List of cities of the ancient Near East facts for kids
| This article contains special characters. Without the correct software, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols. |
The earliest cities in history were in the ancient Near East, a region that covers much of what we call the modern Middle East. Imagine a time over 5,000 years ago when people started building big towns! This amazing history began around 4000 BC and saw many powerful empires rise and fall.
Some of these ancient cities were huge for their time, home to tens of thousands of people. For example, Memphis in ancient Egypt was a giant city with about 30,000 residents. Later, Ur in Mesopotamia grew to have around 65,000 people, and Babylon was home to 50,000 to 60,000! These numbers show how important these cities were as centers of life, trade, and power.
Ancient scribes, who were like writers and record-keepers, used special signs to mark cities. In languages like Akkadian and Hittite, a sign that looked like URU (𒌷) was used to show that a word was a city name. Sometimes, it was even combined with the sign for "land" (KUR𒆳) to mean the kingdom controlled by that city, for example, when writing about "the king of the country of (the city of) Ḫattuša" (गोलिक𒆳𒌷𒄩𒀜𒌅𒊭 LUGAL KUR URUHa-ad-tu-sha). Another sign, KI (𒆠), was also used after place names in Sumerian and Akkadian. These signs helped people read and understand ancient texts.
Contents
- Mesopotamia: Where Cities Began
- Ancient Cities of Iran
- Anatolia: Crossroads of Civilizations
- Egypt: Cities Along the Nile
- The Levant: Ancient Cities of the Eastern Mediterranean
- Arabian Peninsula: Desert Cities and Trade Routes
- Cyprus: Island Cities
- Nubia: Kingdoms Along the Nile
- Horn of Africa: Ancient Trade Hubs
- See also
Mesopotamia: Where Cities Began
Mesopotamia, often called the "Cradle of Civilization," was a very important region for the development of early cities. It's located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, in what is now mostly Iraq. The rich soil from these rivers allowed people to grow lots of food. This meant more people could live together in one place. This led to the growth of some of the world's first large cities.
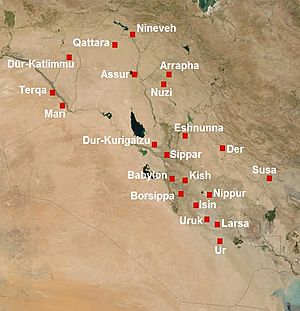
Cities of Lower Mesopotamia
Lower Mesopotamia, in the southern part of the region, was home to some of the very first cities. These cities often grew around temples. They became centers for trade, religion, and government. Famous cities here include Ur, known for its impressive Ziggurat (a type of large temple tower), and Babylon, which later became a powerful empire. Other important cities were Uruk, Nippur, and Eridu. These cities were like small countries, each with its own ruler and laws.
Cities of Upper Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia, located further north, also had many significant cities. This area was important for trade routes. It was often a crossroads for different cultures. Cities like Nineveh and Assur became very powerful, especially during the time of the Assyrian Empire. Other notable cities included Mari, known for its royal palace, and Carchemish, an important trading hub. These northern cities played a key role in connecting different parts of the ancient world.
Ancient Cities of Iran
The land of Iran, once known as Persia, was also home to many ancient and important cities. These cities were often centers of powerful empires. They were known for their grand architecture and rich cultures.
One of the most famous cities was Persepolis, a magnificent capital built by the Persian kings. It had huge palaces and impressive gates. Another significant city was Susa, which was one of the oldest cities in the world. It served as a capital for different empires over thousands of years. Other important sites include Chogha Zanbil, famous for its well-preserved ziggurat, and Pasargadae, the first capital of the Achaemenid Persian Empire. These cities show the incredible history and artistry of ancient Iran.
Anatolia: Crossroads of Civilizations
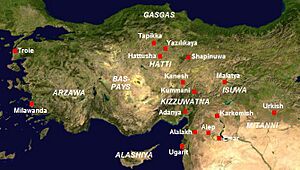
Anatolia, which is modern-day Turkey, was another vital region for ancient cities. It was a bridge between Asia and Europe. This made it a place where many different cultures met and traded.
One of the most famous cities here was Hattusa, the capital of the mighty Hittite Empire. The Hittites were a major power in the Bronze Age. Their city had strong walls and impressive temples. Another well-known city is Troy, famous from ancient Greek stories like the Iliad. While the stories are myths, archaeological finds show that Troy was a real and important city. Çatalhöyük is also incredibly famous as one of the earliest large settlements. It shows how people lived together thousands of years ago. These cities highlight Anatolia's long and rich history.
