Idalium facts for kids
|
Ιδάλιον
|
|
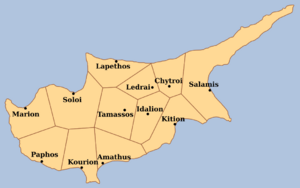
Map showing the ancient city Kingdoms of Cyprus; Idalion is inland at center right
|
|
| Location | Cyprus |
|---|---|
| Region | Nicosia District |
| Coordinates | 35°00′57″N 33°25′23″E / 35.0158°N 33.4230°E |
| Site notes | |
| Archaeologists | Luigi Palma di Cesnola, R. Hamilton Lang, Max Ohnefalsch-Richter, Erik Sjöqvist |
| Management | Cyprus Department of Antiquities |
Idalium, also known as Idalion, was an important ancient city on the island of Cyprus. Today, its ruins are found near the modern town of Dali. The city became very wealthy because of the trade in copper, a valuable metal. It was founded thousands of years ago, in the 3rd millennium BC.
Idalium was so powerful that it was listed as one of the Ten city-kingdoms of Cyprus. These were the most important kingdoms on the island. We know about Idalium from ancient records, like a clay tablet from the Assyrian king Esarhaddon written over 2,600 years ago.
Today, you can visit the archaeological site to see the uncovered buildings. There is also a new museum at the entrance to the site where you can see artifacts found there.
Contents
The Story of Idalium


A City Built on Copper
The first people to live in the area were native to Cyprus. The city of Idalium grew into a major center for trading copper. Its location was perfect for business. It was close to the copper mines in the Troodos Mountains. It was also near the ports on the coast, making it easy to ship goods.
The city was built on both sides of the Gialias River. It had two high points called acropolises, which were like natural hills that were easy to defend. The main palace and a temple to the goddess Athena were on the western acropolis. Other important temples, including ones for the gods Apollo and Aphrodite, were on the eastern acropolis. The rest of the city, where people lived, was on the lower ground between them.
Kings, Gods, and a Famous Tablet

Idalium was a kingdom ruled by its own kings. We know the first kings were Greek because of the language written on their coins. The city was famous for its worship of the "Wanassa," or Queen of Heaven. She was the main goddess of Cyprus, later known as Aphrodite.
One of the most amazing discoveries from Idalium is the Idalion Tablet. This is a large bronze plate with writing on it. It tells us about the city's last king, Stakyspros. The tablet shows that he did not rule alone. He made decisions with a council of citizens.
The tablet also tells a story about a war. When the cities of Kition and Persia attacked Idalium, the king and the city promised to pay a family of doctors for taking care of the wounded soldiers for free. This shows that Idalium had a system to care for its people.
The Fall of the Kingdom

Around 450 BC, the kingdom of Idalium was conquered by its powerful neighbor, Kition. After the conquest, the palace was no longer home to a king. Instead, it became an administrative center for the new rulers.
The city continued to be an important religious center for centuries. The worship of Aphrodite and the Helleno-Phoenician god Resheph-Apollo was very popular there.
Uncovering Idalium's Secrets
For many years, the treasures of Idalium lay buried underground. Over time, archaeologists and explorers began to uncover its secrets.
Early Treasure Hunters
In the 1860s and 1870s, an American diplomat named Luigi Palma di Cesnola dug at Idalium. He was more of a treasure hunter than a modern archaeologist. He found thousands of objects, including helmets, swords, and pottery.
Many of these amazing artifacts were shipped to New York. They helped to start the famous Metropolitan Museum of Art, where you can still see them today. Another early explorer, R. Hamilton Lang from Britain, found an outdoor temple with over 140 limestone statues. These are now in the British Museum in London.
Cracking an Ancient Code
One of the most important discoveries related to Idalium helped us understand an ancient form of writing. This writing is called the Cypro-Syllabic script. For a long time, no one knew how to read it. The key was a stone found at Idalium with the same message written in two languages.
One language was Phoenician, which experts could already read. The other was the mysterious Cypriot script. By comparing the two texts, scholars could match the names and words. This allowed them to "crack the code" of the ancient script. Thanks to this discovery, we can now read other texts like the Idalion Tablet and learn more about ancient Cyprus.
Modern Archaeology

In the 20th century, archaeologists began to study Idalium more scientifically. A team from the Swedish Cyprus Expedition carefully excavated the western acropolis in 1928. They uncovered a fortified sanctuary and the royal palace. They found many objects that people had left as gifts for the gods, like weapons, tools, and jewelry.
Since the 1970s, teams from American universities have continued the work. Using modern techniques, they have learned a lot about how the city was built and how people lived there over thousands of years.
See also