicles, aircraft, watercraft, robotics, and even medical devices!
Mechanical engineering really grew during the Industrial Revolution in Europe in the 1700s. But people have been using mechanical engineering ideas for thousands of years! Today, mechanical engineers are working on exciting new things like super strong new materials, mechatronics (combining mechanics and electronics), and nanotechnology (working with tiny, tiny things). This field often works closely with other types of engineering, like aerospace engineering and electrical engineering.
Contents
A Look at Mechanical Engineering History
The ideas behind mechanical engineering have been used by people for a very long time!
Ancient Inventions
People in ancient times knew about the six classic simple machines. These include the wedge and the inclined plane (ramp), which were used even in prehistoric times. The wheel was invented in Mesopotamia (modern Iraq) around 5,000 BC.
The lever first appeared about 5,000 years ago in the Near East. It was used in simple scales and to move huge objects in ancient Egyptian technology. The lever was also part of the shadoof, a water-lifting machine from Mesopotamia around 3000 BC. The first signs of pulleys come from Mesopotamia in the early 2000s BC.
Water Power and Early Machines
The Sakia, a water wheel powered by animals, was developed in the Kingdom of Kush around 400 BC. This helped people lift water without using as much human energy. In Kush, they also built reservoirs called Hafirs to store water for farming.
The first practical water-powered machines, like the water wheel and watermill, appeared in the Persian Empire by the early 300s BC. In ancient Greece, Archimedes (287–212 BC) made big contributions to mechanics. In Roman Egypt, Heron of Alexandria (around 10–70 AD) created the first steam-powered device, called the Aeolipile.
In China, Zhang Heng (78–139 AD) improved water clocks and invented a seismometer (for earthquakes). Ma Jun (200–265 AD) invented a chariot with differential gears. Later, the Chinese engineer Su Song (1020–1101 AD) built an amazing clock tower with an escapement mechanism, which was a key part of clocks. He also invented the world's first known endless chain drive for power.
The Islamic Golden Age
During the Islamic Golden Age (from the 600s to the 1400s), Muslim inventors made many important advances in mechanical technology. One famous inventor, Al-Jazari, wrote a book in 1206 called Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices. It showed many clever mechanical designs.
Modern Mechanical Engineering
In the 1600s, big steps forward happened in England and Europe. Christiaan Huygens invented the pendulum clock in 1657, which was the most accurate clock for almost 300 years. Isaac Newton developed Newton's Laws of Motion and calculus, which became the math foundation for physics.
During the early 1800s Industrial Revolution, new machine tools were developed. This helped mechanical engineering become its own field. These tools helped create manufacturing machines and the engines to power them. The first professional group for mechanical engineers in Britain was formed in 1847.
In the United States, the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) was created in 1880. The first schools in the U.S. to offer engineering education were the United States Military Academy in 1817 and Norwich University in 1819. Mechanical engineering education has always been based on strong math and science skills.
Becoming a Mechanical Engineer
Many universities around the world offer degrees in mechanical engineering. These programs usually take four to five years to complete. When you finish, you earn a degree like a Bachelor of Engineering (B.Eng.) or Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.).
In the United States, most mechanical engineering programs are checked by an organization called ABET. This helps make sure that all universities teach similar things and that students learn what they need to become good engineers. Other countries have similar groups that check engineering degrees.
Some mechanical engineers decide to study even more after their first degree. They might get a Master's degree or even a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.), which often involves a lot of research.
What You Study
Mechanical engineering programs teach you many important subjects. These usually include:
- Mathematics (like calculus and linear algebra)
- Basic sciences (like physics and chemistry)
- Statics (how things stay still under forces) and dynamics (how things move when forces act on them)
- Strength of materials (how strong different materials are)
- Materials science (what materials are made of)
- Thermodynamics (how energy and heat work)
- Fluid mechanics (how liquids and gases move)
- Machine design (how to create parts and machines)
- Manufacturing engineering (how to make things)
- Robotics (designing and building robots)
- Engineering design (the process of creating new things)
- Drafting and computer-aided design (CAD)
Mechanical engineers also need to understand some basic ideas from other fields like electrical engineering. Many programs also include projects or internships where students get real-world experience solving problems.
What Mechanical Engineers Do
Mechanical engineers research, design, develop, build, and test mechanical and thermal devices. This includes tools, engines, and many different kinds of machines.
Here are some common tasks mechanical engineers do:
- They look at problems to figure out how machines or heat-related devices can help.
- They design or improve mechanical and thermal devices using computer tools.
- They build and test early versions (prototypes) of their designs.
- They check the test results and make changes to their designs if needed.
- They supervise the process of making the device.
- They might lead a team of experts in areas like drafting or 3D printing.
Mechanical engineers design and oversee the making of many products, from medical tools to new types of batteries. They also design machines that create power, like electric generators and engines. They also work on machines that use power, like refrigerators and air conditioners.
Like other engineers, mechanical engineers use computers a lot. They use them to create and analyze designs, run simulations, and predict how a machine will work.
Getting Licensed
In many countries, engineers can get a special license from the government. This license shows that they have the right knowledge and experience to work as a professional engineer. For example, in the U.S., a licensed engineer is called a Professional Engineer (PE). In the UK, they might be a Chartered Engineer.
This is important because for some big projects, like designing bridges or power plants, only a licensed engineer can approve the plans.
Different Areas of Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering has many different special areas. Here are some of them:
Mechanics: How Things Move and React
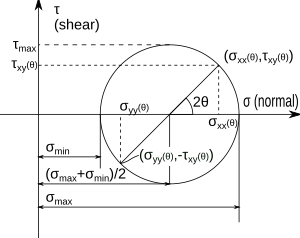
Mechanics is the study of forces and what they do to objects. Mechanical engineers use mechanics to figure out how objects will move or change shape under different forces.
