Computer-aided design facts for kids
Computer-aided design (CAD) is when people use computers to help them create, change, look at, or make designs better. This special software helps designers work faster, make better designs, share their ideas more easily, and create a digital record for making things. CAD designs can even help protect new ideas when applying for patents. The designs often become digital files that can be printed, used by machines, or sent to factories. Sometimes, people also call it computer-aided drafting or CADD.
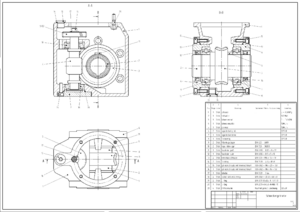
When CAD is used for designing electronic things, it's called electronic design automation (EDA). For designing mechanical parts, it's known as mechanical design automation (MDA). This includes making technical drawings using computer software.
CAD software for mechanical design uses either vector graphics (like lines and shapes) or raster graphics (like pictures made of tiny dots) to show what designed objects look like. But CAD is more than just shapes! It also includes important information like what materials to use, how to make the product, its dimensions (size), and how exact it needs to be.
CAD can be used to draw curves and shapes in two-dimensional (2D) space, which is flat like a piece of paper. It can also create curves, surfaces, and solid objects in three-dimensional (3D) space, which is like real life.
CAD is a very important tool used in many areas, such as designing cars, ships, and airplanes. It's also used in industrial and architectural design (like designing buildings), for artificial body parts, and much more. CAD is even used to make computer animation for special effects in movies, commercials, and instruction manuals. This is often called digital content creation. Today, even everyday items like perfume bottles are designed using CAD. Because CAD is so important for businesses, it has helped a lot of research in computational geometry and computer graphics.
Sometimes, designing the shapes of objects using computers is called computer-aided geometric design (CAGD).
Contents
What is CAD Used For?
CAD is one of many tools that engineers and designers use. It helps them in different ways depending on their job and the type of software they are using.
How CAD Fits into Product Design
CAD is a key part of creating products digitally. It works with other tools in the process of managing a product's entire life, from idea to finished item. These other tools can be built into the CAD software or be separate programs. Some of these include:
- Computer-aided engineering (CAE): This helps engineers test designs virtually, like seeing how strong a part is.
- Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM): This uses CAD designs to give instructions to machines that build things.
- Photorealistic rendering: This creates very realistic pictures of the design.
- Document management: This helps organize all the design files and keep track of changes.
CAD for Planning and Visualization
CAD is also used to create accurate computer pictures that show what new buildings or projects will look like in a real place. For example, designers can put a CAD model of a new building onto a photo of an existing area to show how it will fit in. They can also use CAD to check if a new building will block views or create shadows.
Different Kinds of CAD
There are several types of CAD, and each one requires designers to think differently about how they create virtual objects. Most CAD tools use "constraints," which are rules that define how parts of a design relate to each other.
2D CAD: Drawing on a Digital Canvas
Many companies make 2D sketching systems, including some that are free. These systems let you draw flat designs, like blueprints. You can easily change the size and placement of things on the digital drawing sheet, which is much easier than drawing by hand.
3D CAD: Building Virtual Objects
3D CAD lets you create objects that have height, width, and depth, just like real objects.
3D Wireframe Models
3D wireframe models are like drawing a 2D picture but in three dimensions. You have to draw each line yourself. These models don't have "mass" (they aren't solid), so you can't easily add features like holes directly to them. However, you can use wireframe models to create engineering drawings.
3D "Dumb" Solids
3D "dumb" solids are made by combining or cutting basic 3D shapes, like adding a cylinder to a box or cutting a hole out of a sphere. It's like building with digital blocks. You can easily get 2D views from these models. These basic 3D solids usually don't have tools to easily move parts, set limits on their movement, or check if parts crash into each other.
Advanced 3D Solid Modeling
There are several types of advanced 3D solid modeling:
- Parametric modeling: This allows designers to build in "design intent." This means that objects and features are created in a way that makes them easy to change later. If you want a hole to always be in the center of a part, you design it that way. If you change the part's size, the hole will stay in the center. This helps keep the design working correctly even after changes.