Egypt: Cities Along the Nile
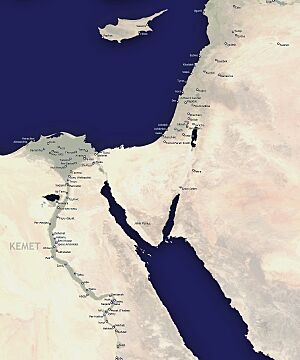
Ancient Egypt, centered along the fertile Nile River, developed many grand cities. The Nile was like a highway. It connected different parts of the kingdom and allowed cities to thrive.
Memphis was one of the earliest and most important capitals of ancient Egypt. It was located near the delta of the Nile. It was a center of power and religion for thousands of years. Later, Thebes became a major capital. It was famous for its huge temples like Karnak and Luxor, and the nearby Valley of the Kings where pharaohs were buried. Other significant cities included Amarna, a unique city built by Pharaoh Akhenaten, and Abydos, an ancient holy city. These cities were not just places to live; they were monuments to the power and beliefs of the pharaohs and their people.
The Levant: Ancient Cities of the Eastern Mediterranean
The Levant, a region along the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea (including modern-day Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, and Jordan), was a very busy place in ancient times. It was a crossroads for trade and cultures between Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Anatolia.
Many important cities grew here, often becoming powerful city-states. Byblos was famous for its trade in cedar wood and papyrus, which was used for writing. Ugarit was another major port city, known for its advanced writing system. Damascus is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, with a history stretching back thousands of years. Other key cities included Jericho, one of the very first towns ever, and Jerusalem, a city with deep historical and religious significance. These cities were vital links in the ancient world's network of trade and communication.
Arabian Peninsula: Desert Cities and Trade Routes
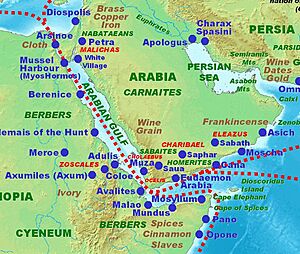
The Arabian Peninsula, with its vast deserts, also had important ancient cities. These were especially found along trade routes and near fertile oases. These cities were crucial stops for caravans carrying valuable goods like spices and incense.
One of the most famous ancient cities was Ma'rib in modern-day Yemen. It was known for its impressive dam that supported a large agricultural area. Dedan (modern Al-'Ula) was another significant city, a major oasis and trade center in the north. The city of Petra (though often associated with Jordan, it's geographically part of the broader Arabian cultural sphere) is famous for its buildings carved directly into rock cliffs. These cities show how ancient people adapted to their environment. They created thriving communities even in challenging landscapes.
Cyprus: Island Cities
The island of Cyprus, located in the eastern Mediterranean, was an important hub for trade and copper production in the Bronze Age. Its cities played a key role in connecting different parts of the ancient world.
Important ancient cities on Cyprus included Enkomi, a major Bronze Age center known for its copper workshops, and Kition, a significant port city. These cities show Cyprus's long history as a bridge between cultures.
Nubia: Kingdoms Along the Nile
South of Egypt, along the Nile River, lay the ancient region of Nubia (modern-day Sudan). This area was home to powerful kingdoms with their own unique cities.
Key Nubian cities included Kerma, one of the earliest urban centers in Africa outside of Egypt. It was known for its distinctive pottery and large circular buildings. Later, Napata and Meroë became capitals of the Kingdom of Kush. They were famous for their pyramids and iron production. These cities were rich in gold and other resources. They had strong connections with ancient Egypt.
Horn of Africa: Ancient Trade Hubs
The Horn of Africa, across the Red Sea from the Arabian Peninsula, also had ancient cities that were important for trade.
Aksum (or Axum) in modern-day Ethiopia became the capital of a powerful kingdom. It was known for its tall stone obelisks and its role in international trade. It connected Africa with the Middle East and India. Adulis was a major port city on the Red Sea coast, vital for trade. These cities show the ancient connections and rich history of this part of Africa.
See also
- City-state
- Sumerian King List
- Historical urban community sizes
- Short chronology timeline
- List of oldest continuously inhabited cities
- Ancient towns in Saudi Arabia
- List of Ancient Settlements in the UAE
- List of largest metropolitan areas of the Middle East