Mechatronics facts for kids
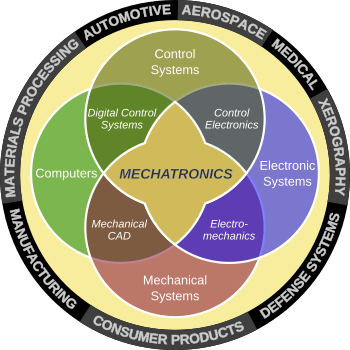
Mechatronics is a cool and exciting field of engineering that mixes different areas of study. Think of it as combining mechanical engineering (how things move), electronic engineering (circuits and electricity), and computer engineering (software and programming). It also includes ideas from robotics, control engineering, and telecommunication.
The main goal of mechatronics is to create smarter, more efficient machines and systems by bringing these different fields together. For example, a robot needs mechanical parts to move, electronic parts to power it, and computer programs to tell it what to do. Mechatronics engineers learn how to design all these parts to work perfectly together.
The word mechatronics comes from two words: mechanics and electronics. It was first used in Japan by an engineer named Tetsuro Mori in 1969. His company, Yaskawa Electric Corporation, even registered it as a trademark. Later, they allowed everyone to use the word, and now it's known all over the world!
Many people think of mechatronics when they hear words like automation (machines doing tasks by themselves) and robotics. It's all about making technology work better and smarter.
Contents
What is Mechatronics?
A mechatronics engineer is like a super-designer who combines ideas from mechanics, electronics, and computers. Their job is to create systems that are simpler, cheaper, and more reliable.
For example, an industrial robot is a perfect example of a mechatronics system. It has mechanical parts that allow it to move its arm, electronic parts that power its motors, and computer programs that tell it exactly how to perform its tasks. All these parts work together to make the robot useful.
Mechatronics also involves control theory, which is about making sure systems do exactly what they're supposed to do. This helps machines operate smoothly and accurately. Many modern machines, like those in factories, use mechatronic parts that work together to make products.
You can find mechatronic systems in many everyday things. Think about your car's anti-lock braking system (ABS), which uses sensors and computers to help you stop safely. Or an autofocus camera, a hard disk drive, or even a CD player – they all use mechatronics to function!
What Do Mechatronics Students Learn?
If you study mechatronics, you'll take courses that cover a wide range of subjects. This helps you understand all the different parts that make up a mechatronic system. Some of the main subjects include:
- Engineering Mathematics: The math needed to solve engineering problems.
- Mechanical engineering: How machines work and how to design them.
- Materials science: Understanding different materials and their properties.
- Electronic engineering: How to design and build electronic circuits.
- Electrical engineering: How electricity works and how to use it.
- Computer engineering: How computers work and how to program them.
- Systems engineering: How to design and manage complex systems.
- Control engineering: How to make systems behave in a desired way.
- Robotics: How to design, build, and operate robots.
Where is Mechatronics Used?
Mechatronics is used in many different industries and products. Here are some examples:
- Automation and robotics: Designing robots for factories or homes.
- Machine vision: Systems that allow machines to "see" and understand images.
- Automotive engineering: Creating smart features in cars, like anti-lock braking systems.
- Building automation: Smart homes that control lighting, heating, and security.
- Computer-controlled machines: Like CNC milling machines that precisely cut materials.
- Medical mechatronics: Designing medical imaging systems or robotic surgery tools.
- Consumer products: Many everyday items like washing machines, cameras, and phones.
- Biomechatronics: Combining mechanical parts with living things, like prosthetic limbs.
How Mechatronics Systems are Built
Building mechatronic systems involves understanding how different physical parts work together. Engineers use special tools and methods to design and test these systems. They think about how different materials behave and how to make the system strong and efficient.
Sometimes, the biggest challenge is not just controlling a system, but making the parts that actually move it. These moving parts are called actuators. Mechatronics engineers choose the best technologies to create movement, whether it's with electric motors, hydraulic systems, or other methods.
Different Types of Mechatronics
There are some special areas within mechatronics:
- Biomechatronics: This field combines mechanical parts with human beings. For example, it's used to create advanced exoskeletons or robotic prosthetics that help people move. It's like bringing science fiction to life!
- Motion Control for Advanced Mechatronics: This is about making sure machines move very precisely and reliably. It's key for robots that need to perform delicate tasks.
- Avionics: This is a type of mechatronics used in aviation. It combines electronic engineering and telecommunication with aerospace engineering to create the complex systems found in airplanes and spacecraft.
Mechatronics and the Internet of Things
The Internet of things (IoT) is all about connecting everyday physical devices to the internet. Imagine your smart fridge ordering groceries or your smart lights turning on when you arrive home. These devices have electronics, software, sensors, and actuators built into them, allowing them to collect and share data.
Mechatronics and the IoT go hand-in-hand. Many of the "smart" parts in IoT devices are actually mechatronic systems. As the IoT grows, mechatronics engineers are learning new ways to design these smart devices, thinking about things like data security and how humans will interact with these intelligent machines.
See also
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |




 In Spanish:
In Spanish: