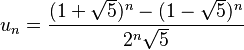Jacques Philippe Marie Binet facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Jacques Philippe Marie Binet
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Born | 2 February 1786 Rennes, France
|
| Died | 12 May 1856 (aged 70) Paris, France
|
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Mathematics, physics, and astronomy |
Jacques Philippe Marie Binet (born February 2, 1786 – died May 12, 1856) was a smart French scientist. He was a mathematician, a physicist, and an astronomer. Binet was born in Rennes, France, and later passed away in Paris.
He made many important discoveries in number theory. He also helped create the basic ideas for matrix algebra. This is a type of math that uses grids of numbers. His work later helped other mathematicians like Arthur Cayley.
Binet is known for "Binet's theorem." This theorem helps explain how objects move and spin. He was also the first to describe how to multiply matrices in 1812. You might also hear about "Binet's formula." This formula helps find numbers in the Fibonacci sequence. Even though another scientist, Abraham de Moivre, knew about it earlier, it is named after Binet.
Contents
Binet's Amazing Career
Jacques Binet was a very dedicated student and teacher.
Early Education and Teaching
He finished his studies at a famous school called l'École Polytechnique in 1806. Just one year later, in 1807, he returned to the same school, but this time as a teacher! He kept getting promoted. By 1816, he became an inspector of studies at the school. This meant he helped oversee how students learned.
Changes and Recognition
Binet held his important job until November 13, 1830. At that time, a new king, King Louis-Philippe, came to power in France. Binet was removed from his position. This was likely because he had strongly supported the previous king, Charles X.
Even after this, Binet continued his important work. In 1823, he took over as the professor of astronomy at the Collège de France. He replaced another famous scientist named Delambre. Binet was also honored for his achievements. In 1821, he became a Chevalier in the Légion d'Honneur. This is a very high award in France. In 1843, he was chosen to be a member of the Académie des Sciences. This is a group of France's top scientists.
Binet's Fibonacci Formula Explained
Binet's formula is a cool way to find any number in the Fibonacci sequence.
What is the Fibonacci Sequence?
The Fibonacci sequence is a special list of numbers. It starts with 0 and 1. Then, each new number is found by adding the two numbers before it.
- The first number is 0.
- The second number is 1.
- To find the next number, you add the two before it. So, 0 + 1 = 1.
- Then, 1 + 1 = 2.
- Next, 1 + 2 = 3.
- And so on! The sequence looks like this: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, and so on.
How Binet's Formula Works
Normally, to find a Fibonacci number far down the list, you would have to calculate all the numbers before it. But Binet's formula gives you a shortcut! It's a "closed-form expression." This means you can just plug in the number you want (like the 10th or 20th Fibonacci number) and get the answer directly.
Here is what Binet's formula looks like:
In this formula, u represents the Fibonacci number, and n is its position in the sequence. For example, if you want the 5th Fibonacci number, you would put 5 in place of n.
See also
 In Spanish: Jacques Philippe Marie Binet para niños
In Spanish: Jacques Philippe Marie Binet para niños
- Binet–Cauchy identity
- Binet equation
- Cauchy–Binet formula
- Matrix multiplication