- Direct or explicit modeling: This lets you change the shape of an object directly without needing to go back to the original drawing steps. Once you create a shape, you can just grab and pull its faces or edges to change it. It can also keep relationships between parts, like making sure two surfaces always touch.
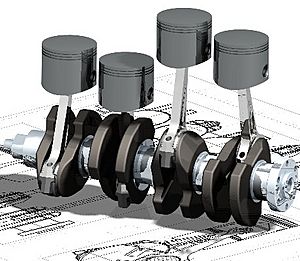
- Assembly modelling: This is where you put together all the individual parts you've designed into a complete product. Assemblies can be complex, like building a whole car from many smaller parts.
Freeform CAD: Smooth and Organic Shapes
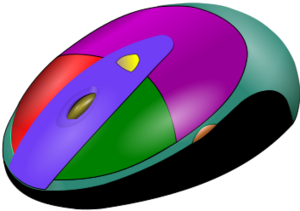
High-end CAD systems can create more natural, artistic, and comfortable shapes. Freeform surface modeling is often used with solid models to design products that fit the human body well or look visually appealing, like the smooth curves of a car or a computer mouse.
How CAD Works (Technology)
In the past, CAD software was written using older computer languages. But now, with modern programming, it's very different. Today's CAD systems are built from many parts, often using the C language. They have a graphical user interface (GUI) that you see on the screen, and they use special math (like NURBS geometry) to create shapes. A "geometric modeling kernel" is like the brain that handles all the shapes and how they connect. There's also a "geometry constraint engine" that makes sure parts stay connected or aligned as you design.
These smart connections have led to something called digital prototyping. Instead of building a physical model of something, you can create a digital one on the computer. This saves a lot of time compared to making physical prototypes. Sometimes, physical prototypes are scanned using special machines to create CAD models.
Today, you can find CAD systems for all major computer types, like Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X. Most CAD software doesn't need super special hardware, but for complex tasks, a good graphics card, fast CPU, and lots of RAM are helpful.
You usually control CAD with a computer mouse, but you can also use a special pen and drawing tablet. To move around and look at your 3D model on the screen, some people use a Spacemouse. Some systems even let you wear special glasses to see the 3D model pop out of the screen!
CAD Software: A Brief History
CAD systems started in the mid-1960s. At first, they just helped people draw things electronically, but soon they could do much more. Companies quickly saw that switching to CAD saved money. The software began to do many tasks automatically, like creating lists of parts needed for a product or checking if parts would crash into each other. CAD also started to help with engineering calculations. This was a huge change in engineering, as the jobs of drafters, designers, and engineers began to combine. CAD showed how much computers were changing industries.
Today's CAD software ranges from simple 2D drawing programs to complex 3D modelers. Modern CAD programs can rotate designs in three dimensions, letting you see an object from any angle, even from the inside! Some CAD software can even do dynamic math modeling.
CAD technology is used to design tools, machines, and all kinds of buildings, from small houses to huge hospitals and factories.
CAD is mainly used for making detailed 3D models or 2D drawings of physical parts. But it's also used throughout the whole engineering process, from the first idea of a product to testing how strong it is and planning how it will be made. It can also design things like jewelry, furniture, and appliances. Many CAD programs now offer advanced ways to make designs look real and even animate them, so engineers can better see their products.
CAD has become a super important technology because it helps lower the costs of developing products and makes the design process much faster. CAD lets designers create and change their work on a computer screen, print it, and save it for later, saving a lot of time.
Popular CAD Software
CAD software helps engineers and architects design, check, and manage their projects using a computer. Most programs let you create solid 3D models and publish them in different file types.
Based on how much they are used, commercial software from companies like Autodesk, Dassault Systems, Siemens PLM Software, and PTC are the most popular in the CAD world. Here are some of the main CAD applications:
Commercial Software (You usually buy these)
- AutoCAD
- CATIA
- Fusion 360
- Inventor
- MicroStation
- NX
- PTC Creo
- Revit
- Rhinoceros 3D
- SketchUp
- Solid Edge
- SOLIDWORKS
- TurboCAD
Open-Source Software (Often free and community-made)
- Blender
- FreeCAD
- LibreCAD
- OpenSCAD
Freeware (Free to use)
- Tinkercad
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Diseño asistido por computadora para niños
In Spanish: Diseño asistido por computadora para niños