Observable universe facts for kids

The observable universe is a part of space that we can, in theory, see from Earth. Think of it like this: it's all the light and other signals that have had enough time to travel to us since the universe began expanding. Even though the whole universe might be much bigger, the observable universe is like a giant ball with Earth right in the middle. Every spot in the universe has its own observable universe, and these might or might not overlap with ours.
The word "observable" means that it's possible for light or other signals from an object to reach us. It doesn't mean our current technology can actually see everything. For example, we can only see light from a time when particles could first send out photons (tiny packets of light). Before that, the universe was like a thick fog of plasma, which light couldn't get through.
Scientists sometimes talk about two slightly different ideas:
- The visible universe: This includes signals that started coming to us after the universe cooled down enough for light to travel freely.
- The observable universe: This includes all signals since the very beginning of the universe's expansion.
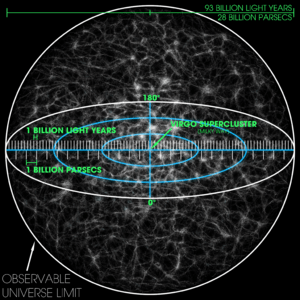
The visible universe has a radius of about 45.7 billion light-years. The observable universe is a bit larger, with a radius of about 46.6 billion light-years. That's only about 2% bigger!
How Big is the Observable Universe?
The universe is about 13.8 billion years old. Because the universe is always expanding, objects that were once close to us are now much farther away. Imagine a balloon with dots on it; as you inflate the balloon, the dots move farther apart.
The total diameter of the observable universe is thought to be about 93 billion light-years. This means the very edge of what we can see is roughly 46 to 47 billion light-years away from us. It's an incredibly vast space!
Images for kids
-
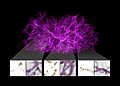
Galaxy clusters, like RXC J0142.9+4438, are like the main hubs in the huge network of matter that fills the entire universe.
-
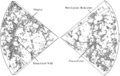
This is a computer picture of a space area more than 50 million light-years wide. It shows how light sources like galaxies and quasars might be spread out in the universe.
-
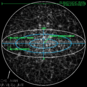
This "panoramic view" of the near-infrared sky shows where galaxies are located beyond our Milky Way. It uses data from over 1.5 million galaxies and nearly 0.5 billion stars from our own galaxy. The galaxies are colored by their redshift, which tells us how far away they are. Blue means they are closer, green means they are at a medium distance, and red means they are the farthest ones we can see with this survey.
See also
 In Spanish: Universo observable para niños
In Spanish: Universo observable para niños