Late Basketmaker II Era facts for kids
Imagine a time long ago, between AD 50 and 500. This was the Late Basketmaker II Era. During this period, a group of people known as the Ancient Pueblo People lived in the American Southwest. They started building homes called pit-houses, which were partly dug into the ground.
These early people were skilled at growing their own food. They raised maize (corn) and squash. They were also amazing at making baskets and weaving. Besides farming, they hunted animals and collected wild foods like pinyon nuts.
The Late Basketmaker II Era is part of a larger time called the "Basketmaker period." It came after the Early Basketmaker II Era and before the Basketmaker III Era.
Contents
Homes and Communities
The main homes during this time were round or circular pit-houses. These houses were built on open land. They were partly underground, which helped keep them cool in summer and warm in winter.
The entrance to these homes usually faced east or south. People often used logs and rocks to build the foundation of their houses. The walls could be made from stacked logs, or from a mix of poles and brush called jacal. In the center of each home, there was a fire pit for cooking and warmth.
Some of these early people also built their homes inside natural rock shelters. This was especially common at the beginning of the Late Basketmaker II period, as rock shelters offered natural protection.
Farming and Food
The Basketmaker II people were the first in the northern American Southwest to grow maize and squash. Because they farmed, they needed to live close to water sources and good soil.
Scientists have studied the bones of Basketmaker people. They found that these people ate a lot of maize. This shows how important farming was to their diet.
They used special tools to prepare their food. Manos and metates were stones used to grind maize and other foods into flour. They stored their food underground in special storage pits called cists. These pits were often lined with stone slabs to keep the food safe and dry.
Tools and Goods
Archaeologists have found many interesting items from the Late Basketmaker II Era. These items show how clever and skilled these ancient people were.
Some of the things they found include:
- High-quality, tightly woven baskets. These were very important for carrying and storing food.
- Woven bags, sandals, and blankets made from yucca plants.
- Warm robes and blankets made from feathers and animal fur.
- Stone tools like projectile points (for spears), scrapers, and knives.
- The atlatl and throwing spears. These were their main tools for hunting animals.
- Tools made from bone, such as stitching awls (for sewing), whistles, and pieces for games.
- Strong cords made from yucca and cedar bark.
- Oval-shaped cradles, likely used for babies.
- Stone pipes.
Around AD 200, people started experimenting with making a simple, rough type of brown pottery. This was a new skill that would become more common later on.
Ancient Cultures
During the Late Basketmaker II Era, different cultural groups lived in various parts of the American Southwest and beyond. These groups shared some similar ways of life, but also had their own unique traditions.
Some of these groups included:
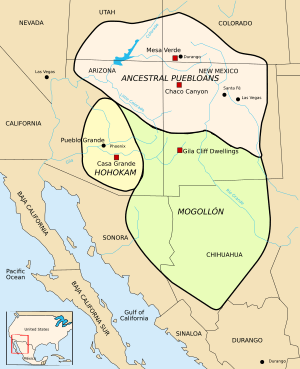
- The Ancestral Puebloans: They lived in areas that are now southern Utah, southern Colorado, northern Arizona, and northern and central New Mexico.
- The Mogollon: Their territory was in southeastern Arizona, southern New Mexico, and northern Mexico.
- The Patayan: They lived in western Arizona, California, and Baja California.
Important Places from the Late Basketmaker II Era
Many important archaeological sites help us learn about the Late Basketmaker II people. These places show us where they lived and what their daily lives were like.
Some notable sites include:
- Chaco Culture National Historical Park in New Mexico.
- Darkmold Site in Colorado.
- Durango Rock Shelters Archeology Site in Colorado, which is a key site for understanding this period.
- Glen Canyon in Utah and Arizona.
- Hovenweep National Monument in Colorado.
- Petrified Forest National Park in Arizona.
- Virgin Anasazi sites in the Colorado Plateau regions of Nevada, Utah, and Arizona.