Hildegard of Bingen facts for kids
Quick facts for kids SaintHildegard of Bingen OSB |
|
|---|---|

|
|
| Virgin, Abbess, Doctor of the Church | |
| Born | Hildegard von Bingen c. 1098 Bermersheim vor der Höhe, County Palatine of the Rhine, Holy Roman Empire |
| Died | 17 September 1179 (aged 81) Bingen am Rhein, County Palatine of the Rhine, Holy Roman Empire |
| Venerated in | |
| Beatified | 26 August 1326 (Formal confirmation of Cultus) by Pope John XXII |
| Canonized | 10 May 2012 (equivalent canonization), Vatican City by Pope Benedict XVI |
| Major shrine | Eibingen Abbey, Germany |
| Feast | 17 September |
Hildegard of Bingen (born around 1098, died September 17, 1179) was an amazing German woman. She was also known as Saint Hildegard or the Sibyl of the Rhine. She was a Benedictine abbess, which is like the leader of a group of nuns.
Hildegard was a true "polymath," meaning she was skilled in many different areas. She was a writer, composer, philosopher, and a mystic. She also wrote about medicine and practiced it. She lived during the High Middle Ages, a time long ago.
She is famous for her sacred music, especially songs with a single melody (called monophony). She wrote both the music and the words for her songs. Many of her chants still exist today. She also created an early play called Ordo Virtutum, which teaches about good and evil. Hildegard even invented her own language, called Lingua Ignota.
In 1136, the nuns in her convent chose her as their leader, or magistra. She later started two new monasteries: Rupertsberg in 1150 and Eibingen in 1165.
The Roman Catholic Church has considered her a saint for hundreds of years. In 2012, Pope Benedict XVI officially recognized her as a saint for the whole Catholic Church. He also named her a Doctor of the Church. This title is given to saints who have made important contributions to theology and faith.
Contents
Who Was Hildegard of Bingen?
Hildegard was born around 1098. Her parents were Mechtild of Merxheim-Nahet and Hildebert of Bermersheim. They were a noble family, but not very rich. Hildegard was often sick from a young age. People believe she was the youngest of ten children.
Early Visions
From a very young age, Hildegard said she experienced special visions. She used the Latin word 'visio' to describe these experiences. She knew it was a special gift that was hard to explain to others. Hildegard said she saw everything in the light of God, using all her senses.
Life in the Monastery
Hildegard's parents sent her to live at a Benedictine monastery called Disibodenberg. This was a common practice for children at the time. She was placed under the care of Jutta von Sponheim, another visionary woman. Jutta was about six years older than Hildegard.
Learning and Growing
Hildegard and Jutta lived together at the monastery. They became the center of a growing group of women who joined the monks' monastery. Jutta taught Hildegard to read and write. Hildegard also learned how to play the ten-stringed psaltery, an ancient musical instrument. A monk named Volmar, who visited often, might have taught her simple music notes. This was likely the start of her amazing musical journey.
Becoming a Leader
When Jutta died in 1136, Hildegard was chosen by all the nuns to be their new leader, the magistra. The abbot (male leader) of Disibodenberg wanted Hildegard and her nuns to stay under his control. But Hildegard wanted more independence for her community.
She asked to move her nuns to a new, simpler monastery at Rupertsberg. The abbot said no at first. Hildegard then became very ill, unable to move. She believed this was a sign from God that she needed to follow His command to move. When the abbot saw she couldn't move, he finally agreed.
In 1150, Hildegard and about 20 nuns moved to the St. Rupertsberg monastery. Volmar, her old tutor, became her secretary and helped her. Later, in 1165, Hildegard started a second monastery for her nuns in Eibingen.
Hildegard's Visions and Writings
Hildegard said she first saw "The Shade of the Living Light" when she was three years old. By age five, she understood these were visions. She was nervous to share them at first, only telling Jutta, who then told Volmar.
God's Instruction
In 1141, when she was 42, Hildegard had a vision she believed was a direct instruction from God. He told her to "write down that which you see and hear." She was still hesitant, and because of her doubt, she became physically sick.
In her first major book, Scivias (which means "Know the Ways"), Hildegard wrote about how hard it was for her to start writing:
- She doubted herself and worried about what people would think.
- She felt humble and didn't want to seem proud.
- She became very sick, which she believed was a sign from God.
- Finally, she felt forced by her illness and encouraged by others to write.
- She wrote that she didn't invent these things herself. She heard and received them from God in a special way.
Papal Approval
Between 1147 and 1148, Pope Eugenius III heard about Hildegard's writings. He gave her official approval to write down her visions as messages from the Holy Spirit. This made her instantly respected and believed.
When Hildegard died on September 17, 1179, her sisters said they saw two streams of light in the sky. These lights crossed over the room where she was dying.
