Thermodynamics facts for kids
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that helps us understand how heat and energy move and change. It looks at how things like pressure and volume change in different objects. This science helps us connect the tiny world of atoms to the big world we see every day.
Thermodynamics has two main parts: classical thermodynamics and statistical thermodynamics. A key idea in this field is a thermodynamic system.
Imagine a brick. It's a good example of a thermodynamic system. A brick is made of many tiny atoms. All thermodynamic systems have two types of features: extensive and intensive.
- Extensive properties are things you get by adding up all the parts. For a brick, its volume, energy, mass, and charge are extensive. If you put two identical bricks together, you get twice the mass.
- Intensive properties are averages over all the parts. Things like temperature, pressure, and density are intensive. If you have two identical bricks, they still have the same temperature as one brick alone.
Contents
Laws of Thermodynamics
There are four main rules, or laws, in thermodynamics. These laws explain how energy moves between objects, often as heat.
The Zeroth Law
This law is about temperature and heat flow. If two systems are at the same temperature as a third system, then all three systems are at the same temperature. Think of it like this: if object A is as warm as object B, and object B is as warm as object C, then object A must also be as warm as object C.
The First Law
This law is about energy conservation. It says that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only change from one form to another. If a system gains energy, it's because energy was given to it as heat or work. The total amount of energy in the universe stays the same.
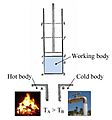
The Second Law
This law explains how heat moves naturally. If you have two objects touching, one hot and one cold, heat will always flow from the hot object to the cold object. This continues until both objects reach the same temperature. It's why your hot drink cools down and your cold drink warms up.
The Third Law
This law talks about what happens at the coldest possible temperature. This temperature is called absolute zero, which is 0 Kelvin. At this super-cold point, the entropy (which is energy that can't be used to do work) of a system becomes zero. This means everything is perfectly ordered and still.
How We Use Thermodynamics
Long ago, people studied thermodynamics to make steam engines work better. Today, the ideas from thermodynamics are used in many different ways.
Scientists use these ideas to design better engines and refrigerators. They also use it to understand the features of everyday materials. This helps them make materials stronger or more useful in the future.
Thermodynamics is also important in chemistry. It helps chemists understand which chemical reactions will happen and which won't. This study is sometimes called chemical kinetics. Thermodynamics is powerful because simple ideas about atoms can explain how large systems, like bricks, behave.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Termodinámica para niños
In Spanish: Termodinámica para niños