Some parts of mechanics include:
- Statics: Studying objects that are not moving and how forces affect them.
- Dynamics: Studying how forces affect objects that are moving. This includes how fast they move (kinematics) and what forces cause that movement (kinetics).
- Strength of materials: How different materials change shape or break under stress.
- Fluid mechanics: How liquids and gases react to forces.
For example, if engineers are designing a car, they might use statics to design the car's frame to see where the strongest forces will be. They might use dynamics to design the engine and understand the forces inside. Fluid mechanics could help design the car's air conditioning system.
Mechatronics and Robotics
Mechatronics is a cool mix of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and software engineering. It's about putting electrical and mechanical parts together to create smart, automated systems. A good example is a CD-ROM drive. Mechanical parts open and close the tray, spin the CD, and move the laser. Electrical parts read the data. And software controls everything.
Robotics is when you use mechatronics to create robots! Robots are often used in factories to do jobs that are dangerous, boring, or need to be done very precisely. Robots can be any shape or size, but they are programmed to interact with the world physically.
Robots help businesses save money and make things better quality. Many factories use robots on assembly lines, especially in the car industry. Robots are also used for things like bomb disposal, space exploration, and even in homes for fun or chores.
Thermodynamics: The Science of Heat and Energy
Thermodynamics is the study of energy, how it's used, and how it changes form. Mechanical engineers use thermodynamics to design things that involve heat and energy.
For example, car engines use thermodynamics to turn the chemical energy in fuel into heat, and then into the mechanical work that makes the wheels turn.
Mechanical engineers use thermo-science to design engines, power plants, heating and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems, heat exchangers, and refrigerators.
Design and Drafting
Drafting is how mechanical engineers draw their designs and create instructions for making parts. A technical drawing can be a computer model or a hand-drawn picture that shows all the sizes needed to make a part. It also includes notes about how to put it together and what materials to use.
Today, engineers often use computer-aided design (CAD) programs. These programs let them create designs in 3D, which is much easier than drawing in 2D.
Once a part is designed, instructions for making it are sent to machines, often using computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) programs. This is called computer numerically controlled (CNC) manufacturing. This means machines can make parts without a person constantly guiding them.
Drafting is used in almost every area of mechanical engineering and many other engineering fields. 3D models from CAD are also used for testing how designs will work, like with finite element analysis (FEA).
Modern Tools for Engineers
Many mechanical engineering companies use computer-aided engineering (CAE) programs. These include 2D and 3D solid modeling computer-aided design (CAD) tools. These tools make it easier to see products, create virtual versions of parts, and make sure parts fit together correctly.
Other CAE programs help engineers run complex simulations. They can predict how a product will react to different forces or how long it will last. These tools include finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD).
Using CAE programs, engineers can quickly try out many different designs. This helps them create products that are better, cheaper, and perform well. They don't have to build a physical model until the design is almost perfect.
Exciting Areas of Research
Mechanical engineers are always trying to find new ways to make machines and systems safer, cheaper, and more efficient. Here are some cutting-edge areas they are working on:
Micro Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS)
This involves creating tiny mechanical parts, like springs and gears, that are smaller than a human hair! These MEMS parts are used in things like car airbag sensors, modern cell phones, and medical devices.
Friction Stir Welding (FSW)
This is a new type of welding that was invented in 1991. It can join materials that were previously very hard to weld, like some aluminum alloys. It's important for building airplanes and even parts of rockets, like the Space Shuttle external tank.
Composites: New Materials
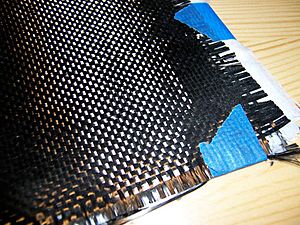
Composites are materials made by combining two or more different materials to create something with new, better properties. For example, carbon fiber composites are super strong and light. Mechanical engineers research how to design and use these materials to make things lighter, stronger, and more resistant to rust. They are used in everything from spacecraft to fishing rods!
Nanotechnology: Working with the Tiny
Nanotechnology is about working with materials at a super small scale, like atoms and molecules. Mechanical engineers are researching things like nanofilters (for super-fine filtering) and nanostructures (tiny structures with special properties).
Biomechanics: Engineering for Life
Biomechanics is when mechanical engineering principles are used to study living systems, like humans, animals, plants, and even cells. Biomechanics helps in creating things like prosthetic limbs (artificial arms or legs) and artificial organs for people.
Engineers in this field often use computer models to understand how bones or muscles work. They even study how materials found in nature, like bone, are designed to be strong and light.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
CFD uses computers to solve problems involving how liquids and gases flow. Engineers use powerful computers to simulate how air moves around a car or how water flows through a pipe. This helps them design things like airplane wings or cooling systems more efficiently.
Acoustical Engineering: The Science of Sound
Acoustical engineering is about the study of Sound and Vibration. These engineers work to reduce noise pollution in machines and buildings. They might design quieter engines, soundproof rooms, or improve the sound quality in concert halls. They also study how different mechanical systems vibrate.
Related Fields
Some other engineering fields are very similar to mechanical engineering. These include Manufacturing engineering, aerospace engineering (designing aircraft), and automotive engineering (designing cars). If you study these, you'll find that many of the classes are similar to mechanical engineering, with just a few specialized ones.
See also
 In Spanish: Ingeniería mecánica para niños
In Spanish: Ingeniería mecánica para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |