Liebig's law of the minimum facts for kids
Liebig's law of the minimum, also known as Liebig's law or the law of the minimum, is an important idea in agricultural science. It was first suggested by Carl Sprengel in 1840 and later made popular by Justus von Liebig. This law says that the growth of a plant or animal is not limited by the total amount of all resources available. Instead, it is limited by the resource that is the most scarce or hardest to find. This scarce resource is called the limiting factor.
This law also applies to groups of living things, like animal populations, and how ecosystem models work. It helps us understand factors like sunlight or important mineral nutrients that living things need.
Contents
How Liebig's Law Works
This law was first used to understand how plants and crops grow. Farmers noticed that adding more of a nutrient that was already plentiful did not make plants grow bigger. Plants only grew better when the nutrient that was most scarce was increased.
Think of it like this: "A chain is only as strong as its weakest link." This means that the strongest part of a chain doesn't matter if one link is very weak. The whole chain will break at that weak link. In the same way, a plant's growth is limited by the nutrient it has the least of, even if it has plenty of other nutrients.
Plants and Animals
Liebig's law helps us understand how different living things grow. For example, a plant needs many things to grow, like sunlight and mineral nutrients such as nitrogen or phosphorus. The amount of these things can change. At any time, one of them might be harder to get than the others. Liebig's law tells us that the plant will only grow as fast as the most limiting factor allows.
This idea is often used in models of ecosystems. It helps scientists understand why some populations of plants or animals might not grow as much as expected.
Protein and Nutrition
Liebig's law has also been used to understand human nutrition. For example, William Cumming Rose used this idea in 1931 to find out which essential amino acids our bodies need. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. Our bodies cannot make essential amino acids, so we must get them from the food we eat.
Scientists found that our bodies can only build protein molecules when all the necessary amino acids are present at the same time. If even one essential amino acid is missing, our bodies cannot use the others properly. This is why some people, like vegetarians, learn about "protein combining." They eat different plant foods together to make sure they get all the essential amino acids their bodies need.
Natural Resources
More recently, Liebig's law is being used in managing natural resources. It suggests that growth in industries that depend on natural resources is limited by the most scarce resource. Our planet has a limited amount of natural resources. So, Liebig's law encourages scientists to figure out how scarce important resources are. This helps us plan for how we use resources for many generations to come.
Some people believe that new technologies or finding different materials can solve resource problems. For example, we might use nuclear power instead of coal, or plastics instead of wood. But for some resources, like phosphorus, there are no good substitutes. If there are no substitutes, then recycling becomes very important. This often needs careful long-term planning.
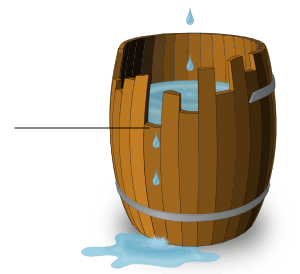
Liebig's Barrel
A scientist named Dobenecks used the image of a barrel to explain Liebig's law. This is often called "Liebig's barrel." Imagine a wooden barrel made of staves (the vertical planks) of different lengths. The amount of water the barrel can hold is limited by the shortest stave. Even if all the other staves are very long, the water will spill out at the level of the shortest one.
In the same way, a plant's growth is limited by the nutrient that is in the shortest supply. If you want to hold more water in the barrel, you have to make the shortest stave longer. For a plant, you have to increase the most limiting nutrient to help it grow more.
In nature, living things often adapt to their environment. This means they try to use their resources in a way that makes the "shortest stave" (the limiting factor) less of a problem.
Biotechnology and Growth
One way humans try to overcome limiting factors is through biotechnology. For example, plant genetics can be used to change plants. Scientists can use genetic modification to make plants less dependent on a certain resource that is hard to find.
These new technologies can help plants grow more, pushing the limits of what they can achieve. However, even with biotechnology, plants and other living things still depend on natural capital (natural resources) from the Earth.
See also
 In Spanish: Ley del Mínimo de Liebig para niños
In Spanish: Ley del Mínimo de Liebig para niños
- Bottleneck (disambiguation)
- Limiting factor
- Sustainability