Hildegard's Importance
Hildegard likely learned basic Latin and Christian beliefs. But she probably didn't get the full education that many learned men received in the Middle Ages. This education included grammar, logic, public speaking, math, geometry, astronomy, and music.
A Powerful Voice
Even without this formal education, Hildegard became a very important figure. She used her writing, letters, and even public speaking to share her ideas. This was unusual for a woman at that time. She believed her monastery should only have nuns from noble families. She thought this would prevent social divisions within the community.
Hildegard also made a strong statement about women: "woman may be made from man, but no man can be made without a woman."
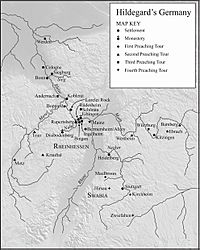
Hildegard was a powerful speaker. She traveled on four preaching tours across Germany. She spoke to both church leaders and regular people. She often criticized corruption in the church and called for changes.
Many abbots and abbesses (leaders of monasteries) asked her for prayers and advice. She had loyal followers, like Guibert of Gembloux, who became her secretary. She also exchanged letters with other visionary women, like Elisabeth of Schönau.
Hildegard wrote to important people like popes, emperors, and famous church leaders. Her letters are a big part of her written works.
Honoring Hildegard
Hildegard was one of the first people for whom the official process to become a saint was started. However, it took a very long time. Even so, her name was added to the list of saints in the Catholic Church in the late 1500s. Her feast day is September 17. Many popes have called Hildegard a saint.
Doctor of the Church
On May 10, 2012, Pope Benedict XVI officially recognized Saint Hildegard for the entire Catholic Church. Then, on October 7, 2012, he named her a Doctor of the Church. He said Hildegard was "always important" and "an authentic teacher of theology and a deep scholar of natural science and music."
Hildegard of Bingen is also honored in the calendars of various Anglican churches, including the Church of England, on September 17.
Hildegard's Influence Today
In recent years, many people have become interested in Hildegard.
Feminist Scholars
Some scholars who study women's history find Hildegard especially interesting. She often called herself an "unlearned woman" and said she wasn't capable of explaining the Bible. However, this actually helped her. It made her claims that her writings and music came from God's visions more believable. This gave Hildegard the authority to speak out when few women were allowed to have a public voice. She used her voice to criticize corruption in the church.
New Age Movement
Hildegard is also admired in the modern New Age movement. This is because of her focus on natural healing and her mystic experiences. Her medical writings have inspired "Hildegard-Medicine." She also inspired the Hildegard Network, a healing center that connects spirituality, arts, and wellness. Her reputation as a healer was even used by early feminists to argue for women's right to attend medical schools.
Music and Art
Recordings of Hildegard's music have become very popular since 1979. Many modern musical works are inspired by her or use her texts.
- Hildegard von Bingen, a play with her music and texts (1998).
- O Vis Aeternitatis and O Euchari by Azam Ali (2020).
- Alma Redemptoris Mater by Cecilia McDowall.
- Rainbow Body, for orchestra by Christopher Theofanidis (2000).
- Lux Vivens (Living Light): The Music of Hildegard Von Bingen by David Lynch and Jocelyn Montgomery (1998).
- Für Hildegard von Bingen, a song by Devendra Banhart (2013).
- The Trillion Souls by Gordon Hamilton quotes Hildegard's O Ignee Spiritus.
- O splendidissima gemma by Ludger Stühlmeyer (2012).
- Hildegard von Bingen, a musical by Peter Janssens (1997).
- Vision: The Music Of Hildegard Of Bingen by Richard Souther, Emily Van Evera, Sister Germaine Fritz OSB (1994).
- Aus den Visionen der Hildegard von Bingen by Sofia Gubaidulina (1994).
- Monatsbilder (nach Hildegard von Bingen), twelve songs by Tilo Medek (1997).
- De visione secunda by Wolfgang Sauseng (2011).
- "Electric Fields" by David Chalmin and Bryce Dessner (2022).
Hildegard has also been honored in other ways:
- The famous artwork The Dinner Party includes a place setting for Hildegard.
- A small planet, 898 Hildegard, is named after her.
- The plant genus Hildegardia is named for her contributions to herbal medicine.
- The musical In the Green tells her story.
- The neurologist Oliver Sacks wrote about Hildegard in his book, suggesting her visions might have been related to migraines.
Films About Hildegard
Hildegard has been shown in several films:
- Patricia Routledge played her in a BBC documentary (1994).
- Ángela Molina played her in the film Barbarossa (2009).
- Barbara Sukowa played her in the film Vision (2009).
- A documentary film, The Unruly Mystic: Saint Hildegard, was released in 2014.
Hildegard even appears in a book for younger readers: The Baby-Sitters Club #101: Claudia Kishi, Middle School Drop-Out. In this book, a character dresses as Hildegard for Halloween.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Hildegarda de Bingen para niños
In Spanish: Hildegarda de Bingen para niños