Inflation (cosmology) facts for kids
Have you ever wondered how our amazing universe got to be the way it is today? The idea of cosmic inflation is a big theory in physical cosmology. It helps explain many things about the universe we see, like why there are huge groups of stars called galaxies. A scientist named Alan Guth first suggested this idea in the 1970s.
Contents
What is Cosmic Inflation?
The Big Bang theory tells us that the universe started very small and has been growing ever since. The usual Big Bang idea says the universe expanded at a steady speed.
But the inflation theory adds a twist! It says the universe didn't always expand at the same speed. Instead, it had super-fast growth spurts. During these short bursts, the universe grew incredibly fast. It could have doubled in size many times in less than a second!
After these quick growth spurts, the expansion slowed down. Then, another fast inflation period might have happened, making the universe much bigger again.
Why Do We Need Inflation Theory?
Inflation theory helps solve some big puzzles about our universe.
How Galaxies Formed
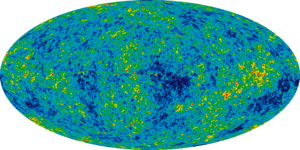
One puzzle is how huge structures like galaxies came to be. Inflation theory suggests that during the universe's slow expansion, there were tiny, tiny wobbles or "quantum fluctuations."
When the universe had a super-fast inflation period, these tiny wobbles got stretched out. They became much larger, creating areas with slightly different densities. Over time, matter gathered in these denser spots, forming stars, planets, and eventually, entire galaxies.
Why the Universe is So Even
Another puzzle is why the temperature across the universe is so smooth and even. If the universe expanded slowly, parts that are far apart now shouldn't have had time to "even out" their temperatures.
Inflation theory explains this by saying that parts of the universe that were once very close together got separated super quickly during an inflation period. This rapid separation happened before they could lose their temperature balance. So, even though they are far apart now, they started out in a balanced state.
Missing Magnetic Monopoles
Scientists also wonder why we don't see "magnetic monopoles." These are like magnets with only a north pole or only a south pole. They are predicted by some theories but haven't been found.
Inflation theory suggests that if these monopoles existed, the rapid expansion during inflation would have spread them out so much. They would be incredibly rare, making them almost impossible to find today.
What Does Inflation Theory Predict?
Inflation theory also makes some interesting predictions about what else might be out there.
Inflatons
The theory suggests there are special particles called inflatons. These particles would have caused the universe's super-fast inflation periods. They come from a special energy field.
However, inflatons would decay very quickly. This quick decay would make sure the inflation periods didn't last too long. Scientists once thought the Higgs boson might be an inflaton, but that idea has been disproven.
Other Universes
Inflation theory also makes us wonder if there are other universes besides our own. If inflation could create our universe, couldn't it also create many others? This idea, called the Multiverse, is still being explored by scientists. We don't have proof for it yet, but it's a fascinating thought!
| Physical cosmology | ||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||
| Universe · Big Bang Age of the universe Timeline of the Big Bang Ultimate fate of the universe
|
||||||||||||||
See also
 In Spanish: Inflación cósmica para niños
In Spanish: Inflación cósmica para niños
 | Bessie Coleman |
 | Spann Watson |
 | Jill E. Brown |
 | Sherman W. White |

