Indian hog deer facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Indian hog deer |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Indian hog deer in Phu Khieo Wildlife Sanctuary, Thailand | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Cervidae |
| Subfamily: | Cervinae |
| Genus: | Hyelaphus |
| Species: |
H. porcinus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hyelaphus porcinus (Zimmermann, 1780)
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
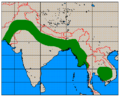
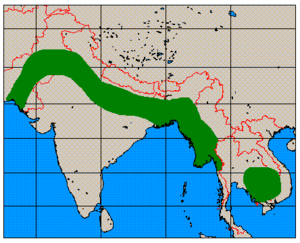
The Indian hog deer (Hyelaphus porcinus) is a small deer that lives in parts of Asia. You can find them in the Indo-Gangetic Plain region. This includes countries like Pakistan, northern India, Nepal, and Bangladesh. They also live in Southeast Asia, specifically western Thailand and southwestern Yunnan Province in China. Some populations have even been introduced to Australia.
Their name comes from how they run. They move through forests like a hog, with their heads held low. This helps them duck under branches and obstacles. Most other deer would jump over these things.
Contents
What Does an Indian Hog Deer Look Like?
A grown male hog deer, called a stag, stands about 70 centimeters (27 inches) tall at the shoulder. They weigh around 50 kilograms (110 pounds). Females, called hinds, are smaller. They stand about 61 centimeters (24 inches) tall and weigh around 30 kilograms (66 pounds).
These deer have a strong, solid body. They have a long body but fairly short legs. Their back slopes upwards from their shoulders to a high rump. Their ears are rounded. Older deer often have lighter colored fur on their face and neck.
Their Coat and Markings
The Indian hog deer's fur coat is quite thick. In winter, it's usually a dark-brown color all over. However, the fur on their belly and legs is lighter. In late spring, their coat changes to a rich reddish-brown for summer. The exact shade can be different for each deer.
Many hog deer have a dark stripe running down their back. This stripe goes from their head, along their neck, and down their spine. In summer, you can often see a line of light-colored spots. These spots are usually on both sides of the dark stripe, from their shoulders to their rump. Their tail is short and brown, with a white tip. The underside of the tail is also white. When a deer is alarmed, it can fan out these white hairs. This creates a clear warning signal.
Special Glands
Indian hog deer have special glands on their face. These are called preorbital glands and are just below their eyes. They also have metatarsal glands high on the side of their back legs. Another type, pedal glands, are found between their toes on their hind hooves. These glands help them communicate, often by leaving scents.
Antlers
The antlers of a grown male hog deer usually have three points. There's a brow tine (a point near the base) and a solid main beam. The main beam ends in two top points, an inner and an outer one. Sometimes, antlers can have even more points.
A unique feature of hog deer antlers is the sharp angle between the brow tine and the main beam. Also, the inner top points tend to be short. They angle back from the main beam and sometimes cross towards the opposite antler.
How Indian Hog Deer Behave
Indian hog deer usually only gather in groups when there's plenty of food or space. Even then, they don't form a tight "unit." If they get scared, they will run away in different directions, not as a herd. When a hog deer is alarmed, it might make a whistling sound or a warning bark.
Their home ranges can vary a lot in size. On average, a hog deer's home area is about 0.70 square kilometers (0.27 square miles). Male deer can be aggressive, especially if there are few deer in an area. They might become territorial, meaning they mark the edges of their space. They do this using secretions from their glands.
Mating Season
During the mating season, called the rut, males gather in open grassy areas. They might paw at the ground when they have conflicts with other males. Unlike some other deer, hog deer males don't create harems (groups of females). Instead, a male will court and protect just one female at a time. Hog deer also don't have a special call they make during the rut.
The number of hog deer in an area can change a lot. In river valleys, there might be as few as 0.1 deer per square kilometer. But in grassy flood plains, there can be over 19 deer per square kilometer.
Predators of the Indian Hog Deer
The main animals that hunt Indian hog deer are large cats. These include the powerful tiger, the agile leopard, and the secretive clouded leopard.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ciervo porcino para niños
In Spanish: Ciervo porcino para niños